Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical characteristics of xanthelasma palpebrarum as well as surgical results of upper blepharoplasty with a local flap technique.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional study including 12 patients who underwent removal of xanthelasma palpebrarum and upper blepharoplasty with the local flap technique from January 2010 to December 2017.
Results
A total of 18 eyelids of 12 patients were included in this study. The average age was 47.0 years and three patients (25.0%) were male and the other nine patients (75.0%) were female. There were seven patients (58.3%) on both sides of xanthelasma palpebrarum, and five patients (41.7%) on one side. There was hyperlipidemia in four patients (33.3%), hyper-triglyceridemia in two patients (18.2%), and hyper-low density lipoproteinemia in two patients (18.2%). Two patients had recurrence and the same surgery was performed. There was no postoperative complication. All patients were satisfied except for asymmetry in the postoperative end, and overall postoperative satisfaction was 83.3% (10/12 patients).
Conclusions
Xanthelasma palpebrarum often develops in both upper eyelids in middle-aged or older patients. Upper blepharoplasty with a local flap technique for the treatment of xanthelasma palpebrarum is an effective treatment for patients, especially in cases of ptosis or blepharochalasis. However, it should be noted that asymmetry of eyelids may occur after the surgery when surgery is performed on only one side.
References
1. Nair PA, Singhal R. Xanthelasma palpebrarum – a brief review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017; 11:1–5.
2. Jónsson A, Sigfŭ sson N. Significance of xanthelasma palpebrarum in the normal population. Lancet. 1976; 76:372.

3. Shin CH, Woo KI, Chang HR. A case of xanthoma presenting with blepharoptosis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:2585–8.
4. Rohrich RJ, Janis JE, Pownell PH. Xanthelasma palpebrarum: a review and current management principles. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002; 110:1310–4.

5. Akyüz AR, Ağ aç MT, Turan T, et al. Xanthelasma is associated with an increased amount of epicardial adipose tissue. Med Princ Pract. 2016; 25:187–90.

6. Bergman R. The pathogenesis and clinical significance of abdominal palpebrarum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994; 30(2 Pt 1):236–42.
7. Lee HY, Jin US, Minn KW, Park YO. Outcomes of surgical abdominal of xanthelasma palpebrarum. Arch Plast Surg. 2013; 40:380–6.
8. Raulin C, Schoenermark MP, Werner S, Greve B. Xanthelasma abdominal: treatment with the ultrapulsed CO2 laser. Lasers Surg Med. 1999; 24:122–7.
9. Borelli C, Kaudewitz P. Xanthelasma palpebrarum: treatment with the erbium:YAG laser. Lasers Surg Med. 2001; 29:260–4.

10. Heng JK, Chua SH, Goh CL, et al. Treatment of xanthelasma abdominal with a 1064-nm, Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017; 77:728–34.
11. Cannon PS, Ajit R, Leatherbarrow B. Efficacy of trichloroacetic acid (95%) in the management of xanthelasma palpebrarum. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010; 35:845–8.

12. Dewan SP, Kaur A, Gupta RK. Effectiveness of cryosurgery in xanthelasma palpebrarum. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1995; 61:4–7.
13. Sonthalia S, Arora R, Sarkar R. Successful cosmetic ablation of xanthelasma palpebrarum with low– voltage radiofrequency: back to the basics! Dermatol Surg. 2014; 40:1443–4.
14. Abdelkader M, Alashry SE. Argon laser versus erbium: YAG laser in the treatment of xanthalasma palpebrarum. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2015; 29:116–20.
15. Mendelson BC, Masson JK. Xanthelasma: follow-up on results abdominal surgical excision. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1976; 58:535–8.
16. Yang Y, Sun J, Xiong L, Li Q. Treatment of xanthelasma abdominal by upper eyelid flap incorporating blepharoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013; 37:882–6.
Figure 1.
Intraoperative photographs of upper blepharoplasty with local flap technique. (A) Incision of local flap. (B) Flap rotation. (C) Adjustment of flap to cover the defect. (D) Apposition of flap margin. (E) Sutured flap. (F) Upper blepharoplasty.

Figure 2.
Photographs of patients. (A) Preoperative photograph of 67-year old woman. (B) Postoperative photograph of 67-year old woman. (C) Preoperative photograph of 47-year old man. (D) Postoperative photograph of 47-year old man.

