Abstract
Gout occurs mainly in monoarthritis and is found in more than 50% of cases in hallux of the foot. In addition, symptoms sometimes begin in the hand, wrist, and elbow, but they are rarely observed in the spine. The patient was referred for tuberculous polyarthritis due to antituberculosis drug failure. Inflammatory findings were observed in the lumbar, elbow, wrist, hand and foot areas. Surgery was performed on the foot area and a pathology diagnosis revealed gouty arthritis. We report this case with a review of the relevant literature.
References
1. Korean Foot and Ankle Society. The foot and ankle. Seoul: Jin;2010. p. 378–86.
2. Barret K, Miller ML, Wilson JT. Tophaceous gout of the spine mimicking epidural infection. Neurosurgery. 2001; 48:1170–2.
3. Rao TP, Shcmitt JK. Gout secondary to pyrazinamide and ethambutol. Va Med Q. 1996; 123:271.
4. Bădulescu M, Macovei L, Rezuş E. Acute gout attack with normal serum uric acid levels. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2014; 118:942–5.
5. Suk KS, Kim KT, Lee SH, Park SW. Gout spondyloarthropathy in the lumbar spine mimicking pyogenic discitis: a case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006; 41:756–60.
6. Watts HG, Lifeso RM. Tuberculosis of bones and joints. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996; 78:288–98.
7. The Korean Orthopaedic Association. Tuberculosis of bone and joint. Suk SI, editor. Orthopaedics. 7th ed.Seoul: Choisin;2013. p. 356–8.
8. Malik A, Schumacher HR, Dinnella JE, Clayburne GM. Clinical diagnostic criteria for gout: comparison with the gold standard of synovial fluid crystal analysis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 15:22–4.
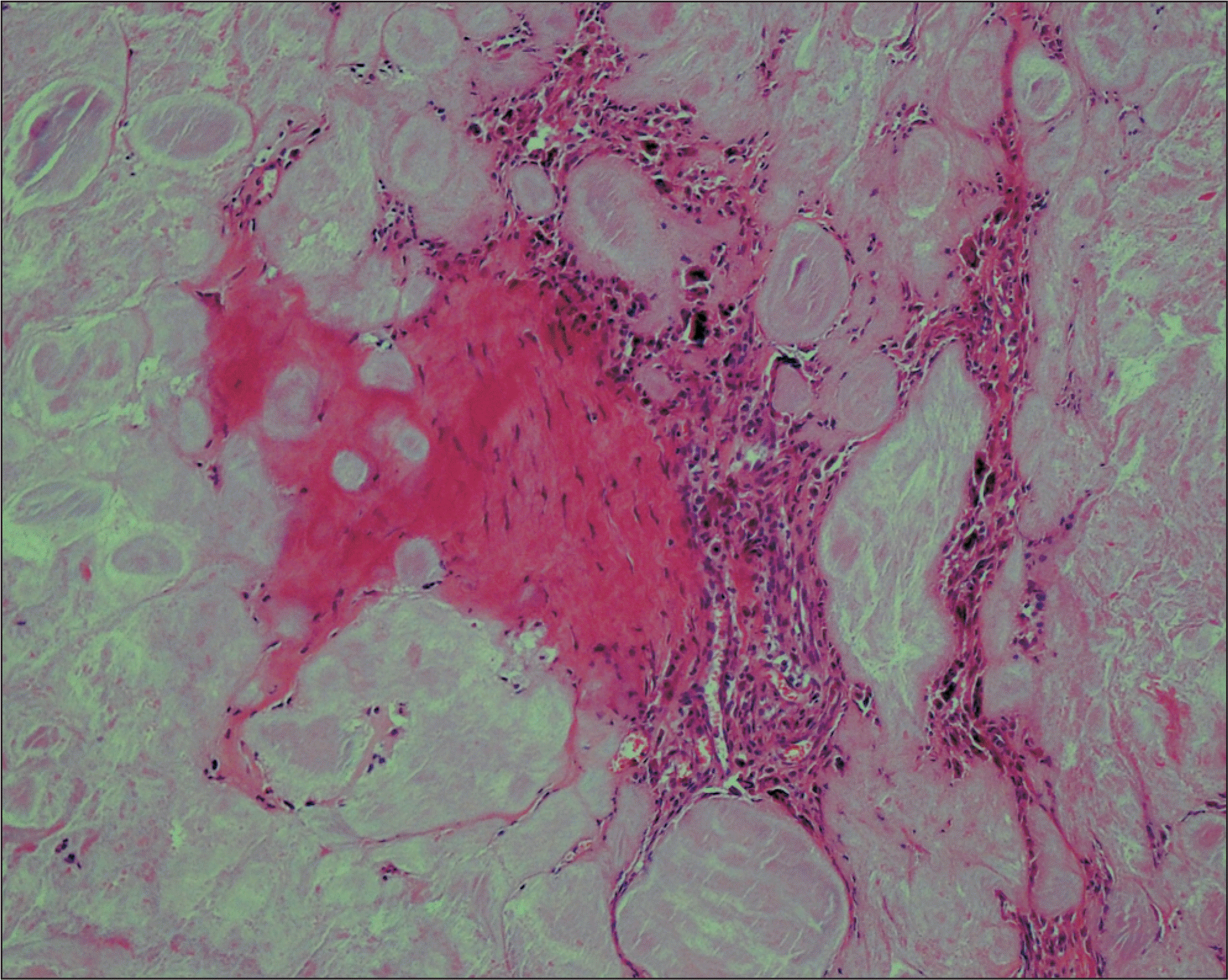
Figure 1.
