초록
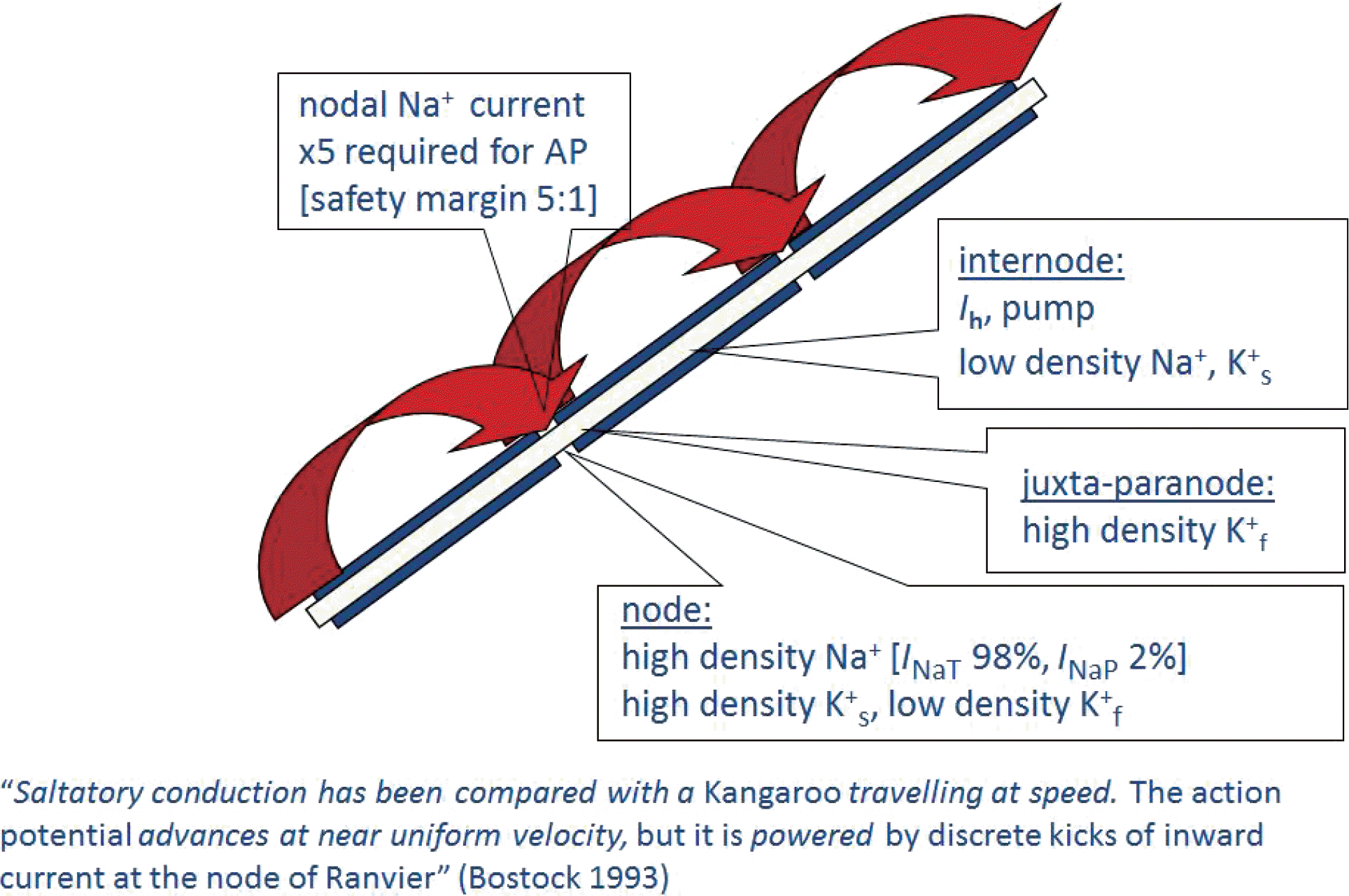
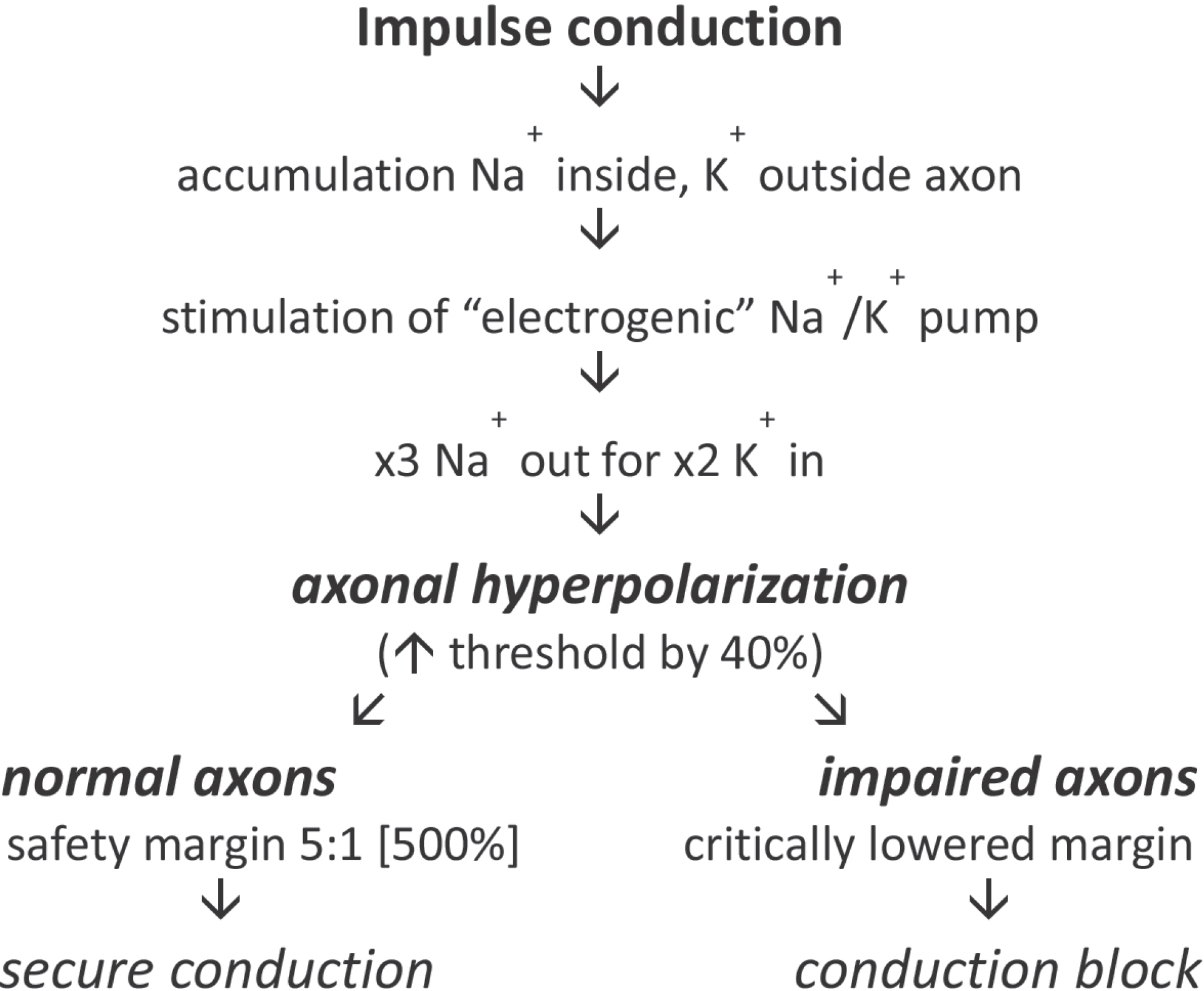
Using threshold tracking, differences have been established between large myelinated sensory and α motor axons in humans. Major differences are that sensory axons are relatively de-polarised at rest such that they have a greater persistent Na+ current, and have greater activity of hyperpolarisation-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels. Sensory axons may thereby be protected from hyperpolarising stresses, and are less likely to develop conduction block. However, the corollary is that sensory axons are more excitable and more likely to be-come ectopically active.
REFERENCES
1.Vogel W., Schwarz JR. Voltage-clamp studies on axons: macro-scopic and single-channel currents. Waxman SG, Stys PK, Koc-sis JD, editors. Oxford: Oxford University Press;1995. p. 257–280.
2.Craner MJ., Newcombe J., Black JA., Hartle C., Cuzner ML., Waxman SG. Molecular changes in neurons in multiple sclerosis: altered axonal expression of Na v1.2 and Na v1.6 sodium channels and Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. 101:8168–8173.
3.Baker M., Bostock H., Grafe P., Martius P. Function and distribution of three types of rectifying channel in rat spinal root myelinated axons. J Physiol. 1987. 383:45–67.

