This article has been
cited by other articles in ScienceCentral.
Dear Editor,
DEL type red blood cells (RBCs) are characterized by the expression of extremely low levels of D-antigen, and thus, they cannot be detected by routine serologic D typing or a weak D test but are revealed by
RHD genotyping or adsorption-elution studies [
1]. The most common DEL phenotype is
RHD (NM_016124.4: c.1227G>A), which is also referred to as Asia type DEL [
2] and accounts for 94.7% of all Korean DEL cases [
1]. Although DEL is a rare phenotype in individuals of European ethnicity [
3], it is found in approximately 10–33% of serologically D-negative East Asian individuals of serologically D-negative East Asian individuals [
1].
Recently, Shao et al. [
2] suggested that individuals with the Asia type DEL allele can safely receive D-positive blood, without the risk of forming anti-D antibodies, since their RBCs have the complete repertoire of D-antigen epitopes. However, this proposal was based on data from Asia type DEL women exposed to D-antigens during pregnancy. The Korean National Guidelines for Blood Transfusion (KNGBT) (revised in 2016) [
4] allow D-positive transfusions in Asia type DEL patients in only emergency cases or severe shortage of D-negative blood. This proviso was established owing to the lack of direct evidence from blood transfusion cases regarding the safety of D-positive blood transfusions in Asia type DEL patients.
We report our recent experience of planned D-positive transfusions in an Asia type DEL patient in a non-emergency situation, suggesting that the KNGBT be modified to embrace the broad use of D-positive blood products for Asia type DEL patients (
Fig. 1). This retrospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Samsung Medical Center (2017-06-068), and informed consent was waived.
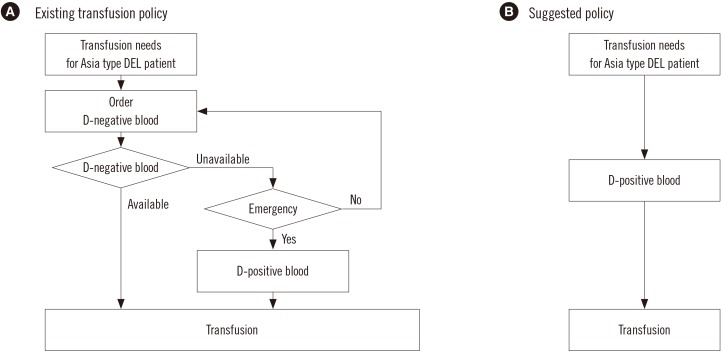 | Fig. 1Comparison of Korean National Guidelines for Blood Transfusion and our suggested policy for blood transfusion in Asia type DEL patients. (A) According to the Korean National Guidelines for Blood Transfusion (revised in 2016), Asia type DEL is regarded as D-negative, and patients can receive D-positive blood in only emergency situations or a D-negative blood shortage. (B) In our proposed policy, an Asia type DEL patient receives D-positive blood without delay in both emergency and non-emergency situations.
|
A 29-year-old male suffering from cardiac arrest due to ventricular tachycardia was admitted to Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, and was successfully resuscitated. He had a history of severe heart failure and multiple cardiac surgeries. Routine serotyping demonstrated an A, CcdEe phenotype, and the antibody screening test was negative. RHD genotyping was performed, and the patient was confirmed as Asia type DEL.
Initial transfusion of one unit of D-positive single donor platelets (SDPs) was accompanied by administration of RhIG. After three months, at the time of heart transplantation, passive anti-D was not detected. During the course of recovery from heart transplantation, the patient received 76 planned D-positive transfusions without RhIG (4, 39, 12, 6, and 15 units of RBCs, SDPs, platelet concentrates, fresh-frozen plasma, and cryoprecipitate, respectively). Antibody screening and direct Coombs tests, checked monthly (last follow-up as of October 2017), were persistently negative for one year after the D-positive transfusions. The patient did not show any rejection episodes related to the heart transplantation. He was discharged from the hospital with an additional transfusion of one unit of D-positive RBCs. Two months after discharge, follow-up antibody screening test showed negative results. Overall, the patient received 77 units of D-positive transfusion products without RhIG prophylaxis and one unit of D-positive SDPs with RhIG, and he did not show alloimmunization.
