INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
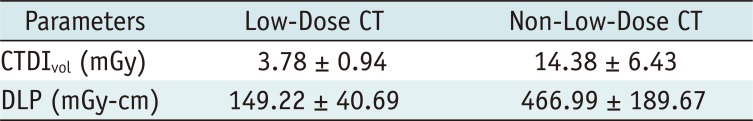
Image Acquisition and Reconstruction
Objective Image Analyses
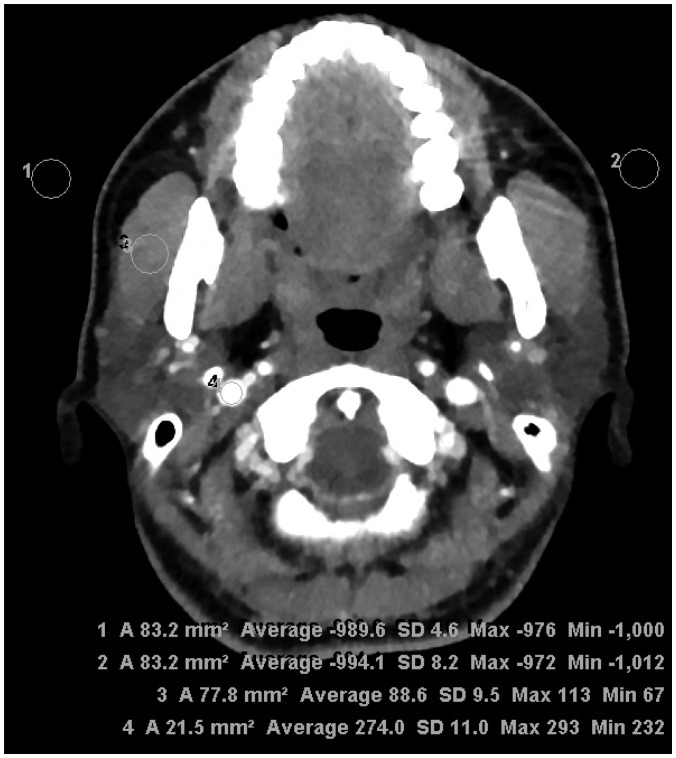 | Fig. 1Assessment of objective image quality at parotid gland level.Regions of interest were drawn to bilaterally measure SD of air (background noise) and attenuation of masseter muscle and internal jugular vein for estimation of signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio. SD = standard deviation
|
Subjective Image Analyses
Statistical Analysis
RESULTS
Table 1
Results of Objective Analyses of Reconstruction Techniques for CT in Evaluation of Parotid Gland Masses
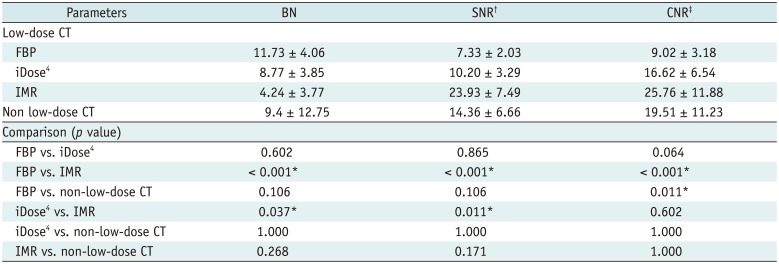
*p < 0.05, †SNR measured at MM, ‡CNR between MM and internal jugular vein. BN = background noise, CNR = contrast-to-noise ratio, FBP = filtered back projection, iDose4 = hybrid iterative reconstruction, IMR = knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction, MM = masseter muscle, SNR = signal-to-noise ratio
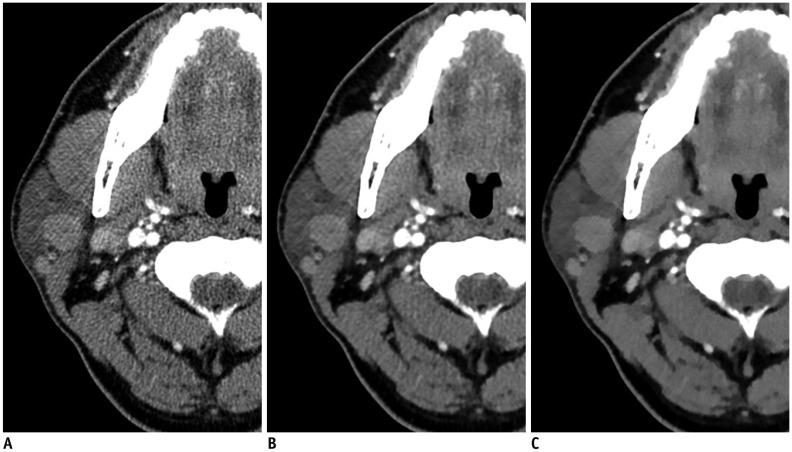 | Fig. 263-year-old woman with right parotid gland mass.Three axial image sets reconstructed using FBP (A), iDose4
(B), and IMR (C) algorithms. Compared with FBP- and iDose4-reconstructed images, significant decrease in streak artifacts related to dental amalgam was observed in parotid area with better conspicuity and definition of tumor margins in iterative model-reconstructed image. However, iterative model-reconstructed