Abstract
Multifocal acquired demyelinating sensory and motor (MADSAM) neuropathy is a variant of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathy. A 65-year-old women presented with up-per arm weakness. A nerve conduction study showed conduction blocks over intermediate segments with sparing of distal compound action potentials. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed asymmetric hypertrophy of the brachial plexus on the affected side. These findings represent important electrophysiological and radiological evidence of MADSAM neuropathy. The condition of the patient began to improve after starting intravenous immunoglobulin administration.
Go to : 
References
1. Kuwabara S, Misawa S. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: clinical subtypes and their correlation with electrophysiology. Clin Exp Neuroimmunol. 2011; 2:41–48.

2. Shibuya K, Sugiyama A, Ito S, Misawa S, Sekiguchi Y, Mitsuma S, et el. Reconstruction magnetic resonance neurography in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol. 2015; 77:333–337.
3. Ad Hoc Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Research criteria for the diagnosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). Neurology. 1991; 41:617–618.
4. Van den Bergh PY, Hadden RD, Bouche P, Cornblath DR, Hahn A, Illa I, et el. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society – first revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010; 17:356–363.
5. Viala K, ReniéL, Maisonobe T, Béhin A, Neil J, Léger JM, et el. Follow-up study and response to treatment in 23 patients with Lewis-Sumner syndrome. Brain. 2004; 127(Pt 9):2010–2017.
Go to : 
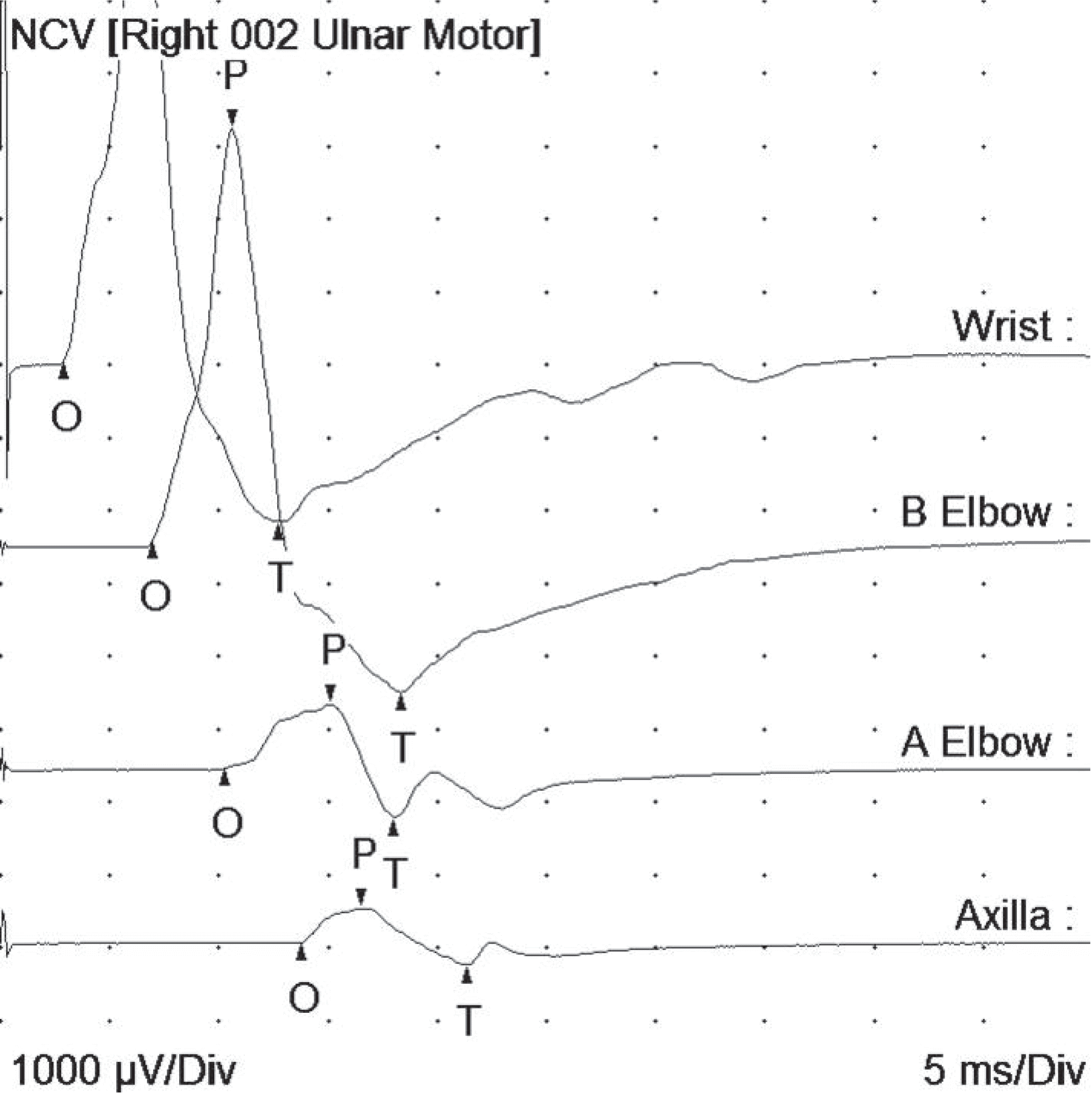 | Fig. 1.Findings of the motor nerve conduction study of the right ulnar nerve. The distal motor latency and the compound muscle action potentials were normal at the wrist and below the elbow. Conduction block was observed between above and below the elbow. NCV, nerve conduction velocity. |
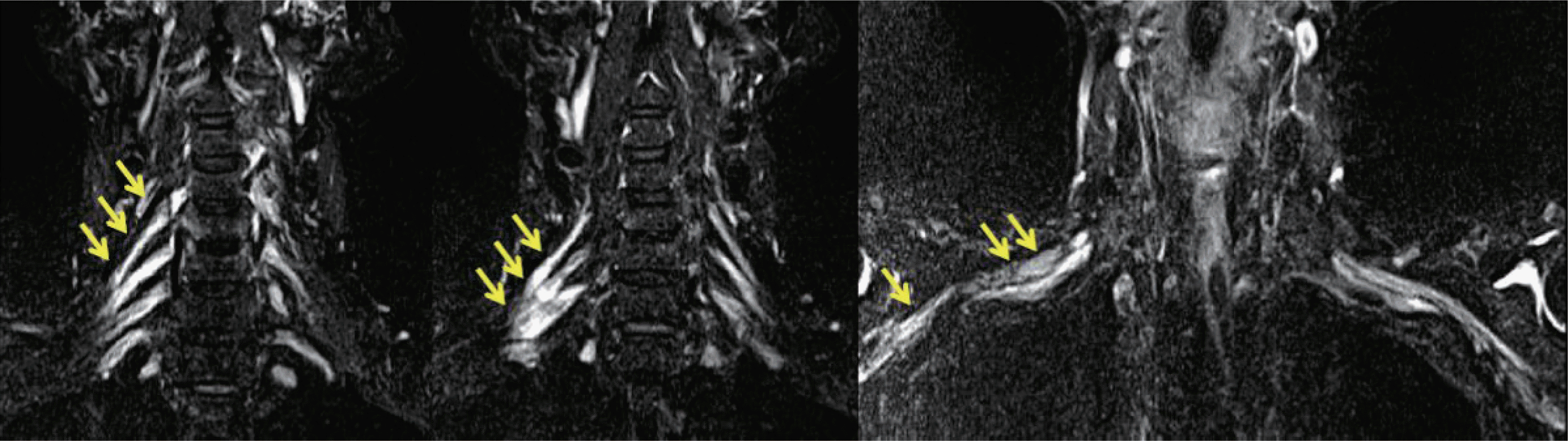 | Fig. 2.Brachial plexus magnetic resonance imaging (Short T1 Inversion Recovery Image, non-contrast enhanced) revealed fusiform hypertrophy of the right C5-C8 roots, and plexus was observed (arrows). No hypertrophy was observed on the left side. |
Table 1.
Findings of the nerve conduction study of the patient




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download