Bone scan shows hot uptake at right elbow, wrist, hand, foot, and lumbar area (black arrows). IV: intravenous.
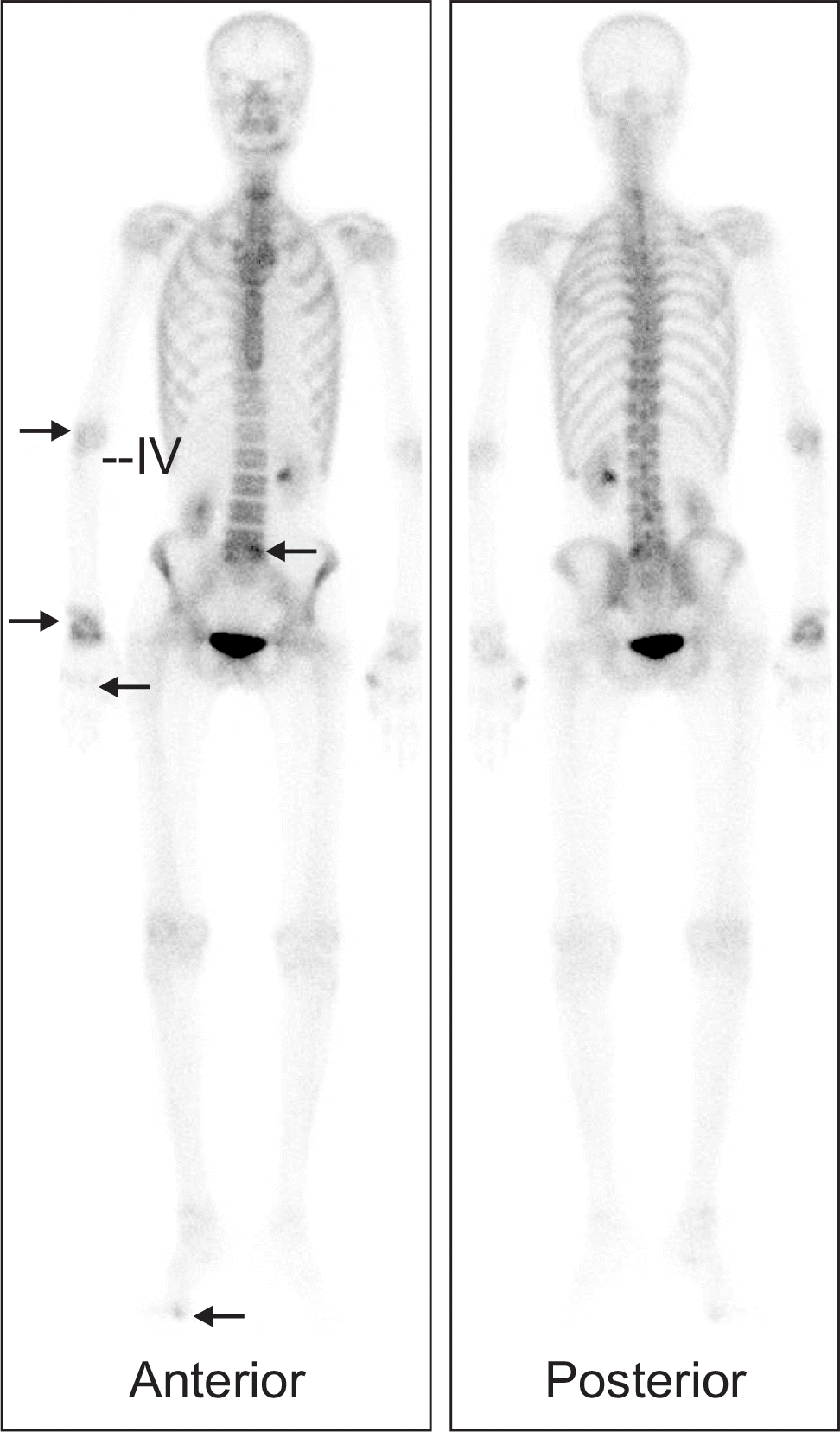
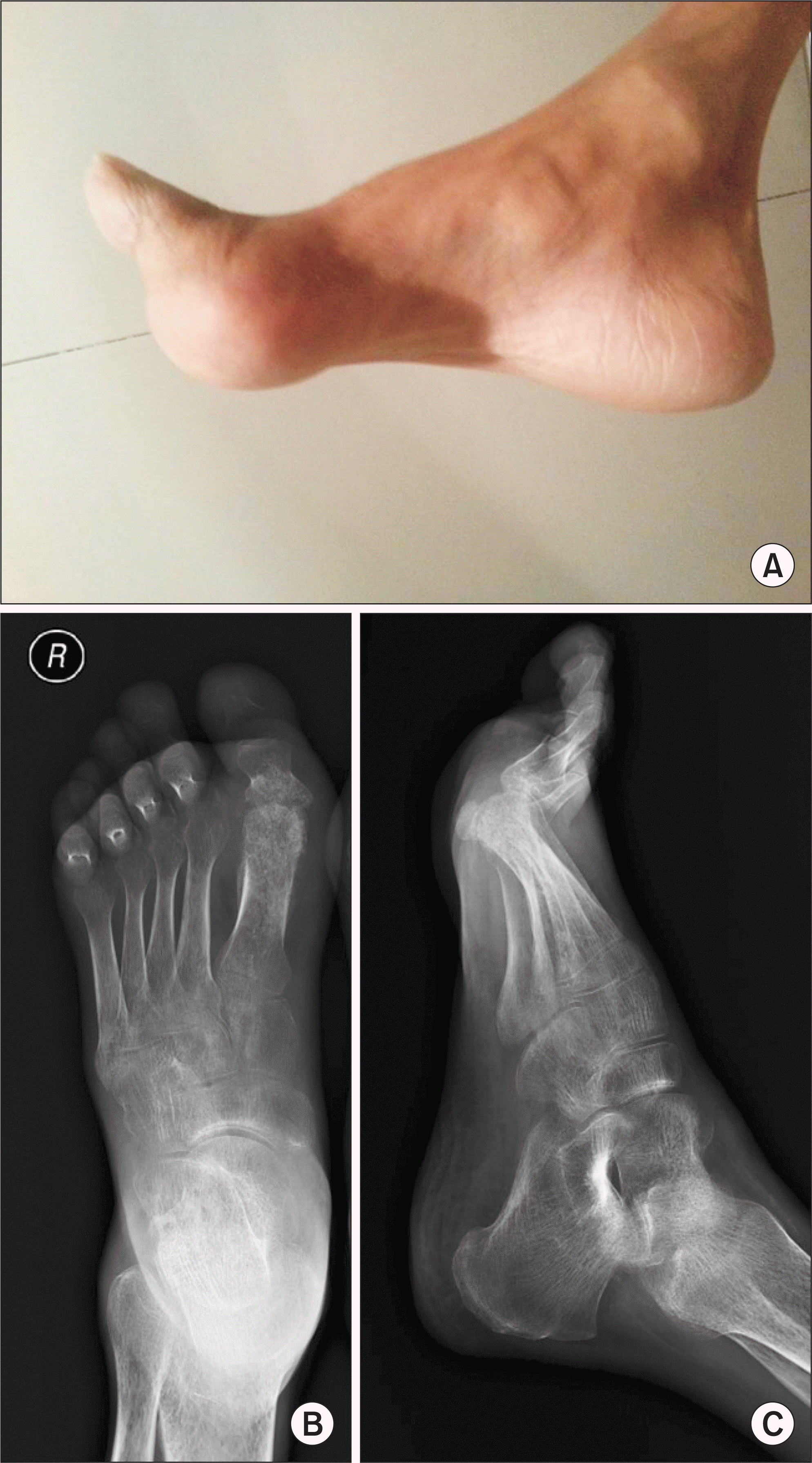
Figure 2.
(A) Gross photo shows swelling on right hallux. (B, C) Plain radiograph shows soft tissue swelling, bony erosion, osteopenia and mild subluxation on 1st metatarsal and phalanx.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download