Abstract
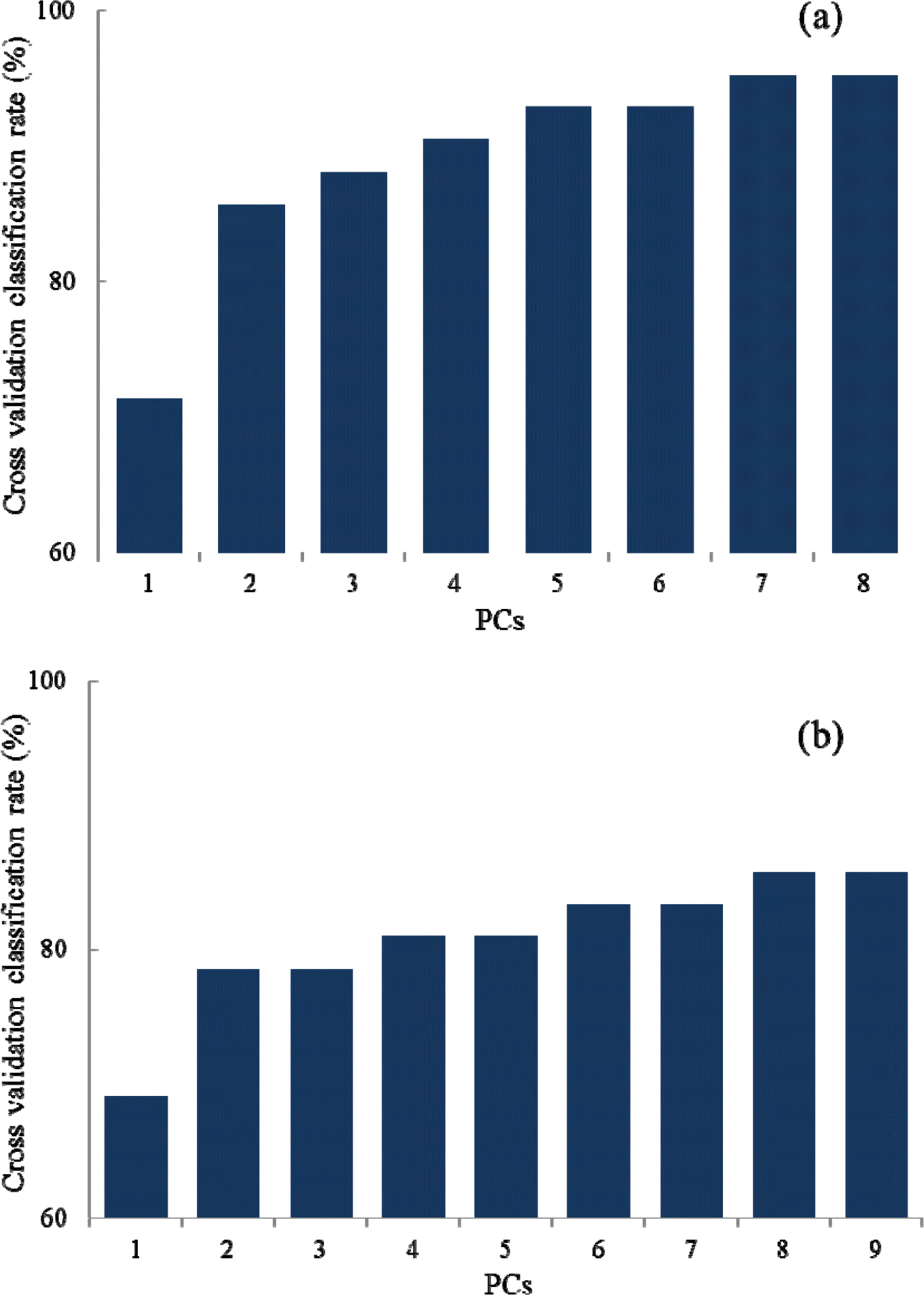
Rapid geographical classification of Bupleuri Radix is important in quality control. In this study, near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) combined with supervised pattern recognition was attempted to classify Bupleuri Radix according to geographical origins. Three supervised pattern recognitions methods, partial least square discriminant analysis (PLS-DA), quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA) and radial basis function support vector machine (RBF-SVM), were performed to establish the classification models. The QDA and RBF-SVM models were performed based on principal component analysis (PCA). The number of principal components (PCs) was optimized by cross-validation in the model. The results showed that the performance of the QDA model is the optimum among the three models. The optimized QDA model was obtained when 7 PCs were used; the classification rates of the QDA model in the training and test sets are 97.8% and 95.2% respectively. The overall results showed that NIRS combined with supervised pattern recognition could be applied to classify Bupleuri Radix according to geographical origin.
