This erratum is being published to correct the printing error on page 517 of the article entitled ‘Seasonal Cycle and Relationship of Seasonal Rhino- and Influenza Virus Epidemics With Episodes of Asthma Exacerbation in Different Age Groups’ by Seung Won Lee, Shinhae Lee, Youn Ho Sheen, Eun Kyo Ha, Sun Hee Choi, Min-Suk Yang, Sohyun Hwang, Sung Soon Kim, Jang-Hoon Choi, Man Yong Han in Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017 November;9(6):517–525, https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2017.9.6.517 as follows.
Corrections for Fig. 1 and main text in page 519 are needed. Changes are marked by underlines. We apologize for any inconvenience that this may have caused.
Before correction
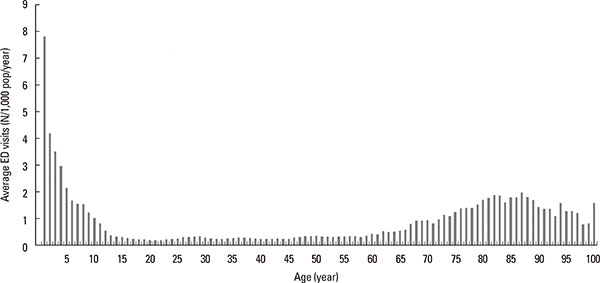
There were 157,559 ED visits (daily mean: 86.2±40.2) for AE in Korea between January 1, 2008 and December 31, 2012, corresponding to a crude ED visitation rate of 0.62 events/1,000 people/year. Overall, the rate was less than 0.1 events/1,000 people/year (n=101) in aged 0-11 months, and highest in those aged 12-23 months (7.8 events/1,000 people/year, n=18,419). The rate quickly declined until it reached 0.4 events/1,000 people/year (n=1,150) in those 13 years. After age 13, the rate did not change until age 61. In the 13 to 61 years' age group, the average ED visit was 0.27±0.06 events/1,000 people/year. The rate again started to increase, which became 0.5 events/1,000 people/year in aged 62 years, and 1.24±0.44 events/1,000 people/year in those aged ≥62 years (Fig. 1). The age-related number of emergency room visits was similar to the age-related prevalence of asthma reported previously.
After correction
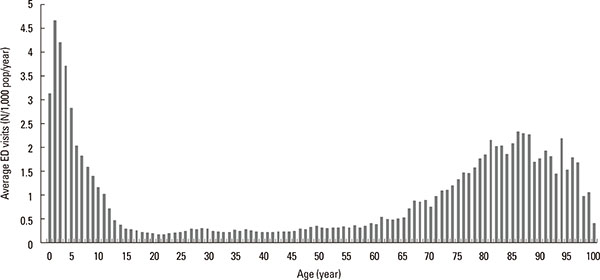
There were 157,559 ED visits (daily mean: 86.2±40.2) for AE in Korea between January 1, 2008 and December 31, 2012, corresponding to a crude ED visitation rate of 0.62 events/1,000 people/year. Overall, the rate was started with 3.1 events/1,000 people/year (n=7,257) in aged 0-11 months, and highest in those aged 12-23 months (4.7 events/1,000 people/year, n=10,993). The rate quickly declined until it reached 0.4 events/1,000 people/year (n=1,150) in those 13 years. After age 13, the rate did not change until age 61. In the 13 to 61 years' age group, the average ED visit was 0.27±0.06 events/1,000 people/year. The rate again started to increase, which became 0.5 events/1,000 people/year in aged 62 years, and 1.24±0.44 events/1,000 people/year in those aged ≥62 years (Fig. 1). The age-related number of emergency room visits was similar to the age-related prevalence of asthma reported previously.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download