1. Al-Tamimi YZ, Bhargava D, Feltbower RG, Hall G, Goddard AJ, Quinn AC, et al. Lumbar drainage of cerebrospinal fluid after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial (LUMAS). Stroke. 2012; 3. 43(3):677–682. PMID:
22282887.
2. Auer LM, Mokry M. Disturbed cerebrospinal fluid circulation after subarachnoid hemorrhage and acute aneurysm surgery. Neurosurgery. 1990; 5. 26(5):804–808. discussion 808-9. PMID:
2352599.

3. Byoun HS, Yi HJ, Choi KS, Chun HJ, Ko Y, Bak KH. Comparison of endovascular treatments of ruptured dissecting aneurysms of the intracranial internal carotid artery and vertebral artery with a review of the literature. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016; 9. 59(5):449–457. PMID:
27651862.

4. Choi JH, Park JE, Kim MJ, Kim BS, Shin YS. Aneurysmal neck clipping as the primary treatment option for both ruptured and unruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysms. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016; 5. 59(3):269–275. PMID:
27226859.

5. Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, Derdeyn CP, Dion J, Higashida RT, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association. Stroke. 2012; 6. 43(6):1711–1737. PMID:
22556195.
6. Degos V, Gourraud PA, Tursis VT, Whelan R, Colonne C, Korinek AM, et al. Elderly age as a prognostic marker of 1-year poor outcome for subarachnoid hemorrhage patients through its interaction with admission hydrocephalus. Anesthesiology. 2012; 12. 117(6):1289–1299. PMID:
22854979.

7. Dorai Z, Hynan LS, Kopitnik TA, Samson D. Factors related to hydrocephalus after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 2003; 4. 52(4):763–769. discussion 769-71. PMID:
12657171.

8. Fisher CM, Kistler JP, Davis JM. Relation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning. Neurosurgery. 1980; 1. 6(1):1–9. PMID:
7354892.

9. Gonzalez NR, Boscardin WJ, Glenn T, Vinuela F, Martin NA. Vasospasm probability index: a combination of transcranial doppler velocities, cerebral blood flow, and clinical risk factors to predict cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 2007; 12. 107(6):1101–1112. PMID:
18077946.

10. Gruber A, Reinprecht A, Bavinzski G, Czech T, Richling B. Chronic shunt-dependent hydrocephalus after early surgical and early endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 1999; 3. 44(3):503–509. discussion 509-12. PMID:
10069587.

11. Hirashima Y, Hamada H, Hayashi N, Kuwayama N, Origasa H, Endo S. Independent predictors of late hydrocephalus in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage--analysis by multivariate logistic regression model. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003; 16(3):205–210. PMID:
12865606.
12. Hunt WE, Hess RM. Surgical risk as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1968; 1. 28(1):14–20. PMID:
5635959.

13. Jartti P, Karttunen A, Jartti A, Ukkola V, Sajanti J, Pyhtinen J. Factors related to acute hydrocephalus after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Radiol. 2004; 5. 45(3):333–339. PMID:
15239431.

14. Kasuya H, Shimizu T, Kagawa M. The effect of continuous drainage of cerebrospinal fluid in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: a retrospective analysis of 108 patients. Neurosurgery. 1991; 1. 28(1):56–59. PMID:
1994282.

15. Lanzino G, Kassell NF, Germanson TP, Kongable GL, Truskowski LL, Torner JC, et al. Age and outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: why do older patients fare worse? J Neurosurg. 1996; 9. 85(3):410–418. PMID:
8751625.

16. Lawton MT, Vates GE. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2017; 7. 20. 377(3):257–266. PMID:
28723321.

17. Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, Clarke M, Sneade M, Yarnold JA, et al. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet. 2005; 9. 3-9. 366(9488):809–817. PMID:
16139655.

18. Ohwaki K, Yano E, Nakagomi T, Tamura A. Relationship between shunt-dependent hydrocephalus after subarachnoid haemorrhage and duration of cerebrospinal fluid drainage. Br J Neurosurg. 2004; 4. 18(2):130–134. PMID:
15176553.