REFERENCES
(1). Ashour M. L., Wink M. J.Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011; 63:305–321.
(2). Bermejo Benito P., Abad Martínez M. J., Silván Sen A. M., Sanz Gómez A., Fernández Matellano L., Sánchez Contreras S., Díaz Lanza A. M.Life Sci. 1998; 63:1147–1156.
(3). Cheng X. Q., Li H., Yue X. L., Xie J. Y., Zhang Y. Y., Di H. Y., Chen D. F. J.Ethnopharmacol. 2010; 130:363–368.
(4). Sun X. B., Matsumoto T., Yamada H. J.Pharm. Pharmacol. 1991; 43:699–704.
(5). Wen S., Huifu X., Hao H.Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2011; 33:433–437.
(6). Zhu L., Liang Z. T., Yi T., Ma Y., Zhao Z. Z., Guo B. L., Zhang J. Y., Chen H. B.BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017; 17:305–316.
(7). Li X., Jia Y., Song A., Chen X., Bi K.Yakugaku Zasshi. 2005; 125:815–819.
(8). Bao Y., Li C., Shen H., Nan F.Anal. Chem. 2004; 76:4208–4216.
(9). Liau B. C., Hsiao S. S., Lee M. R., Jong T. T., Chiang S. T. J.Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007; 43:1174–1178.
(10). Lee J., Yang D. H., Suh J. H., Kim U., Eom H. Y., Kim J., Lee M. Y., Kim J., Han S. B. J. Chromatogr. B.Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011; 879:3887–3895.
(11). Huang H. Q., Su J., Zhang X., Shan L., Zhang W. D. J.Chromatogr. A. 2011; 1218:1131–1138.
(12). Tian R. T., Xie P. S., Liu H. P. J.Chromatogr. A. 2009; 1216:2150–2155.
(13). Qin X., Dai Y., Liu N. Q., Li Z., Liu X., Hu J., Choi Y. H., Verpoorte R.Planta Med. 2012; 78:926–933.
(14). Lin X., Xue L., Zhang H., Zhu C.Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005; 382:1610–1615.
(15). Gong F., Wang B. T., Chau F. T., Liang Y. Z.Anal. Lett. 2005; 38:2475–2492.
(16). McGoverin C. M., Weeranantanaphan J., Downey G., Manley M. J.Near Infrared Spec. 2010; 18:87–111.
(17). Chen Y., Xie M. Y., Yan Y., Zhu S. B., Nie S. P., Li C., Wang Y. X., Gong X. F.Anal. Chim. Acta. 2008; 618:121–130.
(18). Luo X. F., Yu, X.;Wu, X. M.;Cheng, H. B.;Qu H. B.Microchem. J. 2008; 90:8–12.
(19). Wang L., Lee F. S. C., Wang X.LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007; 40:83–88.
(20). Chen Q., Zhao J., Lin H. Spectrochim.Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009; 72:845–850.
(21). Lin H., Zhao J., Chen Q., Zhou F., Sun L. Spectrochim Acta. A.Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011; 79:1381–1385.
(22). Lee D. Y., Kim S. H., Kim Y. C., Kim H. J., Sung S. H.Microchem. J. 2011; 99:213–217.
(23). Berrueta L. A., Alonso-Salces R. M., Héberger K.J. Chromatogr. A. 2007; 1158:196–214.
(24). Li B., Wei Y., Duan H., Xi L., Wu X.Vib. Spectrosc. 2012; 62:17–22.
(25). Chiang L. H., Russell E. L., Braatz R. D.Chemometrics Intell. Lab. Syst. 2000; 50:243–252.
