초록
Neurolymphomatosis (NL) is a rare disease characterized by lymphomatous invasion of the cranial or peripheral nerves by lymphoma. A high suspicion is important due to the various presenting symptoms mandating consideration of many differential diagnoses. We report a case of NL of the cranial nerves and plexus presenting as diplopia, facial palsy, and weakness of the upper and lower limbs in sequence.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Grisariu S., Avni B., Batchelor TT., van den Bent MJ., Bokstein F., Schiff D, et al. Neurolymphomatosis: an International Primary CNS Lym-phoma Collaborative Group report. Blood. 2010. 115:5005–5011.

2.Lagarde S., Tabouret E., Matta M., Franques J., Attarian S., Pouget J, et al. Primary neurolymphomatosis diagnosis and treatment: a retrospective study. J Neurol Sci. 2014. 342:178–181.

3.Misdraji J., Ino Y., Louis DN., Rosenberg AE., Chiocca EA., Harris NL. Primary lymphoma of peripheral nerve: report of four cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000. 24:1257–1265.
4.Baehring JM., Damek D., Martin EC., Betensky RA., Hochberg FH. Neurolymphomatosis. Neuro Oncol. 2003. 5:104–115.

5.Descamps MJ., Barrett L., Groves M., Yung L., Birch R., Murray NM, et al. Primary sciatic nerve lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006. 77:1087–1089.

6.Matsue K., Hayama BY., Iwama K., Koyama T., Fujiwara H., Ya-makura M, et al. High frequency of neurolymphomatosis as a relapse disease of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer. 2011. 117:4512–4521.

7.Choi YJ., Shin JA., Kim YH., Cha SJ., Cho JY., Kang SH, et al. Neurolymphomatosis of brachial plexus in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013. 2013:492329.

8.Sakai N., Ito-Yamashita T., Takahashi G., Baba S., Koizumi S., Yamasaki T, et al. Primary neurolymphomatosis of the lower cranial nerves presenting as Dysphagia and hoarseness: a case report. J Neurol Surg Rep. 2014. 75:e62–e66.

