Abstract
Figures and Tables
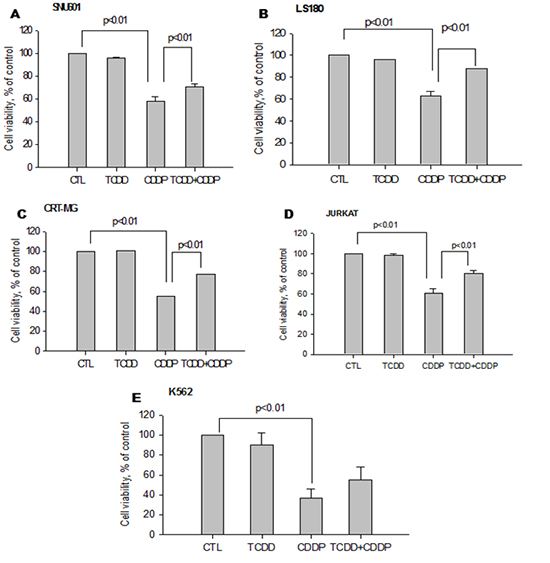
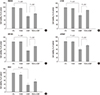 | Fig. 1Increase in cell viability of cisplatin-treated cancer cells pretreated with TCDD. Human (A) gastric (SNU601), (B) colon (LS180), (C) brain (CRT-MG), (D) lymphocyte (Jurkat) and (E) leukemia (K562) cancer cells were pretreated by 10 nM TCDD for two days. SNU601, CRT-MG and Jurkat cells were subsequently treated with 5 µg/mL cisplatin, and LS180 and K562 cells were treated with 10 and 15 µg/mL cisplatin, respectively, for one day. Cells grown in culture medium without any treatment were used as negative control (CTL). Cell viability is expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical significance difference (P values) is indicated. TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; CDDP, cisplatin. |
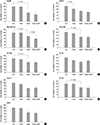 | Fig. 2Decrease in cell viability of cisplatin-treated liver (Hep3B) and breast (MDA-MB-231) cancer cells pretreatment with TCDD. Cells were pretreated with TCDD for two days: (A) liver (Hep3B), (D, E) brain (U373-MG, U87-MG), (F) blood (HL-60) and (H, I) lung (H460, A549) cancer cells were treated with 10 nM TCDD; (B) liver (HepG2) and (C) breast (MDA-MB-231) cells were treated with 5 nM, and (G) colon (Caco-2) cells were treated with 4 nM TCDD. Subsequently one-day treatment with cisplatin was 5 µg/mL for Hep3B, MDA-MB-231 and A549 cells, 15 µg/mL for U373-MG, U87-MG, and HL-60 cells and 10 µg/mL for H460 cells. HepG2 and Caco-2 cells were treated with 4 and 40 µg/mL cisplatin, respectively. Control cells were treated as described for Fig. 1. Cell viability is expressed as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical significance (P values) is indicated for each Figure. CTL, control; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; CDDP, cisplatin. |
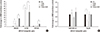 | Fig. 3Induction of the ABCG2 gene in cancer cells pretreated with TCDD. (A) SNU601, LS180 and CRT-MG cancer cells with acquired resistance to cisplatin were pretreated with 10 nM TCDD for two days. After which SNU601 and CRT-MG cells were treated with 5 µg/mL cisplatin and LS180 cells were treated with 10 µg/mL cisplatin for one day. (B) Hep3B and MDA-MB-231 cells with unchanged sensitivity to cisplatin were pretreated with 10 and 5 nM TCDD, respectively, for two days. Subsequently, all cells were treated with 5 µg/mL cisplatin for one day. Control cells were treated as described for Fig. 1. Gene expression was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR described in Materials and Methods. Results are represented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. Human GAPDH was used as an internal control. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; CTL, control; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; CDDP, cisplatin. |
 | Fig. 4Effect of the TCDD-pretreatment on the expression of drug transporter genes in cancer cells with acquired resistance to cisplatin. SNU601, LS180, and CRT-MG cells were pretreated with 10 nM TCDD for two days. (A) SNU601 and (C) CRT-MG cells were treated with 5 µg/mL cisplatin and (B) LS180 cells were treated with 10 µg/mL cisplatin for one day. Control cells were as described for Fig. 1. The mRNA level was assessed by multiplex RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Relative mRNA expression was evaluated in one experiment performed in duplicate. Human GAPDH was used as an internal control. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; CTL, control; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; CDDP, cisplatin. |
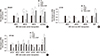
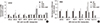 | Fig. 5Expression of drug transporter genes in hematological cancer cells treated with TCDD. (A) Jurkat and (B) K562 cells were pretreated with 10 nM TCDD for two days and then, treated with 5 and 15 µg/mL cisplatin, respectively, for one day. Control cells grown in culture medium as described for Fig. 1. Expression of mRNA was detected by multiplex RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Relative mRNA expression was evaluated in one independent experiment performed in duplicate. Human GAPDH was used as an internal control. *P < 0.05; CTL, control; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; CDDP, cisplatin. |
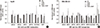 | Fig. 6Effect of TCDD pretreatment on expression of drug transporter genes in cells with unchanged sensitivity to cisplatin. (A) Hep3B and (B) MDA-MB-231 cells were pretreated with 10 nM and 5 nM TCDD, respectively, for two days and then treated with 5 µg/mL cisplatin for one day. Control cells were as described for Fig. 1. mRNA expression was detected by multiplex RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Relative mRNA expression was evaluated in one independent experiment run in duplicate. Human GAPDH was used as an internal control. *P < 0.05; CTL, control; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; CDDP, cisplatin. |
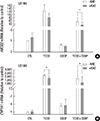 | Fig. 7AhR-dependent increase of the ABCG2 gene expression. LS180 cells were pretreated with 10 µM of an AhR-antagonist kaempferol for two hours, and then treated with 10 nM TCDD for two days and followed with 10 µg/mL cisplatin for one day. Expression of the (A) ABCG2 and (B) CYP1A1 genes was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. Control cells were treated as described for Fig. 1 and GAPDH was used as an internal control. Results were obtained from two independent experiments performed in duplicate and are shown as the mean ± SD. The Student,s t-test was used to compare ABCG2 and CYP1A1 expression between untreated and kaempferol-treated cells. **P < 0.01; CTL, control; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; CDDP, cisplatin; KAE, kaempferol. |
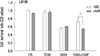 | Fig. 8Acquired cisplatin resistance induced by pretreatment with TCDD is AhR-dependent. LS180 cells were pretreated with 10 µM kaempferol for two hours and 10 nM TCDD for two days, and then with 10 µg/mL cisplatin for one day. Cell survival rate was assessed by MTT assay as described in Materials and Methods. Results were obtained from two independent experiments performed in duplicate and are shown as the mean ± SD. The Student,s t-test was used to compare the cell survival rate between untreated and kaempferol-treated cells. **P < 0.01; CTL, control; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; CDDP, cisplatin; KAE, kaempferol. |
Table 2
Gastric (SNU601), colon (LS180), and liver (Hep3B) cells were treated with 10 nM and breast (MDA-MB-231) cells were treated with 5 nM TCDD for two days. LS180 cells were then treated with 10 µg/mL cisplatin, and all other cells were treated with 5 µg/mL cisplatin for one day. Cell lysates were analyzed by ICP-MS after measuring protein concentration by Bradford assay. Data are expressed as mean±SEM of three independent experiments. *P<0.05 compared to cisplatin.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download