(26). Jiang H., Liu G. H., Xiao X., Yu S., Mei C., Ding Y.Food Anal. Methods. 2012; 5:928–934.
(27). Luts J., Ojeda F., Van de Plas R., De Moor B., Van Huffel S., Suykens J. A.Anal. Chim. Acta. 2010; 665:129–145.
(28). Ballabio D., Consonni V.Anal. Methods. 2013; 5:3790–3798.
(29). Rubin T. N., Chambers A., Smyth P., Steyvers M.Mach. Learn. 2012; 88:157–208.
Table 1.
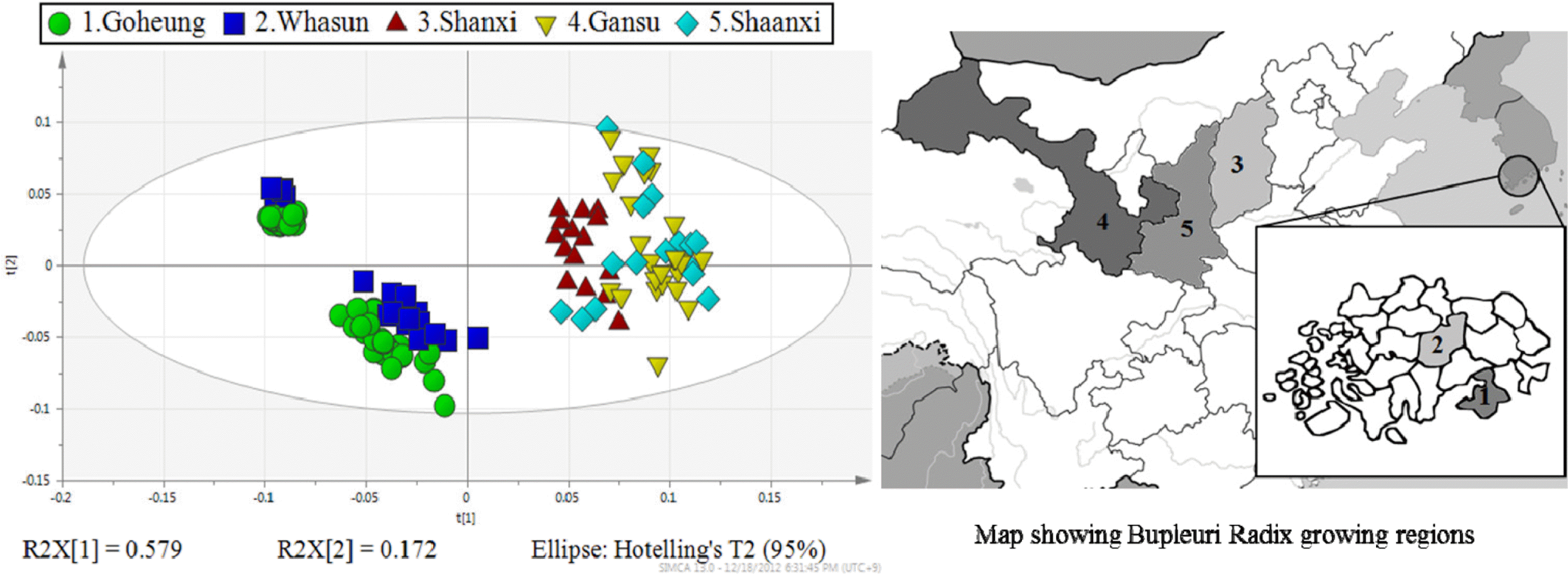
Summary of testing Bupleuri Radix samples
| Geographical origins | Number of samples | |
|---|---|---|
| Training set | Test set | |
| South Korea | ||
| Goheung | 35 | 17 |
| Whasun | 16 | 7 |
| China | ||
| Shanxi | 10 | 5 |
| Gansu | 17 | 8 |
| Shaanxi | 11 | 5 |
Table 2.
Classification results by PLS-DA model
Table 3.
Classification results by QDA model
Table 4.
Classification results by RBF-SVM model




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download