Abstract
Background:
Bortezomib has been used to treat antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) that usually develops after kidney transplantation (KT). Although it has been used in various clinical situations, it is difficult to precisely define how the drug affects the clinical course. We used bortezomib to treat eight cases of AMR that developed immediately following KT in patients who were resistant to conventional treatment.
Methods:
Eight cases of refractory AMR that developed immediately after KT were treated with bortezomib on days 1, 4, 8, and 11.
Results:
The resolution rate was 75%, and the 2-year rejection-free survival rate was 83%. Six cases underwent immunologically high-risk KT. Six recovering patients exhibited clinical improvement within 2 weeks of the first dose of bortezomib and recovered completely within 2 months. The effects of bortezomib seemed to be prolonged; only one additional rejection episode was observed. The two failed patients never exhibited any clinical improvement and progressed aggressively to graft failure soon after transplantation. Their donor specific anti-human leukocyte antigen antibody were sustained at high levels.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Everly MJ., Everly JJ., Susskind B., Brailey P., Arend LJ., Alloway RR, et al. Bortezomib provides effective therapy for antibody-and cell-mediated acute rejection. Transplantation. 2008. 86:1754–61.
2). Flechner SM., Fatica R., Askar M., Stephany BR., Poggio E., Koo A, et al. The role of proteasome inhibition with bortezomib in the treatment of antibody-mediated rejection after kidney-only or kidney-combined organ transplantation. Transplantation. 2010. 90:1486–92.

3). Nigos JG., Arora S., Nath P., Hussain SM., Marcus RJ., Ko TY, et al. Treatment of antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplant recipients: a single-center experience with a bortezomib-based regimen. Exp Clin Transplant. 2012. 10:609–13.

4). Hardinger KL., Alford K., Murillo D. Bortezomib as rescue therapy for antibody mediated rejection: a single-center experience. Clin Transpl. 2010. 24:429–36.
5). Pavlakis M. Case presentations on two patients who received bortezomib for antibody mediated rejection at BIDMC. Clin Transpl. 2009. 23:343–5.
6). Hardinger KL., Alford K., Murillo D. Bortezomib for acute humoral rejection in two repeat transplant recipients. Clin Transpl. 2009. 23:479–83.
7). Chung BH., Hong YA., Sun IO., Piao SG., Kim JI., Moon IS, et al. Determination of rituximab dose according to immunologic risk in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Ren Fail. 2012. 34:974–9.

8). Tobian AA., Shirey RS., Montgomery RA., Tisch DJ., Ness PM., King KE. Therapeutic plasma exchange reduces ABO titers to permit ABO-incompatible renal transplantation. Transfusion. 2009. 49:1248–54.

9). Walsh RC., Brailey P., Girnita A., Alloway RR., Shields AR., Wall GE, et al. Early and late acute antibody-mediated rejection differ immunologically and in response to proteasome inhibition. Transplantation. 2011. 91:1218–26.

10). Kim M., Martin ST., Townsend KR., Gabardi S. Antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplantation: a review of pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Pharmacotherapy. 2014. 34:733–44.

11). Roberts DM., Jiang SH., Chadban SJ. The treatment of acute antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review. Transplantation. 2012. 94:775–83.
12). Bonomini V., Vangelista A., Frasca GM., Di Felice A., Liviano D'Arcangelo G. Effects of plasmapheresis in renal transplant rejection. A controlled study. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1985. 31:698–703.
13). Allen NH., Dyer P., Geoghegan T., Harris K., Lee HA., Slapak M. Plasma exchange in acute renal allograft rejection. A controlled trial. Transplantation. 1983. 35:425–8.

14). Kirubakaran MG., Disney AP., Norman J., Pugsley DJ., Mathew TH. A controlled trial of plasmapheresis in the treatment of renal allograft rejection. Transplantation. 1981. 32:164–5.