4.Grafe P., Bostock H., Schneider U. The effects of hyperglycae-mic hypoxia on rectification in rat dorsal root axons. J Physiol. 1994. 480:297–307.

5.Tatsumi H., Katayama Y. Na+ dependent Ca2+ influx induced by depolarization in neurons dissociated from rat nucleus basalis. Neurosci Lett. 1995. 196:9–12.
6.Vucic S., Burke D., Kiernan MC. Fatigue in multiple sclerosis: mech-anisms and management. Clin Neurophysiol. 2010. 121:809–817.

7.Bostock H., Burke D., Hales JP. Differences in behaviour of sensory and motor axons following release of ischaemia. Brain. 1994. 117:225–234.

8.Mogyoros I., Kiernan MC., Burke D., Bostock H. Excitability changes in human sensory and motor axons during hyperventilation and ischaemia. Brain. 1997. 120:317–325.

9.Burke D., Kiernan MC., Mogyoros I., Bostock H. Susceptibility to conduction block: differences in the biophysical properties of cutaneous afferents and motor axons. Kimura J, Kaji R, editors. Physiology of ALS and Related Disorders. Amsterdam: Elsevier;1997. p. 43–53.
10.Kiernan MC., Mogyoros I., Burke D. Differences in the recovery of excitability in sensory and motor axons of human median nerve. Brain. 1996. 119:1099–1105.

11.Mogyoros I., Kiernan MC., Burke D. Strength-duration properties of human peripheral nerve. Brain. 1996. 119:439–447.

12.Bostock H., Rothwell JC. 1997. Latent addition in motor and sensory fibres of human peripheral nerve. J Physiol. 1997. 498(Pt 1):277–294.
13.Lin CS-Y., Kuwabara S., Cappelen-Smith C., Burke D. Responses of human sensory and motor axons to the release of ischaemia and to hyperpolarizing currents. J Physiol. 2002. 541:1025–1039.

14.Tomlinson S., Burke D., Hanna M., Koltzenburg M., Bostock H. In vivo assessment of HCN channel current (I h) in human motor axons. Muscle Nerve. 2010. 41:247–256.
15.Howells J., Trevillion L., Bostock H., Burke D. The voltage depen-dence of I h in human myelinated axons. J Physiol. 2012. 590:1625–1640.
16.Howells J., Bostock H., Burke D. Accommodation to hyperpolarization of human axons assessed in the frequency domain. J Neurophysiol. 2016. 116:322–335.

17.Kiernan MC., Burke D., Andersen KV., Bostock H. Multiple measures of axonal excitability: a new approach in clinical testing. Muscle Nerve. 2000. 23:399–409.

18.Kiernan MC., Lin CS-Y., Andersen KV., Murray NM., Bostock H. Clinical evaluation of excitability measures in sensory nerve. Muscle Nerve. 2001. 24:883–892.

