Dear Editor:
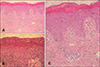
A 5-year-old boy presented with diffuse erythematous patches and fever, started three days earlier. Ten days earlier, second-generation cephalosporin and mupirocin ointment was used for a mosquito bite site on left elbow at another hospital. Three days ago, oral steroids were prescribed in another hospital to treat a trunk rash and perioral crust, but they did not work. At the time of arrival, the whole body skin was rough with erythematous patches and unclear border. Crust and cracks existed around the mouth (Fig. 1A, B). Thin blisters and erosions were on the lower abdomen, but the Nikolsky's sign was negative (Fig. 1C). The patient's body temperature was 37.1℃ and there were no significant abnormalities in the laboratory test. Staphylococcus aureus was identified through bacterial culture from the elbows and throat. From the histopathology of the trunk, mild perivascular lymphocyte infiltration was observed with neutrophils seen in the subcorneal lesion, but blistering was not distinct (Fig. 2A, B). Mild spongiosis and scarce infiltration of inflammatory cells were observed without cell necrosis (Fig. 2C). After admission, third-generation cephalosporin was administered. The desquamation worsened and the erythema gradually faded. He was discharged on the 8th day after admission (Fig. 1D~F). Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (4S) is caused by toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus12. Diagnosis is based on clinical features, and can be confirmed with bacterial culture, toxin isolation or pathologic findings. Diagnosis of causative organisms is based on the discovery of genes involved in the secretion of skin-deprived toxins from bacteria or toxins after isolating the Staphylococcus aureus13. However, isolation and genetic testing are difficult to perform because special facilities are required34. Clinical types are divided into four types: systemic, intermediate, abortive, and local1. The abortive form manifests as whole body scarlatiniform eruptions with a coarse, sandpaper-like surface at the early stage without blister formation45. Later, the healing process with desquamation occurs45. In general, Nikolsky's sign is negative14. It is usually cured with appropriate antibiotics, but the mortality rate is about 3% in children4. The abortive form has not yet been clearly defined. It seems likely that some cases cannot be strictly distinguished into different forms of 4S23. Abortive 4S requires a careful differential diagnosis because it imitates various skin diseases such as scarlet fever and impetigo45. The abortive form of the disease is known to be less common. However, according to previous studies in Korea, intermediate type and abortive type occupy the majority of cases, after reclassifying the clinical types with a retrospective review of medical records45. In this case, at the onset of disease, there were no blisters anywhere on the body and the Nikolsky's sign was negative. As with our patient, abortive 4S proved difficult to diagnose, and thus might be more common than expected. In addition, the incidence has increased in recent years4. In the context of the low awareness of the various forms of 4S, we experienced a case of abortive 4S that may serve as a useful educational case.
Figures and Tables
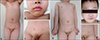
Fig. 1
Diffuse erythroderma involves the neck, trunk, and extremities with sandpaper-like coarseness (A), and perioral crust and fissure (B) were observed. Several vesicobullae and erosive lesions were observed in the lower abdomen, without Nikolsky sign (C). The desquamation worsened and the erythema gradually faded on the 8th day after admission (D~F) (We received the patient's consent form about publishing all photographic materials).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This study was supported by grants of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2017R1 A2B4006252), Korea Healthcare technology R&D project, funded by Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI17C0597), and the Hallym University Research Fund (HURF-2017-35).
References
1. Park AY, Yeon EK, Lee HK, Shin MY. A clinical review of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome for the last 10 years. Soonchunhyang Med Sci. 2012; 18:32–37.

2. Patel GK, Finlay AY. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003; 4:165–175.
4. Park JW, Hwang DK, Yu HJ. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, review of 20 cases. Korean J Dermatol. 2002; 40:1051–1057.
5. Kang JD, Park SD. Reclassification of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome by clinical analysis of 25 cases. Korean J Dermatol. 2004; 42:398–405.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download