초록
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is generally characterized by lancinating, unilateral, paroxysmal pain occurring in the distribution of the fifth cranial nerve. TN is diagnosed clinically based on the typical patient history, negative findings in a neurologic examination, and the response to medication. Idiopathic TN is the most common type, but TN can result from vascular malfor-mation, compression, trauma, neoplasm, multiple sclerosis, or inflammation. We report a TN case diagnosed as recurrent trigeminal neuritis of the maxillary branch confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging.
REFERENCES
1.Krafft RM. Trigeminal neuralgia. Am Fam Physician. 2008. 77:1291–1296.
2.Kedarnath NS., Shruthi R. MRI as an essential diagnostic approach for trigeminal neuralgia. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2015. 14(Suppl 1):462–464.

3.Montano N., Conforti G., Di Bonaventura R., Meglio M., Fernandez E., Papacci F. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Ther Clin Risk Manag 2015 24;11. 289–299.
4.Allsop MJ., Twiddy M., Grant H., Czoski-Murray C., Mon-Williams M., Mushtaq F, et al. Diagnosis, medication, and surgical management for patients with trigeminal neuralgia: a qualitative study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2015. 157:1925–1933.

5.Cruccu G., Finnerup NB., Jensen TS., Scholz J., Sindou M., Svensson P, et al. Trigeminal neuralgia: New classification and diagnostic grad-ing for practice and research. Neurology. 2016. 87:220–228.
6.Strittmatter M., Grauer MT., Fischer C., Hamann G., Hoffmann KH., Blaes F, et al. Autonomic nervous system and neuroendocrine changes in patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Cephalal-gia. 1996. 16:476–480.

7.Choi S., Yu E., Hwang E., Llinás RR. Pathophysiological implication of CaV3.1 T-type Ca2+ channels in trigeminal neuropathic pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. 113:2270–2275.

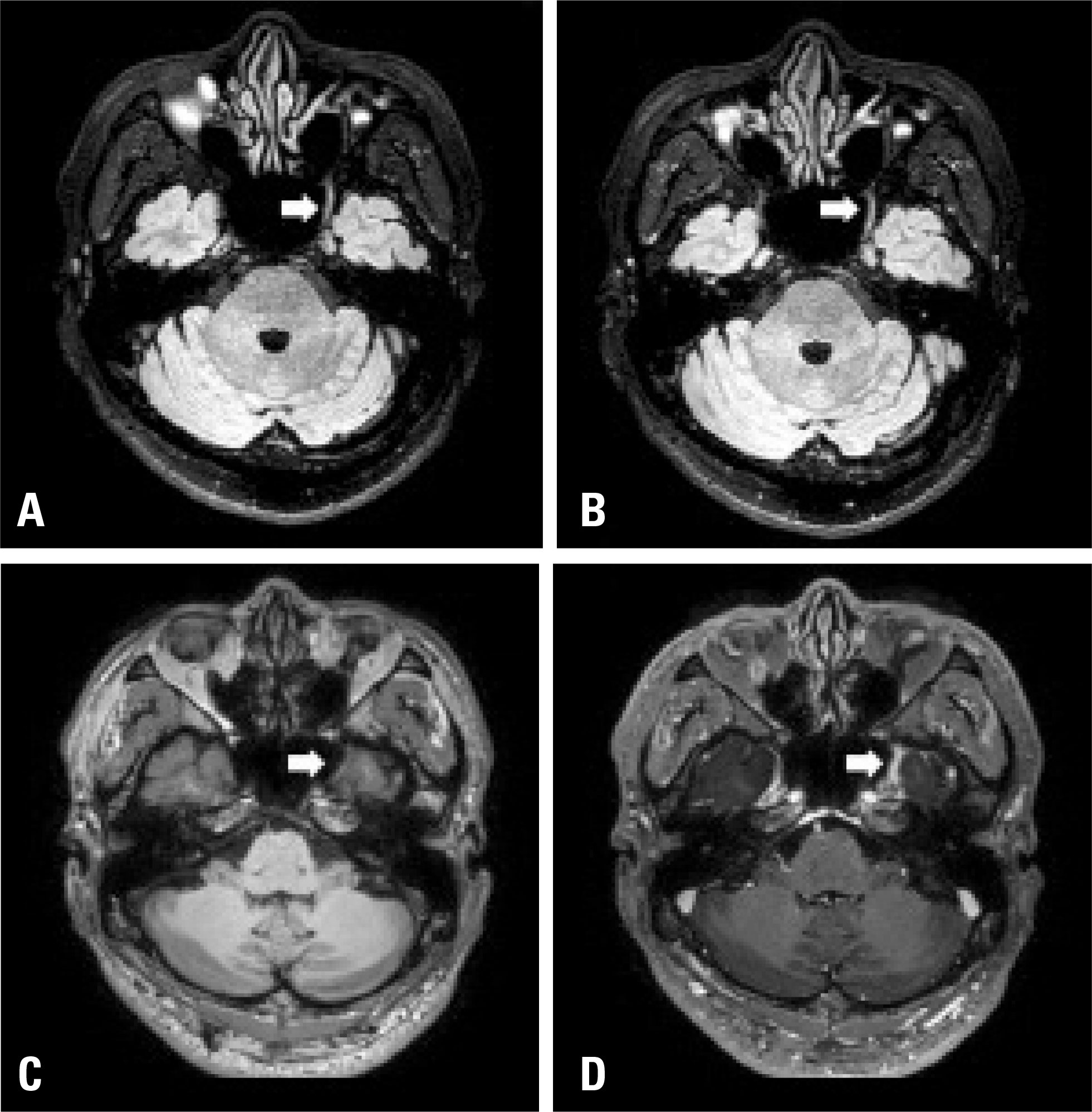
Fig. 1.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the cranial nerve. Diffuse swell-ing and thickening of the maxillary branch of the left trigeminal nerve was noted in a nonenhanced fluid-attenuated inversion recovery with fat saturation axial image (A) and in an enhanced image (B) (arrows). The enhancement on the left maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve at the cavernous portion and foramen rotundum was not detected in an enhanced T1-weighted axial image (D) but not in a nonenhanced image (C) (arrows).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download