19. Otawara Y, Ogasawara K, Kubo Y, Sasoh M, Ogawa A. Effect of continuous cisternal cerebrospinal fluid drainage for patients with thin subarachnoid hemorrhage. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2007; 3(4):401–404. PMID:
17969369.
20. Park S, Yang N, Seo E. The effectiveness of lumbar cerebrospinal fluid drainage to reduce the cerebral vasospasm after surgical clipping for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015; 3. 57(3):167–173. PMID:
25810855.

21. Rosen DS, Macdonald RL, Huo D, Goldenberg FD, Novakovic RL, Frank JI, et al. Intraventricular hemorrhage from ruptured aneurysm: clinical characteristics, complications, and outcomes in a large, prospective, multicenter study population. J Neurosurg. 2007; 8. 107(2):261–265. PMID:
17695378.

22. Schirmer CM, Hoit DA, Malek AM. Decompressive hemicraniectomy for the treatment of intractable intracranial hypertension after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2007; 3. 38(3):987–992. PMID:
17272765.

23. Spetzler RF, McDougall CG, Zabramski JM, Albuquerque FC, Hills NK, Russin JJ, et al. The barrow ruptured aneurysm trial: 6-year results. J Neurosurg. 2015; 9. 123(3):609–617. PMID:
26115467.

24. Sun C, Du H, Yin L, He M, Tian Y, Li H. Choice for the removal of bloody cerebrospinal fluid in postcoiling aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: external ventricular drainage or lumbar drainage? Turk Neurosurg. 2014; 24(5):737–744. PMID:
25269046.
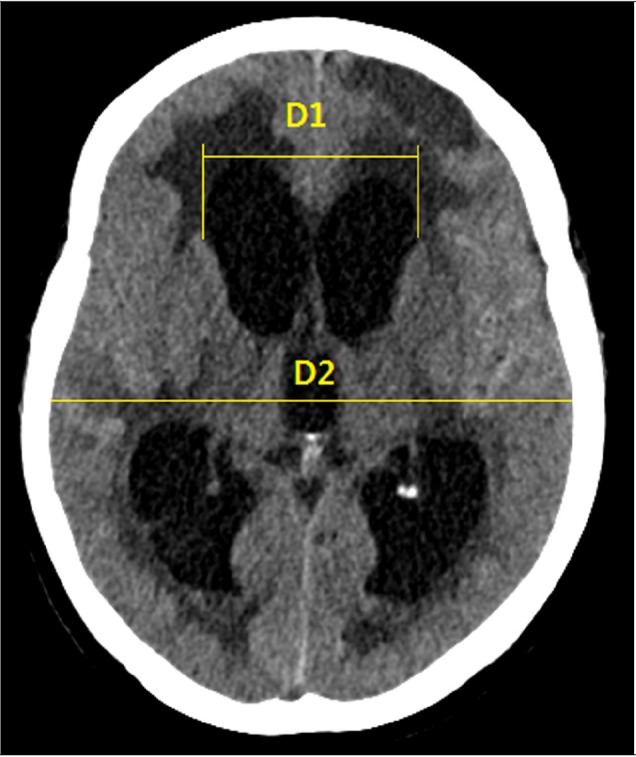
25. Toma AK, Holl E, Kitchen ND, Watkins LD. Evans' index revisited: the need for an alternative in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 2011; 4. 68(4):939–944. PMID:
21221031.

26. Vale FL, Bradley EL, Fisher WS 3rd. The relationship of subarachnoid hemorrhage and the need for postoperative shunting. J Neurosurg. 1997; 3. 86(3):462–466. PMID:
9046303.

27. Vassilouthis J, Richardson AE. Ventricular dilatation and communicating hydrocephalus following spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1979; 9. 51(3):341–351. PMID:
313979.

28. Wartenberg KE, Schmidt JM, Claassen J, Temes RE, Frontera JA, Ostapkovich N, et al. Impact of medical complications on outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Crit Care Med. 2006; 3. 34(3):617–623. quiz 624. PMID:
16521258.

29. Wilson JT, Hareendran A, Grant M, Baird T, Schulz UG, Muir KW, et al. Improving the assessment of outcomes in stroke: use of a structured interview to assign grades on the modified rankin scale. Stroke. 2002; 9. 33(9):2243–2246. PMID:
12215594.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download