Abstract
Methods
Fifteen patients who had chronic infectious arthritis of the wrist and underwent open synovectomy were reviewed retrospectively baesd on preoperative periods, symptoms, results of laboratory tests, radiological findings including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), hospitalization period, and others. Pain scale and subjective satisfaction were checked by phone interview.
Results
Average preoperative period was 96.1 days. Pain on motion and edema were observed in all cases. Four patients had positive bacterial cultures and three were identified as tuberculous infection. Signal changes of bones were observed in MRI of 10 patients. Osteomyelitis was found in 8 patients during the operation and bone resection or fusion should be performed in three. Average number of operation times was 1.53.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Wrist magnetic resonance imaging of 68-year-old female patient, who visited 4 months after onset of the symptoms, shows diffuse synovial hypertrophy, joint effusion, and multiple bony erosions and marrow edema.
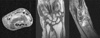
Table 1
Clinical and radiologic data of the patients

MRI: magnetic resonance imaging, S: scaphoid, H: hamate, NTM: nontuberculosis mycobacteria, R: distal radius, C: capitate, MSCNS: methicillin-sensitive coagulase negative Staphylococcus, L: lunate, Tq: triquetrum, Tp: trapezium, MC: metacarpals, U: distal ulna, UC: ulnocarpal (joint), DRUJ: distal radioulnar (joint), RC: radiocarpal (joint), MSSA: methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, MRCNS: methicillin-resistance coagulase negative Staphylococcus.
References
1. Skeete K, Hess EP, Clark T, Moran S, Kakar S, Rizzo M. Epidemiology of suspected wrist joint infection versus inflammation. J Hand Surg Am. 2011. 36:469–474.

2. Rashkoff ES, Burkhalter WE, Mann RJ. Septic arthritis of the wrist. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983. 65:824–828.

5. Kim SM, Park MJ, Kang HJ, Choi YL, Lee JJ. The role of arthroscopic synovectomy in patients with undifferentiated chronic monoarthritis of the wrist. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012. 94:353–358.

6. Cheung JP, Fung BK, Ip WY. Mycobacterium marinum infection of the deep structures of the hand and wrist: 25 years of experience. Hand Surg. 2010. 15:211–216.
7. Chung DW, Han CS, Park BY, Lee GH, Kwon OS. Hand and wrist tuberculosis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1995. 30:635–643.

8. Lall H, Nag SK, Jain VK, Khare R, Mittal D. Tuberculous extensor tenosynovitis of the wrist with extensor pollicis longus rupture: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2009. 3:142.

9. Graif M, Schweitzer ME, Deely D, Matteucci T. The septic versus nonseptic inflamed joint: MRI characteristics. Skeletal Radiol. 1999. 28:616–620.

10. Sammer DM, Shin AY. Comparison of arthroscopic and open treatment of septic arthritis of the wrist. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010. 92:Suppl 1 Pt 1. 107–113.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download