image showed relatively poor image sharpness, compared with FBP- and iDose4-reconstructed images. FBP = filtered back projection, iDose4 = hybrid iterative reconstruction, IMR = knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction
|
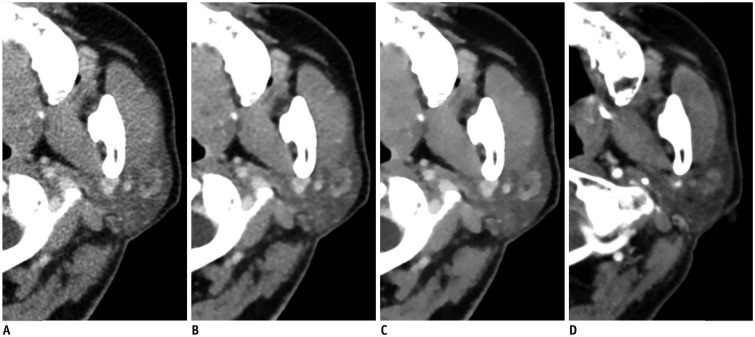 | Fig. 368-year-old man with left parotid gland mass.Four axial image sets of low-dose CT reconstructed using FBP (A), iDose4
(B), and knowledge-based IMR (C) algorithms and non-low-dose CT (D). Compared with FBP- and iDose4-reconstructed images as well as non-low-dose CT, there is significant decrease in noise associated with parotid region and significantly better contrast and characterization of tumor in iterative model-reconstructed image. Parotid tissue appears blotchy and pixelated in iterative model-reconstructed image.
|
Table 2
Results of Subjective Analyses of Reconstruction Techniques for CT in Evaluation of Parotid Gland Masses
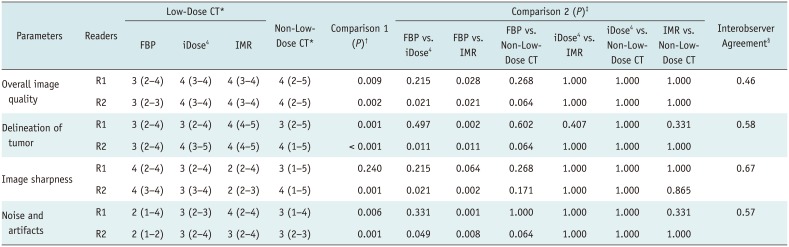
*Values indicate median (range), †p < 0.05 indicates that there was/were pair/pairs showing significant difference for six pairs in four different data sets according to Friedman test, ‡p values indicate comparison results for six pairs in four different data sets according to Wilcoxon signed-rank tests following Friedman tests, §Values indicate kappa scores.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



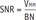
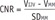
 XML Download
XML Download