15). Blake P., Sutton D., Cardella CJ. Plasma exchange in acute renal transplant rejection. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990. 337:249–52.
Go to : 
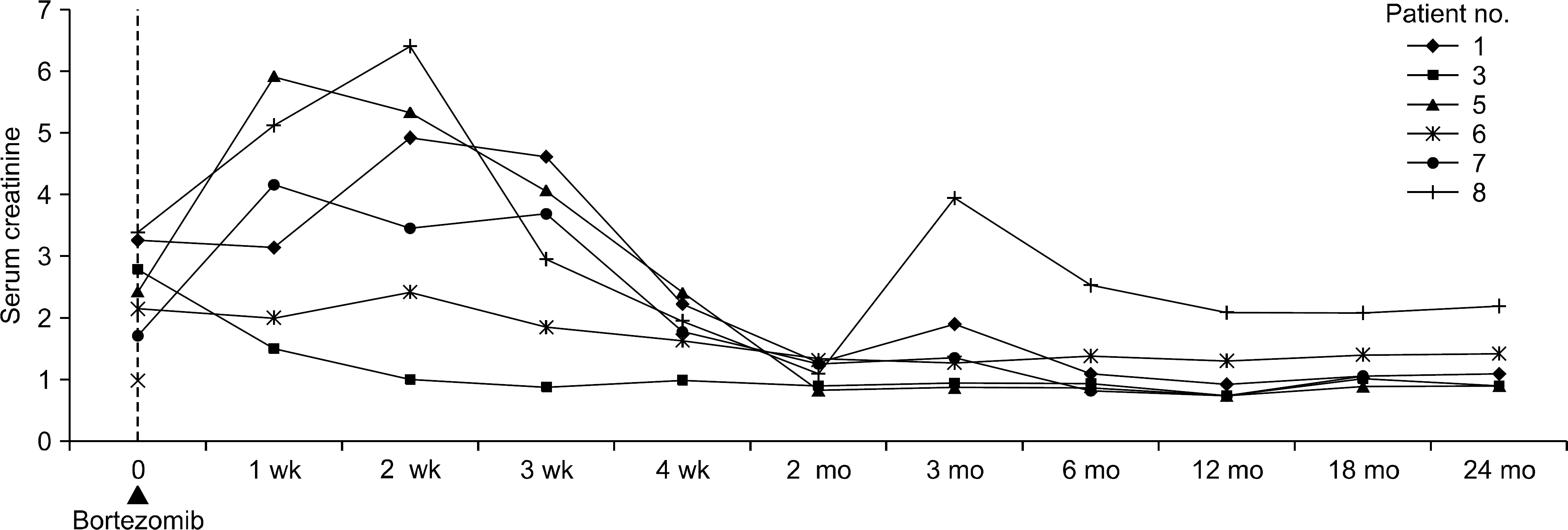 | Fig. 1.Serum creatinine changes after bortezomib treatment of the six patients who recovered. Serum creatinine levels began to decrease within 2 weeks of bortezomib treatment, and recovery was achieved within 2 months. |
Table 1.
Preoperative patient characteristics
| Case no. | Sex (age in yr) | Donor (age in yr) | Previous transplant history | ABO-I | HLA MN | PRA (Class I/II) | DSA | XM | RTX | Induct | PP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Pre-KTa | |||||||||||
| 1 | F (43) | Spouse (48) | 0 | No | 6 | 0/0 | Neg | NA | Neg | No | BSX | 0 |
| 2 | M (38) | Deceased (45) | 2 | No | 5 | 0/25 | NA | B54 9827 | Neg | No | ATG | 0 |
| 3 | F (46) | Son (19) | 0 | No | 3 | 16/0 | Neg | Neg | T, B CDC | 1 | BSX | 9 |
| 4 | F (32) | Spouse (37) | 0 | No | 5 | 0/54 | DR9 8121 | DR9 3472 | B | 1 | BSX | 5 |
| FC | ||||||||||||
| 5 | F (39) | Spouse (40) | 0 | 1 (1:32) | 5 | 16/60 | A2 8578 | A2 2671 | T, B | 1 | BSX | 10 |
| FC | ||||||||||||
| 6 | F (47) | Daughter (29) | 0 | No | 2 | 83/20 | B51 3997 | NA | Neg | 1 | ATG | 0 |
| 7 | F (57) | Spouse (54) | 1 | No | 6 | 91/100 | DR11 16371 | DR11 3346 | T, B | 1 | BSX | 13 |
| DR14 14486 | DR14 3781 | FC | ||||||||||
| 8 | F (27) | Mother (52) | 0 | No | 1 | 0/0 | Neg | Neg | Neg | No | BSX | 0 |
Abbreviations: ABO-I, ABO incompatibility; HLA MN, human leukocyte antigen mismatch number; PRA, panel-reactive antibody; DSA, donor-specific antibody; KT, kidney transplantation; XM, crossmatching; RTX, rituximab; PP, plasmapheresis; Neg, negative; NA, not assessed; BSX, basiliximab; ATG, anti-thymocyte globulin; T, T-cell; B, B-cell; CDC, complement-dependent cytotoxicity; FC, flowcytometry.
Table 2.
Changes in donor-specific antibody levels during the peri-transplantation period
| Case no. | Initial | Pre-KTa | Pre-rejectionb | Rejection (pre-bortezomibc) | Post-bortezomibd | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Neg | NA | NA | DR8 15741 | DR8 3066 | Neg (3, 6 mo) |
| 2 | NA | B54 9827 | NA | B54 13333 | B54 11089 | NA |
| 3 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Neg | Neg | NA |
| 4 | DR9 8121 | DR9 3472 | Neg | DR9 15336 | DR9 16440 | DR9 13371 (7 mo) |
| 5 | A2 8578 | A2 2671 | A2 1996 | A2 4876 | Neg | Neg (2, 8, 11 mo) |
| 6 | B51 3997 | NA | Neg | B51 1901 | Neg | NA |
| 7 | DR11 16371 | DR11 3346 | Neg | Neg | Neg | NA |
| DR14 14486 | DR14 3781 | |||||
| 8 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Neg | Neg | NA |
Table 3.
Treatments for transplant recipients exhibiting antibody-mediated rejection
| Case no. | Rejection (POD) | Initial therapy | Bortezomib (POD) | Post-transplant plasmapheresis | HD start (POD) | HD end (POD) | Bx. (POD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POD | Pre-bortezomiba | Post-bortezomibb | |||||||
| 1 | 4 | Steroid pulse | 19 | 9 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 28 | 8 |
| ATG | |||||||||
| Plasmapheresis | |||||||||
| 2 | 8 | Steroid pulse | 21 | 9 | 6 | 7 | 10 | Maintain | 8 |
| Plasmapheresis | |||||||||
| 3 | 6 | Steroid pulse | 12 | 8 | 2 | 8 | - | - | 10 |
| Plasmapheresis | |||||||||
| 4 | 4 | Steroid pulse | 10 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 | Maintain | 8 |
| Plasmapheresis | |||||||||
| 5 | 3 | ATG | 11 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 5 | 7 | 4 |
| Plasmapheresis | |||||||||
| 6 | 4 | Steroid pulse | 22 | 4 | 7 | 4 | - | - | 6 |
| Plasmapheresis | |||||||||
| 7 | 2 | Steroid pulse | 6 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 17 | 5 |
| Plasmapheresis | |||||||||
| 8 | 3 | Steroid pulse | 13 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 17 | 4 |
| ATG | |||||||||
| Plasmapheresis | |||||||||




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download