Go to : 
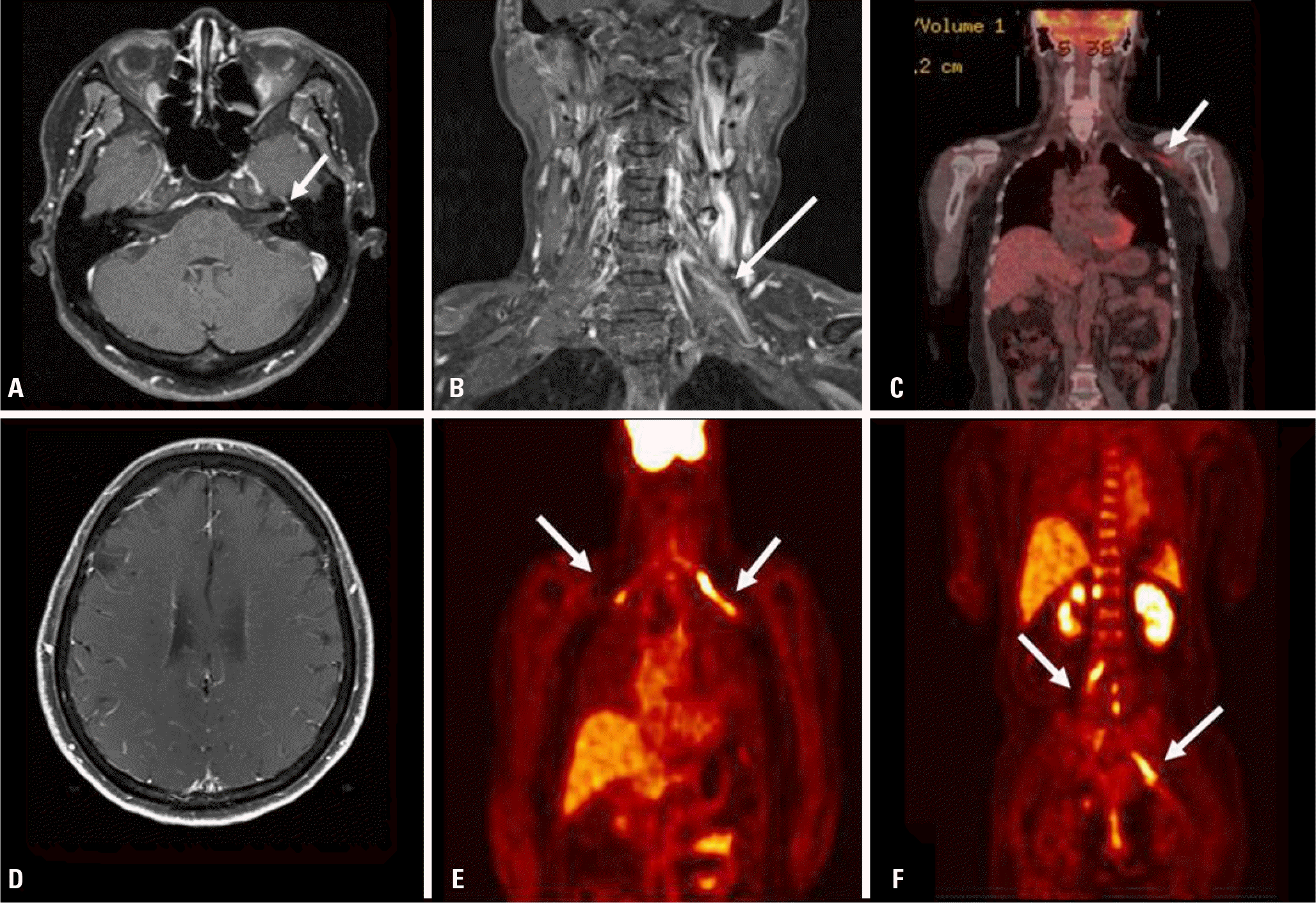 | Fig. 1.Brain and spinal MRI showed thickening and enhancement on the left facial nerve (arrow) (A), and the left brachial plexus (arrow) (B). Initial PET-CT showed mild linear FDG uptake along the left brachial plexus (arrow) (C). Brain MRI revealed multifocal leptomeningeal enhancement of the systemic lymphoma or metastasis (D). FDG-PET revealed intense uptake in the brachial (arrows) (E) and lumbosacral (arrows) (F) plexus. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PET-CT, positron emission tomography–computed tomography; FDG, fluorodexoyglucose. |
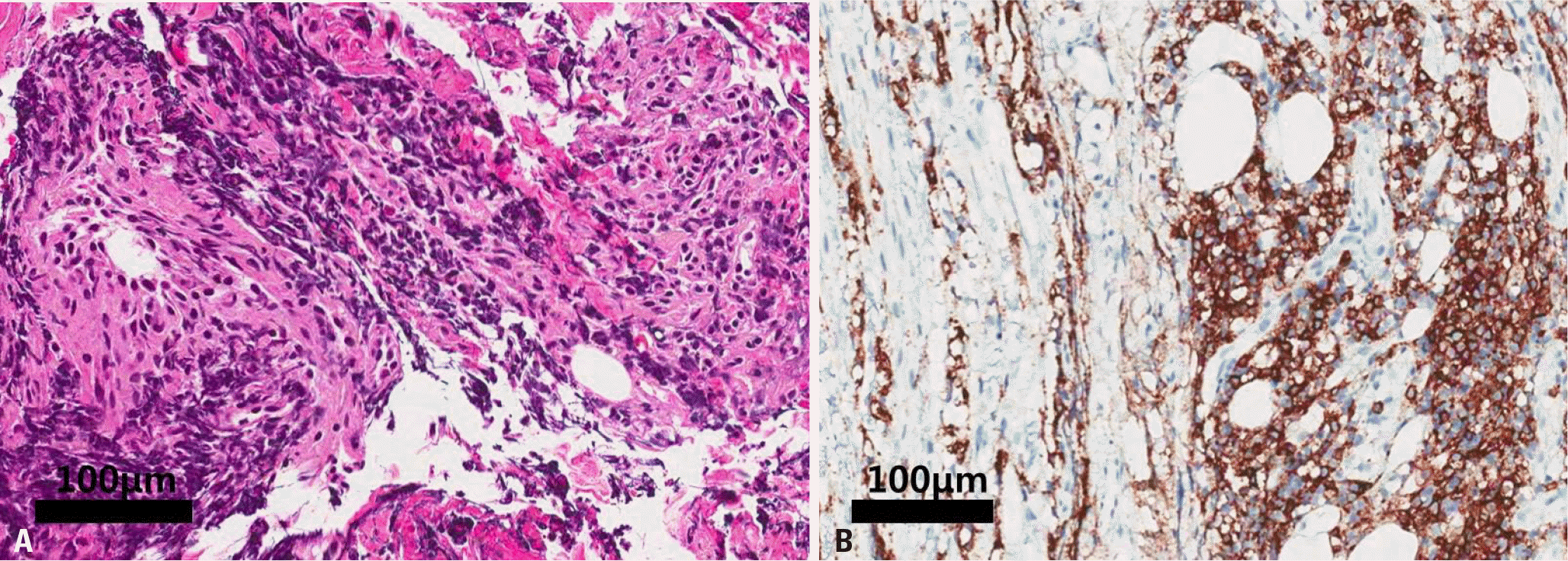 | Fig. 2.Biopsy of the C7 root showed infiltration by predominantly small lymphocytes (hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification ×200) (A), and diffuse CD20-positive cells (immunohistochemical stain, original magnification ×200) (B). |
Table 1.
Electrophysiological findings at the first symptoms of left upper limb weakness




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download