Figure 3.
Algorithm for management of patient with xanthelasma palpebrarum. The underlying medical condition, size and location of the lesion should be considered in treatment of xanthelasma palpebrarum. LDL = low density lipoprotein; IHD = ischemic heart disease; TCA = trichloroacetic acid.
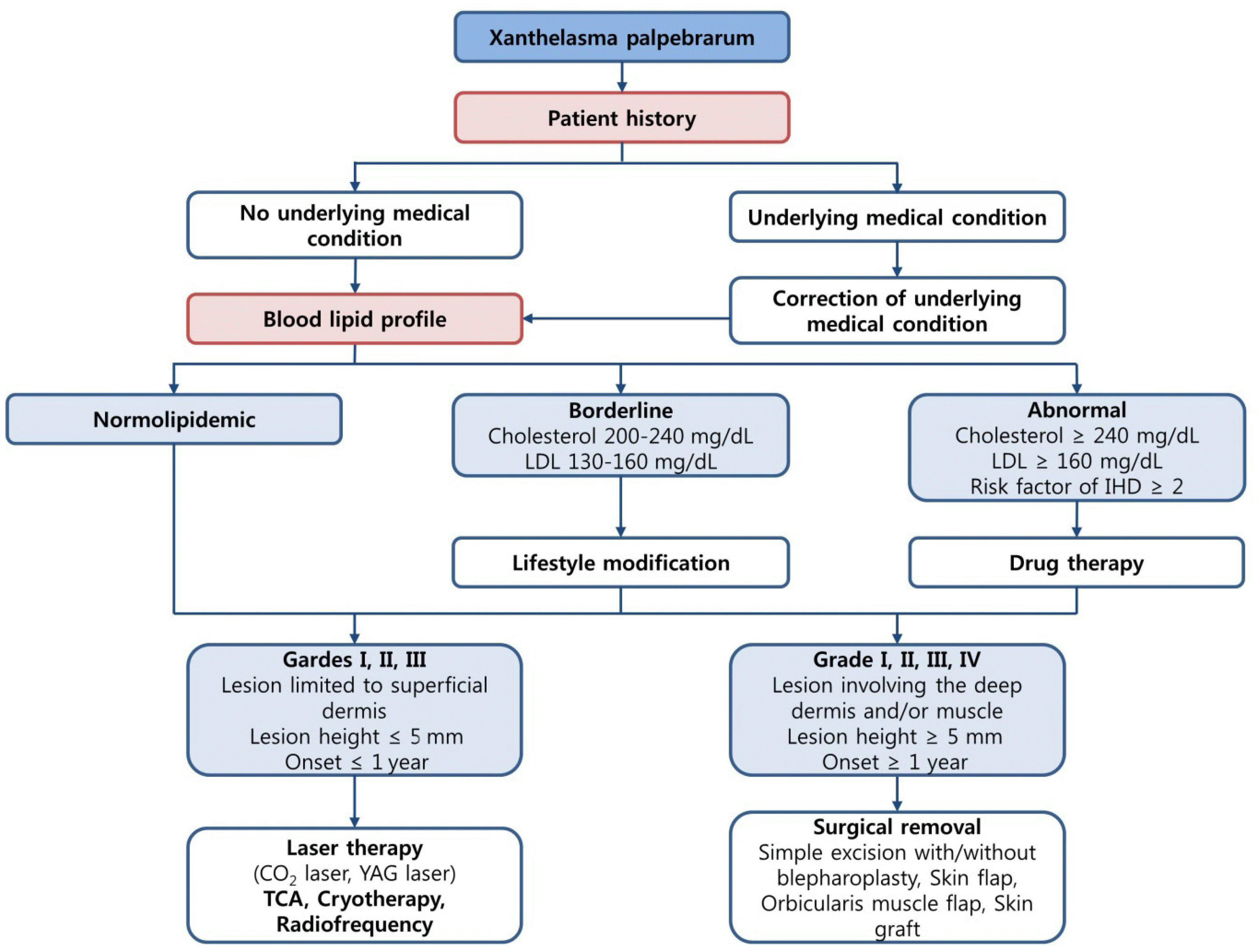
Table 1.
Summary of characteristics of patients
| Factor | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 47.0 ± 11.1 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 3 (25.0) |
| Female | 9 (75.0) |
| Location | |
| Unilateral | 7 (58.3) |
| Bilateral | 5 (41.7) |
| Lipid profile | |
| TG | 2 (16.7) |
| LDL | 2 (16.7) |
| Recurrence | 2 (16.7) |
Table 2.
Demographic characteristics of patients




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download