Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Dry human skull used in this study. The risk of errors during the process of three-dimensional cephalogram construction is minimized by the attachment of titanium fiducial markers to anatomical landmarks prior to the acquisition of radiographs. Description of landmarks are shown in the Table 1.
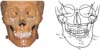
Figure 2
The biplanar imaging system used in this study. Two instrumentariums were positioned at a 90° angle and two arrays of X-ray beams were simultaneously projected toward the subject with the head posture remaining identical for both lateral and frontal cephalogram acquisition.

Figure 3
The three-dimensional (3D) Ceph™ program (Department of Orthodontics, University of Chicago, IL, USA) used in this study. A and B, Input of lateral and frontal cephalograms into the 3D Ceph™ program. C, Landmark correction using vector intercept with manual or averaging algorithm in the 3D Aligner™ program (Department of Orthodontics, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA). D, Generation of a three-dimensional cephalometric image using the “create 3D frame” function and measurement output using the “3D log” function in the program.

Figure 4
Bland–Altman plots for the comparison of three-dimensional (3D) cephalograms constructed from biplanar radiographs and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images.
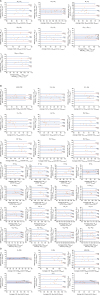
Table 2
Comparison between CBCT-generated cephalograms and 3D cephalograms constructed from conventional cephalograms

Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
CBCT, Cone-beam computed tomography; 3D, three dimensional; cephconv, 3D cephalogram by conventional radiography; cephcbct, 3D cephalogram by CBCT; rt, right; lt, left; post, posterior; inf, inferior.
Significance was determined by the paired t-test.
Descriptions of landmarks are shown in Figure 1 and Table 1.
Table 3
Comparison between CBCT-generated cephalograms and 3D cephalograms constructed from biplanar cephalograms

Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
CBCT, Cone-beam computed tomography; 3D, three dimensional; cephbiplanar, 3D cephalogram by biplanar imaging system; cephcbct, 3D cephalogram by CBCT; rt, right; lt, left; post, posterior; inf, inferior.
Significance was determined by the paired t-test.
Descriptions of landmarks are shown in Figure 1 and Table 1.
Table 4
Bland–Altman analysis of the accuracy of three-dimensional measurements obtained from conventional cephalograms





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download