1. Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS. GOLD Scientific Committee. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:1256–1276. PMID:
11316667.
2. American Thoracic Society. Dyspnea: mechanisms, assessment, and management: a consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 159:321–340. PMID:
9872857.
3. Rothpearl A, Varma AO, Goodman K. Radiographic measures of hyperinflation in clinical emphysema: discrimination of patients from controls and relationship to physiologic and mechanical lung function. Chest. 1988; 94:907–913. PMID:
3180893.
4. Burki NK, Krumpelman JL. Correlation of pulmonary function with the chest roentgenogram in chronic airway obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980; 121:217–223. PMID:
7362131.
5. Simon G, Pride NB, Jones NL, Raimondi AC. Relation between abnormalities in the chest radiograph and changes in pulmonary function in chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Thorax. 1973; 28:15–23. PMID:
4685207.

6. Nicklaus TM, Stowell DW, Christiansen WR, Renzetti AD Jr. The accuracy of the roentgenologic diagnosis of chronic pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966; 93:889–899. PMID:
5942235.
7. Lando Y, Boiselle P, Shade D, Travaline JM, Furukawa S, Criner GJ. Effect of lung volume reduction surgery on bony thorax configuration in severe COPD. Chest. 1999; 116:30–39. PMID:
10424500.

8. Pierce JA, Ebert RV. The barrel deformity of the chest, the senile lung and obstructive pulmonary emphysema. Am J Med. 1958; 25:13–22. PMID:
13559256.

9. Kilburn KH, Asmundsson T. Anteroposterior chest diameter in emphysema: from maxim to measurement. Arch Intern Med. 1969; 123:379–382. PMID:
5778119.

10. Gilmartin JJ, Gibson GJ. Abnormalities of chest wall motion in patients with chronic airflow obstruction. Thorax. 1984; 39:264–271. PMID:
6719373.

11. Bellemare F, Jeanneret A, Couture J. Sex differences in thoracic dimensions and configuration. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 168:305–312. PMID:
12773331.

12. Bellemare JF, Cordeau MP, Leblanc P, Bellemare F. Thoracic dimensions at maximum lung inflation in normal subjects and in patients with obstructive and restrictive lung diseases. Chest. 2001; 119:376–386. PMID:
11171712.

13. Holcombe SA, Wang SC, Grotberg JB. The effect of age and demographics on rib shape. J Anat. 2017; 231:229–247. PMID:
28612467.

14. Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005; 26:319–338. PMID:
16055882.
15. Brooks D, Solway S, Weinacht K, Wang D, Thomas S. Comparison between an indoor and an outdoor 6-minute walk test among individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 84:873–876. PMID:
12808541.
16. Sverzellati N, Colombi D, Randi G, Pavarani A, Silva M, Walsh SL, et al. Computed tomography measurement of rib cage morphometry in emphysema. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e68546. PMID:
23935872.

17. Thurlbeck WM, Simon G. Radiographic appearance of the chest in emphysema. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978; 130:429–440. PMID:
415543.

18. Sharp JT, Beard GA, Sunga M, Kim TW, Modh A, Lind J, et al. The rib cage in normal and emphysematous subjects: a roentgenographic approach. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1986; 61:2050–2059. PMID:
3100493.

19. Thomas AJ, Supinski GS, Kelsen SG. Changes in chest wall structure and elasticity in elastase-induced emphysema. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1986; 61:1821–1829. PMID:
3640762.

20. Walsh JM, Webber CL Jr, Fahey PJ, Sharp JT. Structural change of the thorax in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1992; 72:1270–1278. PMID:
1592714.

21. Cassart M, Gevenois PA, Estenne M. Rib cage dimensions in hyperinflated patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; 154(3 Pt 1):800–805. PMID:
8810622.

22. Arakawa H, Kurihara Y, Nakajima Y, Niimi H, Ishikawa T, Tokuda M. Computed tomography measurements of overinflation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: evaluation of various radiographic signs. J Thorac Imaging. 1998; 13:188–192. PMID:
9671421.
23. Bartynski WS, Heller MT, Grahovac SZ, Rothfus WE, Kurs-Lasky M. Severe thoracic kyphosis in the older patient in the absence of vertebral fracture: association of extreme curve with age. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:2077–2085. PMID:
16155162.
24. Sharma G, Goodwin J. Effect of aging on respiratory system physiology and immunology. Clin Interv Aging. 2006; 1:253–260. PMID:
18046878.

25. Buist AS, McBurnie MA, Vollmer WM, Gillespie S, Burney P, Mannino DM, et al. International variation in the prevalence of COPD (the BOLD Study): a population-based prevalence study. Lancet. 2007; 370:741–750. PMID:
17765523.

26. Thurlbeck WM. Postnatal human lung growth. Thorax. 1982; 37:564–571. PMID:
7179184.

27. Weaver AA, Schoell SL, Stitzel JD. Morphometric analysis of variation in the ribs with age and sex. J Anat. 2014; 225:246–261. PMID:
24917069.

