Abstract
Pachydermodactyly is a form of digital dermal fibromatosis of unknown etiology, characterized by asymptomatic soft tissue swelling on the lateral aspects of the proximal interphalangeal joints of the hands. It usually affects young men and often associated with repetitive mechanical trauma. As a rule, it is a benign condition and a specific therapy or extensive investigation is not necessary in most cases. However, pachydermodactyly is not well recognized by physician. So it can be confused with other rheumatic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile idiopathic arthritis. A prompt diagnosis is crucial for preventing inappropriate or possible toxic treatment. We describe a case of pachydermodactyly in a 20-year-old military man, who had painless swellings of the hand joints.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Curley RK, Hudson PM, Marsden RA. Pachydermodactyly: a rare form of digital fibromatosis: report of four cases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1991; 16:121–3.
2. Fleeter TB, Myrie C, Adams JP. Pachydermodactyly: a case report and discussion of the pathologic entity. J Hand Surg Am. 1984; 9:764–6.

3. Verbov J. Letter: Pachydermodactyly: a variant of the true knuckle pad. Arch Dermatol. 1975; 111:524.

4. Al Hammadi A, Hakim M. Pachydermodactyly: case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Med Surg. 2007; 11:185–7.

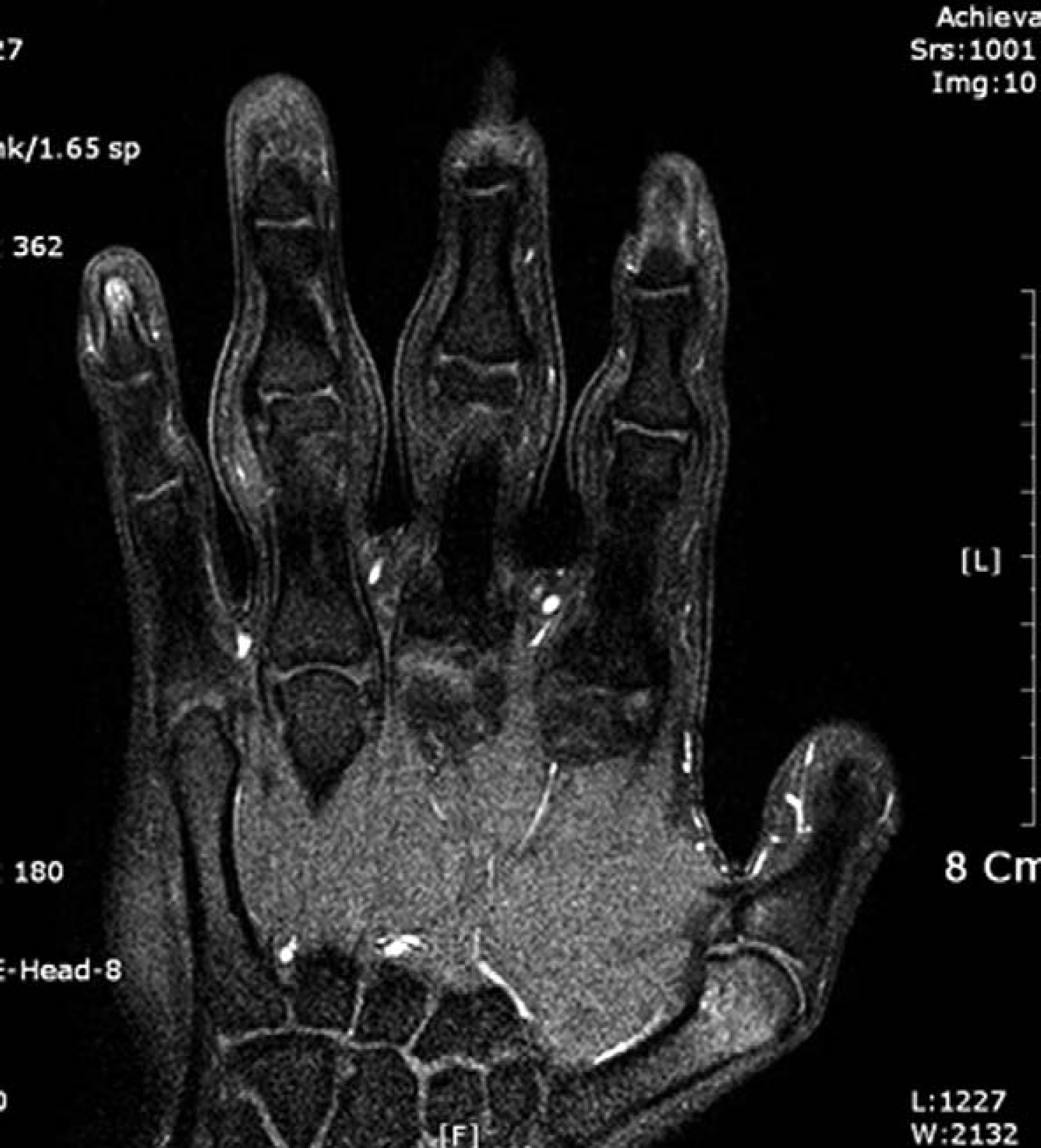
5. Anandacoomarasamy A, Bak HS, Peduto A, Manolios N. Magnetic resonance imaging in pachydermodactyly. J Rheumatol. 2005; 32:2239–41.
