We previously reported that DNA priming and protein boosting can preferentially generate hybridomas secreting IgG antibodies [
10]. To generate IgG antibodies with higher antigen-binding activity, the immunization scheme was modified: mice were injected by IM-EP with pcDNA3-GP (50 µg/mouse) at 0, 4, and 12 weeks, followed by intraperitoneal injection at 20 weeks with recombinant GP (20 µg/mouse) emulsified in incomplete Freund's adjuvant. Four weeks later, the mice were intravenously injected with recombinant GP (20 µg/mouse) in PBS. The mice were sacrificed 3 days after the final injection and the splenocytes were used for fusion. In this fusion experiment, 12 hybridomas, the cell supernatants of which displayed 10 times higher OD values than those of the negative control by ELISA and displayed both heavy and light chains of IgG by Western blot assay, were selected (data not included). These 12 hybridomas were designated C36, D11, D12, D34, E2, E8, E12, E22, E31, E49, E60, and E140. For MAb production, the 12 selected hybridomas were diluted to make a single cell clone using the limiting dilution sub-culture method [
11]. As a result, 7 monoclonal clones were obtained and designated C36-1, D11-3, D12-1, D34-2, E12-10, E49-3, and E140-2 (
Table 1). Unfortunately, we were unable to generate any clones secreting GP-specific IgG antibodies for clones E2, E8, E22, E31 and E60. In addition, we obtained only IgM-secreting single clones (e.g., E12-10 and E49-3) from hybridomas (E12 and E49). Finally, IgG antibodies were purified from the cell supernatants of 5 clones (C36-1, D11-3, D12-1, D34-2, and E140-2) using the protein G column. They all resolved into 2 protein bands (50-kDa H chains and 25-kDa L chains) on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel (
Fig. 2A). They also reacted with Ebola virus GP, but not with MERS coronavirus-spike protein and SFTS virus GP, as determined by ELISA (
Fig. 2B). This result suggests that these purified IgG antibodies are indeed antigen-specific. Furthermore, IgG antibodies from clones C36-1, D11-3, D12-1, D34-2, and E140-2 remained reactive to GP at the lowest tested concentrations of 1.953, 7.8, 7.8, 1.953, and 1.953 ng/mL, respectively (
Fig. 2C). In this case, the lowest tested concentrations are defined as the lowest IgG concentrations showing positive optical density values compared to those of control IgG (2 µg/mL) when IgG samples were serially diluted by 2-fold from the dose (2 µg/mL) and then reacted with recombinant GP in ELISA. When the IgG antibodies from the five clones were further tested for their reactivity to five different GP1 proteins (GP1a, GP1b, GP1c, GP1d, and GP1e), only the IgG antibodies from clone D12-1 reacted with GP1e while the IgG antibodies from clones C36-1, D11-3, D34-2, and E140-2 failed to react with any of the GP1 proteins (
Fig. 2D). This result suggests that the IgG antibodies from clones C36-1, D11-3, D34-2, and E140-2 may recognize either the tertiary structure of GP or the GP regions excluding the receptor-binding domain and mucin-like region, and that the IgG antibodies from clone D12-1 might recognize the mucin-like region of GP. This is illustrated in
Table 1.
