초록
Background
Telbivudine is a nucleoside analogue used for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B, but it often develops mitochondrial toxicity leading to symptomatic myopathy. In this study, three patients with telbivudine induced myopathy were enrolled in order to in-vestigate the nature and pathogenesis of mitochondrial toxicity caused by long-term use of telbivudine.
Methods
Clinical features, laboratory findings, muscle pathology, and quantitation of mitochondrial DNA were studied in three patients.
Results
Patients presented with progressive muscle weakness with high serum creatine kinase levels. Light microscopic findings of muscle pathology showed ragged red fibers that reacted strongly with succinate dehydrogenase stain, but negative for cytochrome c oxidase activities. Electron microscopy revealed abnormal mitochondrial accumulation with rod shaped inclusions. The quantitative peroxidase chain reaction showed a depletion of mitochondrial DNA in skeletal muscle of the patients.
Conclusions
Nucleoside analogues including telbivudine are potent inhibitors of viral DNA polymerases. However, they are not specific for viral DNA and can disturb mitochondrial repli-cation at the same time. All nucleotide analogues should be used with close clinical observation in order to avoid development of mitochondrial myopathy.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.McMahon BJ. The natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2009. 49(5 Suppl):S45–S55.

2.Fattovich G., Bortolotti F., Donato F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors. J Hepatol. 2008. 48:335–352.

3.Liaw YF., Gane E., Leung N., Zeuzem S., Wang Y., Lai CL, et al. 2-year GLOBE trial results: telbivudine is superior to lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2009. 136:486–495.

4.Zou XJ., Jiang XQ., Tian DY. Clinical features and risk factors of creatine kinase elevations and myopathy associated with telbivudine. J Viral Hepat. 2011. 18:892–896.

5.Seok JI., Lee DK., Lee CH., Park MS., Kim SY., Kim HS, et al. Long-term therapy with clevudine for chronic hepatitis B can be associated with myopathy characterized by depletion of mitochondrial DNA. Hepatology. 2009. 49:2080–2086.

6.Masanés F., Barrientos A., Cebrián M., Pedrol E., Miró O., Casade-mont J, et al. Clinical, histological and molecular reversibility of zidovudine myopathy. J Neurol Sci. 1998. 159:226–228.

7.Kim EH., Park H., Lee KH., Ahn SH., Kim SM., Han KH. Two cases of telbivudine-induced myopathy in siblings with chronic hepatitis B. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013. 19:82–86.

8.Wang M., Da Y., Cai H., Lu Y., Wu L., Jia J. Telbivudine myopathy in a patient with chronic hepatitis B. Int J Clin Pharm. 2012. 34:422–425.

9.Dalakas MC., Illa I., Pezeshkpour GH., Laukaitis JP., Cohen B., Griffin JL. Mitochondrial myopathy caused by long-term zidovudine therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990. 322:1098–1105.

10.Lo YL., See SJ., Tan CK. Continuous single motor unit electromyo-graphic activity in adefovir associated myopathy. J Clin Neurosci. 2008. 15:1073–1074.

11.Ambang T., Tan JS., Ong S., Wong KT., Goh KJ. Clinicopatholog-ical features of telbivudine-associated myopathy. PLoS ONE. 2016. 11:e0162760.

Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.Light microscopic findings of patient 1 (A-D), 2 (E-H), and 3 (I-L). In patient 1, single ragged red fiber (asterisk) is observed in serial sections, which is deficient for cytochrome oxidase activity (C) and strongly reactive to succinate dehydrogenase stain (D). In addition, some necrotic and regenerating fibers are observed (A, B). In patient 2, only a few regenerating fibers are observed (E) without evident ragged red fiber (F, H). However, COX negative fibers are abundant (G, black dots). In patient 3, necrotic and regenerating fibers are scattered (I), and a few ragged red fibers (J, arrowhead) with in-creased succinate dehydrogenase activity (L, white dots) are observed. Many muscle fibers are deficient for cytochrome oxidase activities (K, black dots) (A, E, I: hematoxyline and eosin stain, B, F, J: modified Gomori-trichrome stain, C, G, K: cytochrome oxidase stain, D, H, L: succinate dehydrogenase stain. An 100 μm scale bar was used). |
 | Fig. 2.Electron microscopic findings of patient 1 (A, B), 2 (C, D), and 3 (E, F) (scale bar, 2 μm). The rod shaped inclusions are observed within mitochondria (arrows, A). The double-membrane vesicle (long arrowheads) encircling abnormal mitochondria is observed, which indicates the autophagic vesi-cles (B). Abnormal accumulation of mitochondria is observed in degenerated fibers and between myofibrils (C-E). Mitochondria in degenerated fiber is enlarged and abnormally shaped (black short arrowheads, F). |
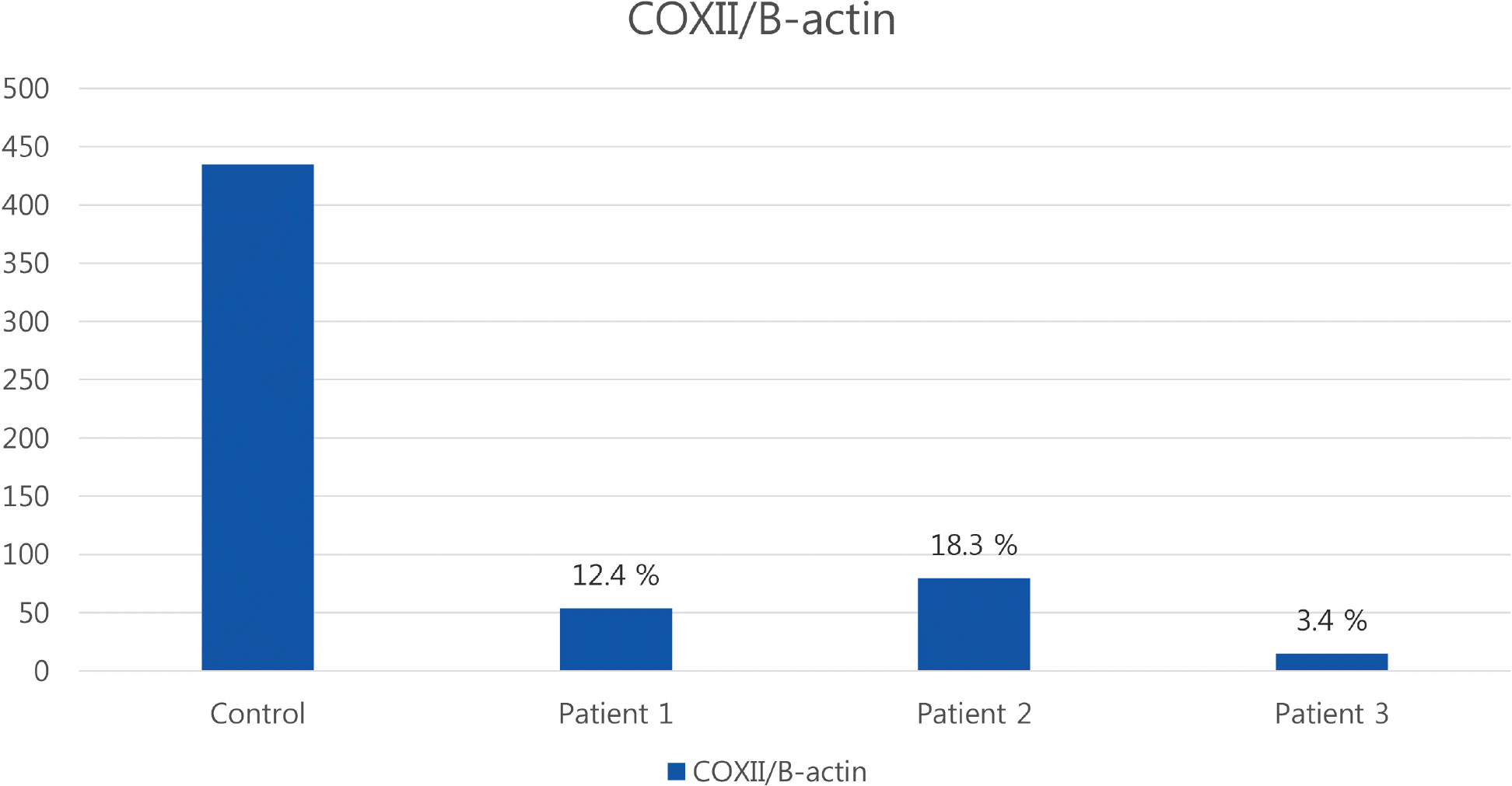 | Fig. 3.Quantitative PCR analysis showed mtDNA/nuclear DNA ratio was markedly reduced in comparison to the normal control (12.4% of normal control in patient 1, 18.3% in patient 2, and 3.5% in patient 3). PCR, peroxidase chain reaction; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA. |
Table 1.
Clinical data of 3 patients




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download