6. Sagransky MJ, Pichardo-Geisinger RO, Munoz-Ali D, Feldman SR, Mora DC, Quandt SA. Pachydermodactyly from repetitive motion in poultry processing workers: a report of 2 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2012; 148:925–8.

7. Bardazzi F, Neri I, Raone B, Patrizi A. Pachydermodactyly: seven new cases. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1998; 125:247–50.
8. Park JH, Lee CW. A case of pachydermodactyly treated by surgical excision. Korean J Dermatol. 2006; 44:369–71.
9. Martin JC, Rennie JA, Kerr KM. Pachydermodactyly: confused with JCA. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992; 51:1101–2.
Go to : 
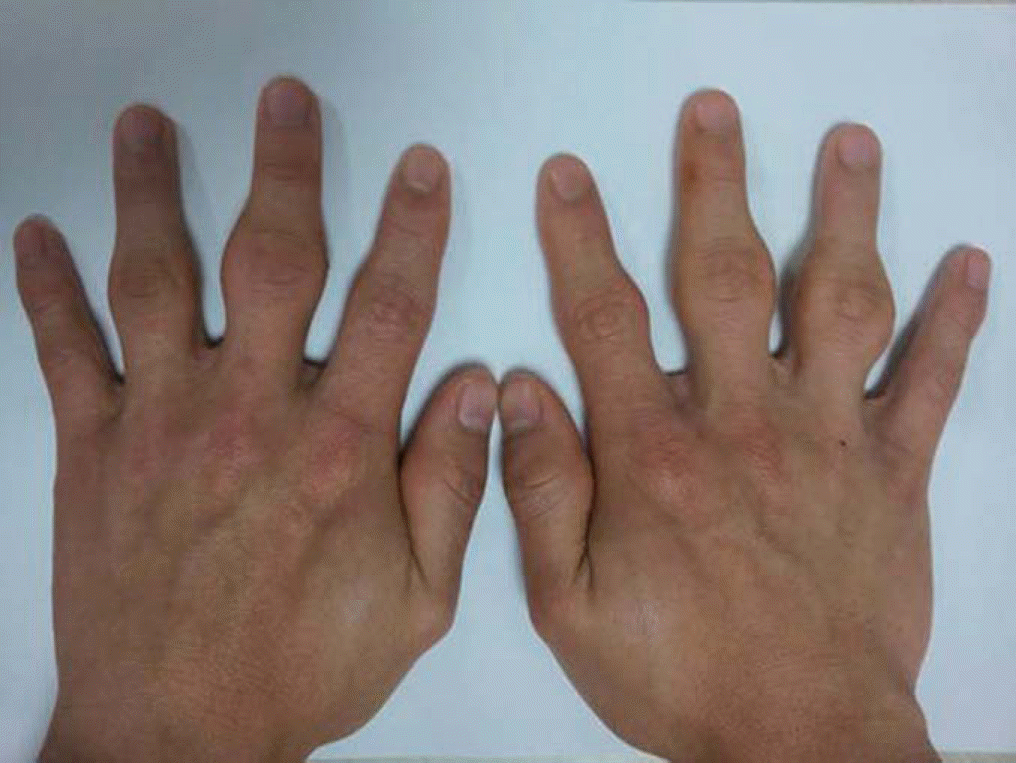 | Fig. 1.Photograph of hands shows bilateral soft tissue swellings of the proximal interphalangeal joints. |
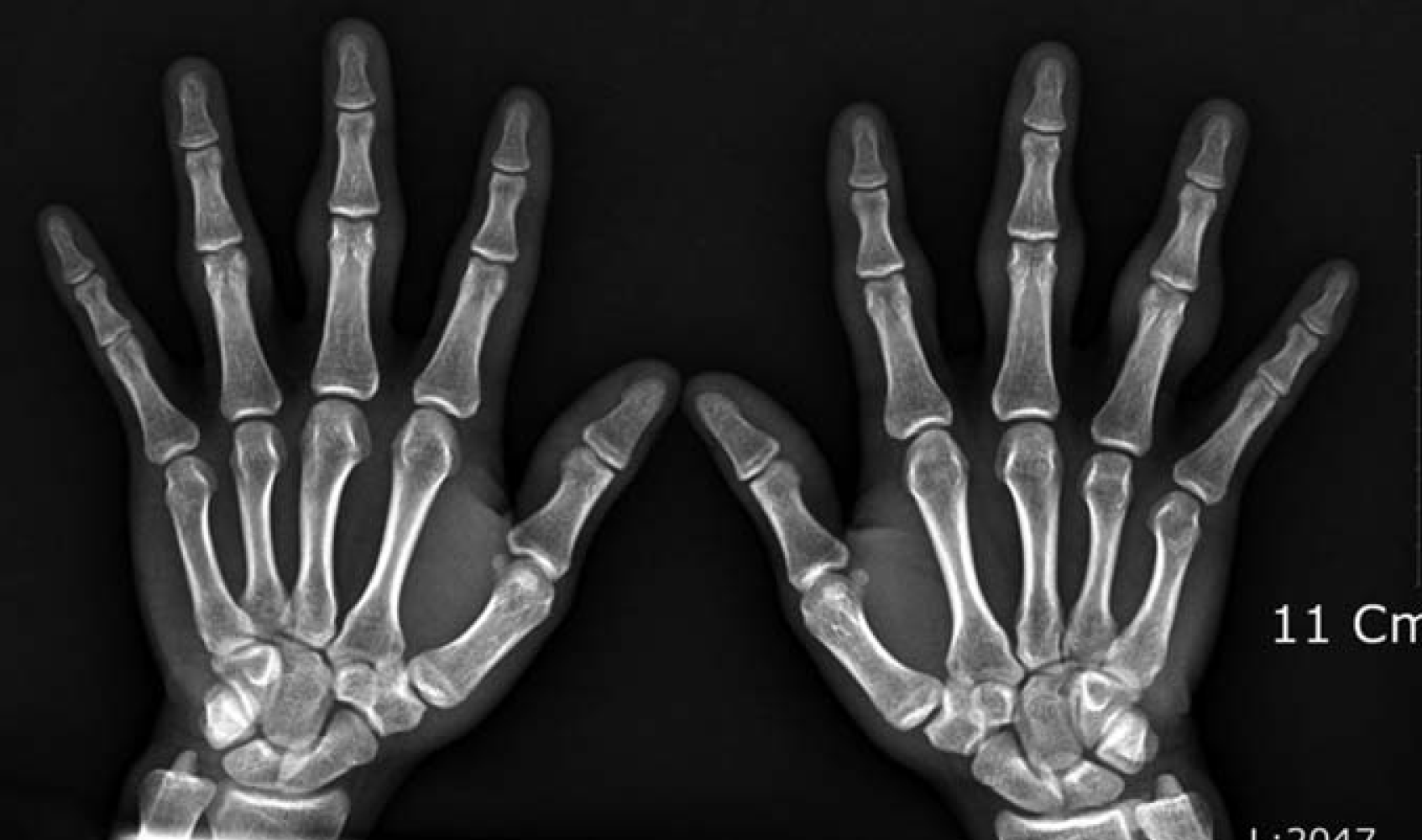 | Fig. 2.Hand radiograph showings soft tissue swelling around the proximal interphalangeal joints without joint narrowing or bony erosions. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download