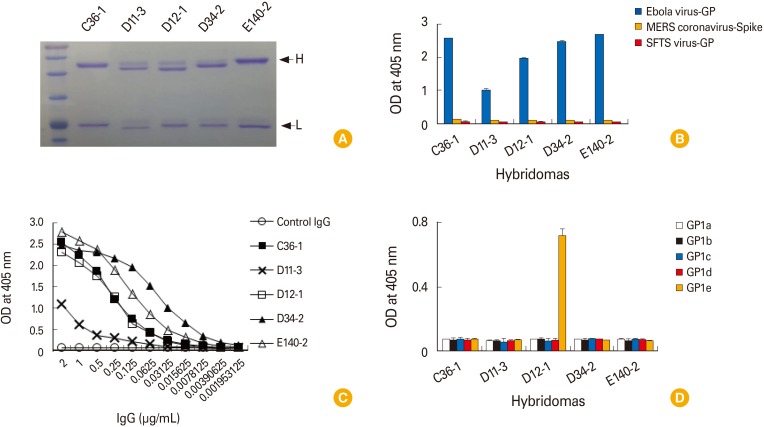 | Fig. 2Purification of the IgG antibodies from the five hybridoma clones, and the evaluation of their Ag-specific binding activity. (A) The hybridomas (D36, D11, D12, D34, and E140) were diluted to make a single cell by the limiting dilution sub-clone method. The resulting monoclonal hybridoma clones were designated C36-1, D11-3, D12-1, and E140-2. IgG antibodies were purified from the cell supernatants using the protein G column. Two µg of the purified IgG antibodies were run on a 12% SDS-PAGE for brilliant blue R staining. (B) The purified IgG (2 µg/mL) were reacted with Ebola virus GP, MERS coronavirus spike protein and SFTS virus GP for ELISA. (C) Evaluation of the lowest GP-binding concentration of IgG antibodies. Two micrograms per milliliter of IgG antibodies from the clones, C36-1, D11-3, D12-1, and E140-2 were serially diluted by 2-fold and then reacted with GP in parallel with control IgG (2 µg/mL) to determine the lowest GP-binding concentration using ELISA. (D) Five recombinant GP1 proteins (1 µg/mL) were coated and reacted with the five purified IgG antibodies (0.2 µg/mL) from clones, C36-1, D11-3, D12-1, and E140-2 for ELISA. SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel; GP, glycoprotein; MERS, Middle East respiratory syndrome; SFTS, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; OD, optical density.
|
Table 1
The binding properties of the purified IgG and IgM antibodies from 7 hybridoma clones
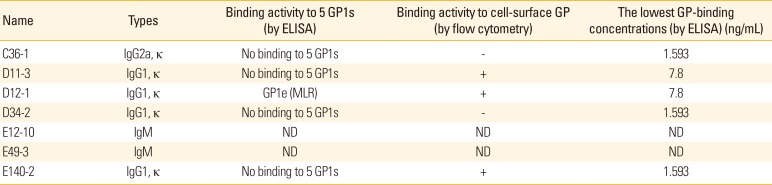
|
Name |
Types |
Binding activity to 5 GP1s (by ELISA) |
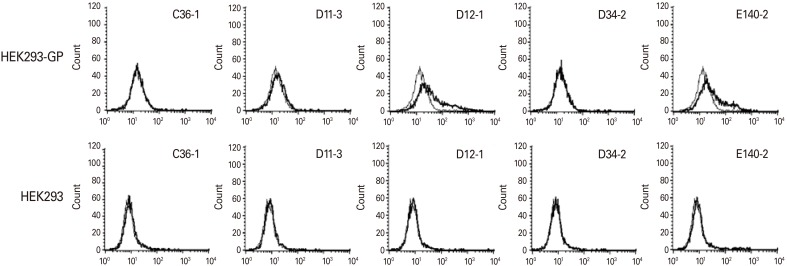
Binding activity to cell-surface GP (by flow cytometry) |
The lowest GP-binding concentrations (by ELISA) (ng/mL) |
|
C36-1 |
IgG2a, κ |
No binding to 5 GP1s |
- |
1.593 |
|
D11-3 |
IgG1, κ |
No binding to 5 GP1s |
+ |
7.8 |
|
D12-1 |
IgG1, κ |
GP1e (MLR) |
+ |
7.8 |
|
D34-2 |
IgG1, κ |
No binding to 5 GP1s |
- |
1.593 |
|
E12-10 |
IgM |
ND |
ND |
ND |
|
E49-3 |
IgM |
ND |
ND |
ND |
|
E140-2 |
IgG1, κ |
No binding to 5 GP1s |
+ |
1.593 |







 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download