19.Howells J., Czesnik D., Trevillion L., Burke D. Excitability and the safety margin in human axons during hyperthermia. J Physiol. 2013. 59:3063–3080.

20.Bostock H., Grafe P. Activity-dependent excitability changes in normal and demyelinated rat spinal root axons. J Physiol. 1985. 365:239–257.

21.Morita K., David G., Barrett JN., Barrett EF. Posttetanic hyperpolarization produced by electrogenic Na+-K+ pump in lizard axons impaled near their motor terminals. J Neurophysiol. 1993. 70:1874–1884.
22.Bostock H., Bergmans J. Posttetanic excitability changes and ectopic discharges in a human motor axon. Brain. 1994. 117:913–928.

23.Vagg R., Mogyoros I., Kiernan MC., Burke D. Activity-dependent hyperpolarization of human motor axons produced by natural activity. J Physiol. 1998. 507:919–925.

24.Kiernan MC., Lin CS-Y., Burke D. Differences in activity-dependent hyperpolarization in human sensory and motor axons. J Physiol. 2004. 558:341–349.

25.Park SB., Lin CS-Y., Burke D., Kiernan MC. Activity-dependent conduction failure: molecular insights. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2011. 16:159–168.

26.Kiernan MC., Isbister GK., Lin CS-Y., Burke D., Bostock H. Acute tetro-dotoxin-induced neurotoxicity after ingestion of puffer fish. Ann Neurol. 2005. 57:339–348.

27.Inglis JT., Leeper JB., Wilson LR., Gandevia SC., Burke D. The development of conduction block in single human axons following a focal nerve injury. J Physiol. 1998. 513:127–133.

28.Vallbo ÅB. Prediction of propagation block on the basis of impulse shape in single unit recordings from human nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976. 97:66–74.
29.Kaji R., Bostock H., Kohara N., Murase N., Kimura J., Shibasaki H. Ac-tivity-dependent conduction block in multifocal motor neuropathy. Brain. 2000. 123:1602–1611.

30.Cappelen-Smith C., Kuwabara S., Lin CS-Y., Mogyoros I., Burke D. Activity-dependent hyperpolarization and conduction block in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol. 2000. 48:826–832.

31.Nodera H., Bostock H., Izumi Y., Nakamura K., Urushihara R., Saka-moto T, et al. Activity-dependent conduction block in multifocal motor neuropathy: magnetic fatigue test. Neurology. 2006. 67:280–287.