Table 1 summarizes this case and other reported cases of DEL individuals exposed to D antigen, all of which suggest that safe D-positive transfusion can be possible in individuals with the Asia type DEL allele (c.1227G>A), not other DEL alleles (i.e., IVS3+1G>A, del Ex8).
Table 1
Reported cases of DEL individuals exposed to D antigen
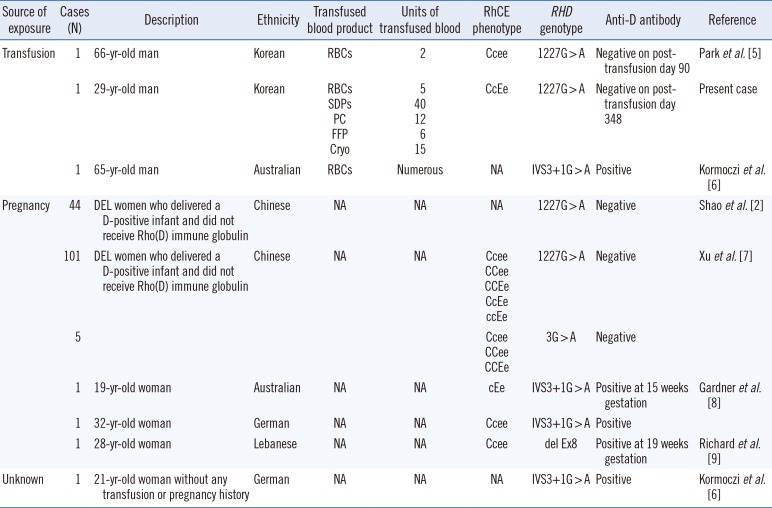
|
Source of exposure |
Cases (N) |
Description |
Ethnicity |
Transfused blood product |
Units of transfused blood |
RhCE phenotype |
RHD genotype |
Anti-D antibody |
Reference |
|
Transfusion |
1 |
66-yr-old man |
Korean |
RBCs |
2 |
Ccee |
1227G>A |
Negative on post-transfusion day 90 |
Park et al. [5] |
|
1 |
29-yr-old man |
Korean |
RBCs |
5 |
CcEe |
1227G>A |
Negative on post-transfusion day 348 |
Present case |
|
SDPs |
40 |
|
PC |
12 |
|
FFP |
6 |
|
Cryo |
15 |
|
1 |
65-yr-old man |
Australian |
RBCs |
Numerous |
NA |
IVS3+1G>A |
Positive |
Kormoczi et al. [6] |
|
Pregnancy |
44 |
DEL women who delivered a D-positive infant and did not receive Rho(D) immune globulin |
Chinese |
NA |
NA |
NA |
1227G>A |
Negative |
Shao et al. [2] |
|
101 |
DEL women who delivered a D-positive infant and did not receive Rho(D) immune globulin |
Chinese |
NA |
NA |
Ccee |
1227G>A |
Negative |
Xu et al. [7] |
|
CCee |
|
CCEe |
|
CcEe |
|
ccEe |
|
5 |
Ccee |
3G>A |
Negative |
|
CCee |
|
CCEe |
|
1 |
19-yr-old woman |
Australian |
NA |
NA |
cEe |
IVS3+1G>A |
Positive at 15 weeks gestation |
Gardner et al. [8] |
|
1 |
32-yr-old woman |
German |
NA |
NA |
Ccee |
IVS3+1G>A |
Positive |
|
|
1 |
28-yr-old woman |
Lebanese |
NA |
NA |
Ccee |
del Ex8 |
Positive at 19 weeks gestation |
Richard et al. [9] |
|
Unknown |
1 |
21-yr-old woman without any transfusion or pregnancy history |
German |
NA |
NA |
NA |
IVS3+1G>A |
Positive |
Kormoczi et al. [6] |

Based on the present case and our literature review [
256789], we suggest modification of the KNGBT to embrace the broad use of D-positive blood products for Asia type DEL patients in both emergency and non-emergency situations. This will relieve the shortage of D-negative blood in Korea by reducing its usage in Asia type DEL patients.






 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download