28. Shi X, Cao L, Reed MP, Rupp JD, Hoff CN, Hu J. A statistical human rib cage geometry model accounting for variations by age, sex, stature and body mass index. J Biomech. 2014; 47:2277–2285. PMID:
24861634.

29. Salito C, Luoni E, Aliverti A. Alterations of diaphragm and rib cage morphometry in severe COPD patients by CT analysis. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015; 2015:6390–6393. PMID:
26737755.

30. Schols AM, Mostert R, Soeters PB, Wouters EF. Body composition and exercise performance in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 1991; 46:695–699. PMID:
1750015.

31. Gosselink R, Troosters T, Decramer M. Peripheral muscle weakness contributes to exercise limitation in COPD. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; 153:976–980. PMID:
8630582.

32. Vogiatzis I, Zakynthinos S. Factors limiting exercise tolerance in chronic lung diseases. Compr Physiol. 2012; 2:1779–1817. PMID:
23723024.

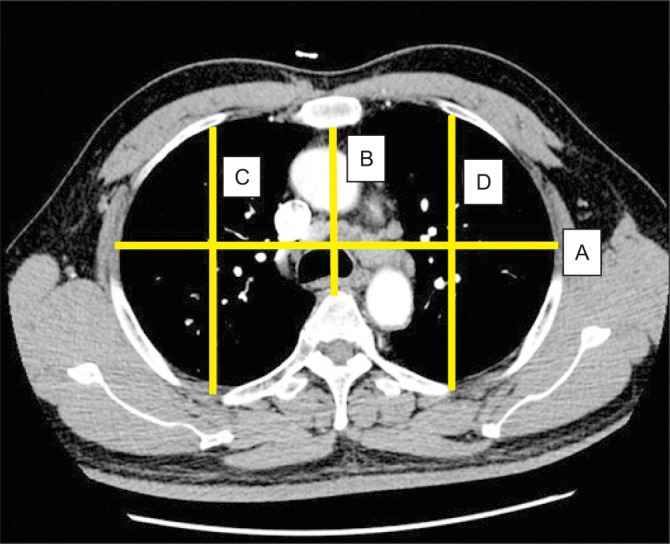
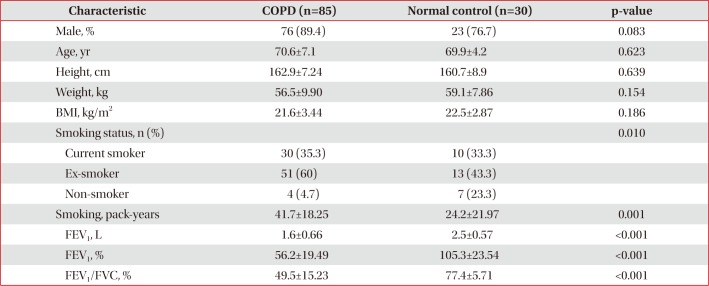
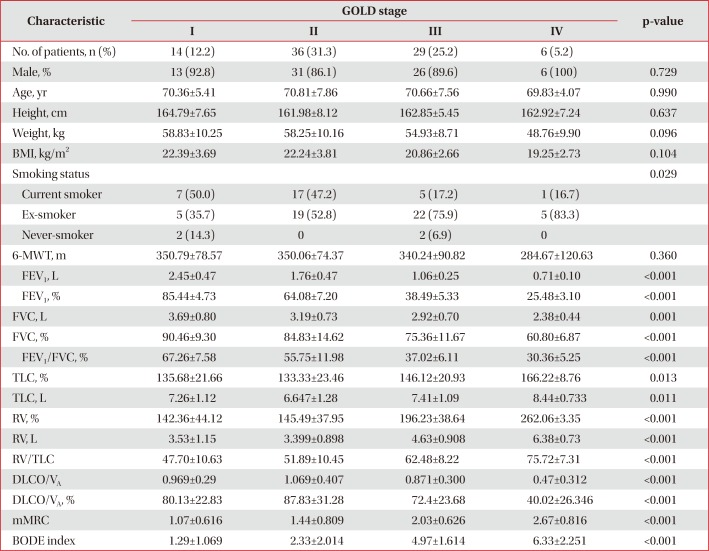
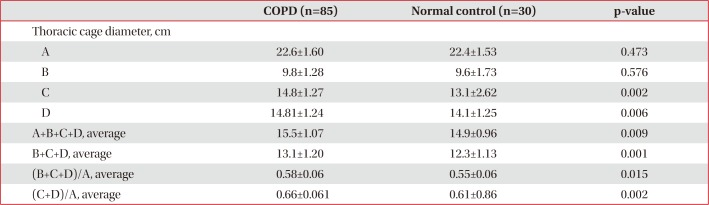




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download