Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
A total of 85 patients were included in the study after excluding patients who underwent salvage liver transplantation due to liver failure (n = 26), patients who underwent deceased donor liver transplantation (n = 9) and patients who underwent locoregional therapy more than 6 months prior to liver resection (n = 3). SLT, salvage liver transplantation; LR, liver resection; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; LT, liver transplantation; LRT, locoregional therapy.
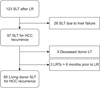
Fig. 2
Multivariate Cox analysis showed that patients who underwent 5 or more locoregional therapies prior to salvage liver transplantation (hazard ratio [HR], 3.74; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.45–9.64, P = 0.006) (A) outside the Milan criteria at the time of transplantation (HR, 2.66, CI, 1.26–5.63, P = 0.011) (B) and α-FP level ≥ 1,000 ng/mL at the time of LT (HR, 3.43, CI, 1.28–9.18, P = 0.014) (C) were significant factors related to recurrence after salvage liver transplantation. HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; LRT, locoregional therapy; SLT, salvage liver transplantation.
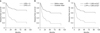
Table 1
Clinicopathological characteristics of patients at the time of initial liver resection
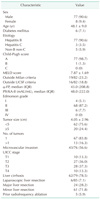
Values are presented as number (%) or mean ± standard deviation unless otherwise indicated.
MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; UCSF, University of California, San Fransisco; IQR, interquartile range; PIVKA-II, protein induced by vitamin K deficiency-II; UICC, Union for International Cancer Control.
Table 2
Clinical characteristics of patients at recurrence after initial liver resection
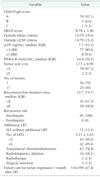
Values are presented as number (%) or mean ± standard deviation unless otherwise indicated.
MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; UCSF, University of California, San Fransisco; IQR, interquartile range; PIVKA-II, protein induced by vitamin K deficiency-II; LRT, locoregional therapy; SLT, salvage liver transplantation.
Table 3
Clinicopathological characteristics of patients at the time of salvage liver transplantation

Values are presented as number (%) or mean ± standard deviation unless otherwise indicated.
MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; UCSF, University of California, San Fransisco; IQR, interquartile range; PIVKA-II, protein induced by vitamin K deficiency-II; UICC, Union for International Cancer Control.
Table 4
Comparison of clinicopathological characteristics of patients divided by five locoretional therapies at the time of initial liver resection and at the time of liver transplantation

Values are presented as number (%) or mean ± standard deviation unless otherwise indicated.
MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; UCSF, University of California, San Fransisco; IQR, interquartile range; PIVKA-II, protein induced by vitamin K deficiency-II; UICC, Union for International Cancer Control.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download