Fig. 2.
Excitability measures for sensory and motor axons. (A) Extended excitability data for motor (●) and sensory (○) axons (n = 10; mean ± SEM [dashed lines]), both recorded using 1 ms test stimuli. (A) threshold electrotonus for conditioning levels of ± 40%, −70% and −100% of control threshold. (B) current–threshold (I–V) relationship for 100 ms and 200 ms conditioning stimuli. The 100 ms conditioning stimuli resulted in a larger decrease in excitability at −100% as less accommodation to hyperpolarization developed over the shorter time span. Note the greater accommodation of sensory axons in A and B. (C) Strength–duration time constant for motor (filled symbols) and sensory (open symbols) studies. Means (continuous lines) ± SEM (dotted lines). Data from published normal control studies are presented on the left (squares). Data from the 10 subjects in the present study (circles; lines link the same subject). The data on the right are the strength–duration time constants as estimated by the mathematical model for sensory and motor axons (triangles). Modified from reference15 with permission. SEM, standard error of the mean.
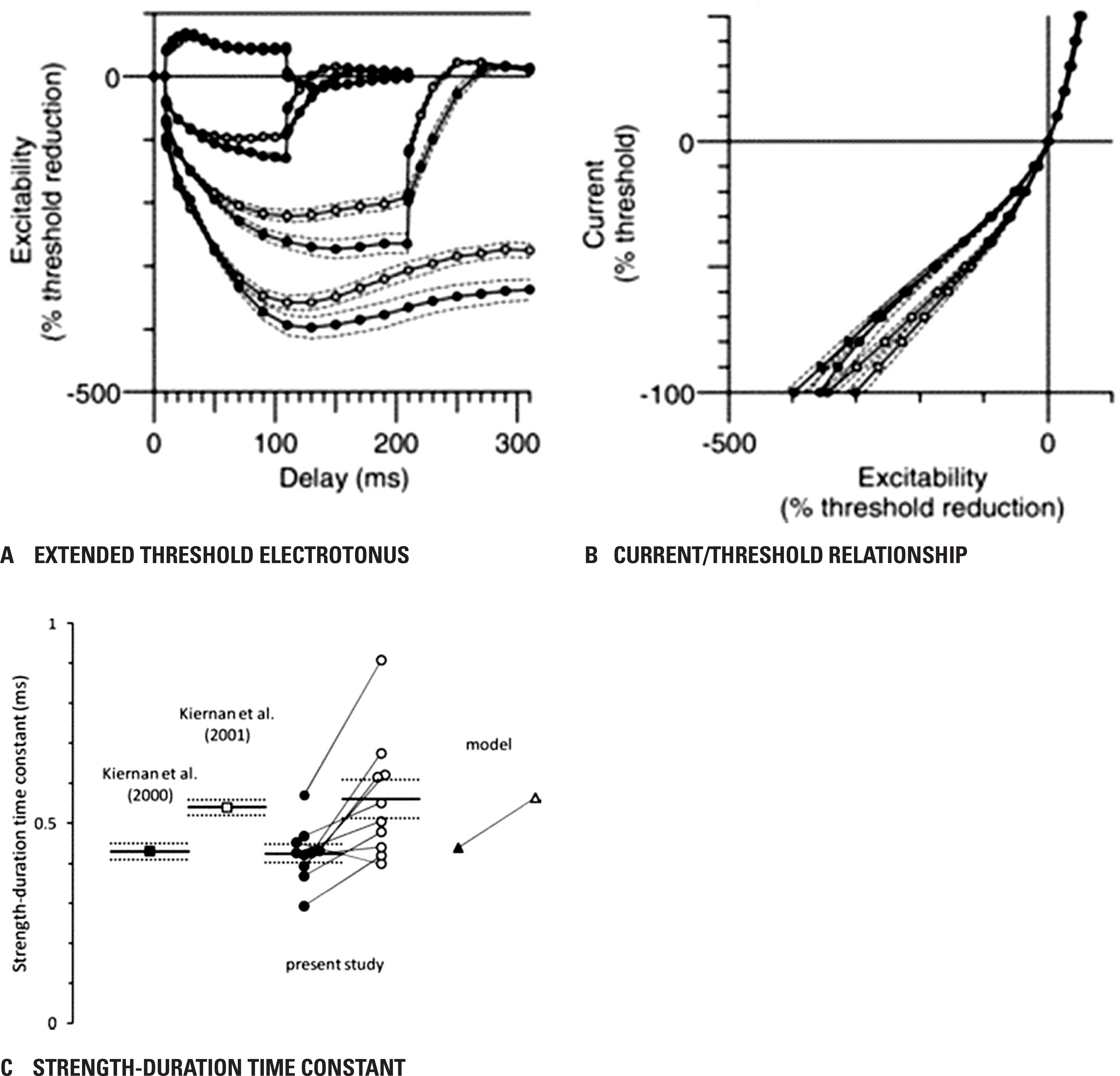
Fig. 3.
Individual motor nerve recordings and motor model. Individual motor nerve recordings (n = 10) of extended threshold electrotonus (A) (conditioning levels of ± 20%, ± 40%, −70% and −100% of unconditioned threshold), and I–V (C) (for clarity, only the 200 ms conditioning stimulus data is dis-played). Threshold electrotonus (B) and I–V (D) as generated by the motor axon model with variation of the voltage for half-activation of I h from −87.3 to −127.3 mV in 5 mV steps. Reused from reference15 with permission.
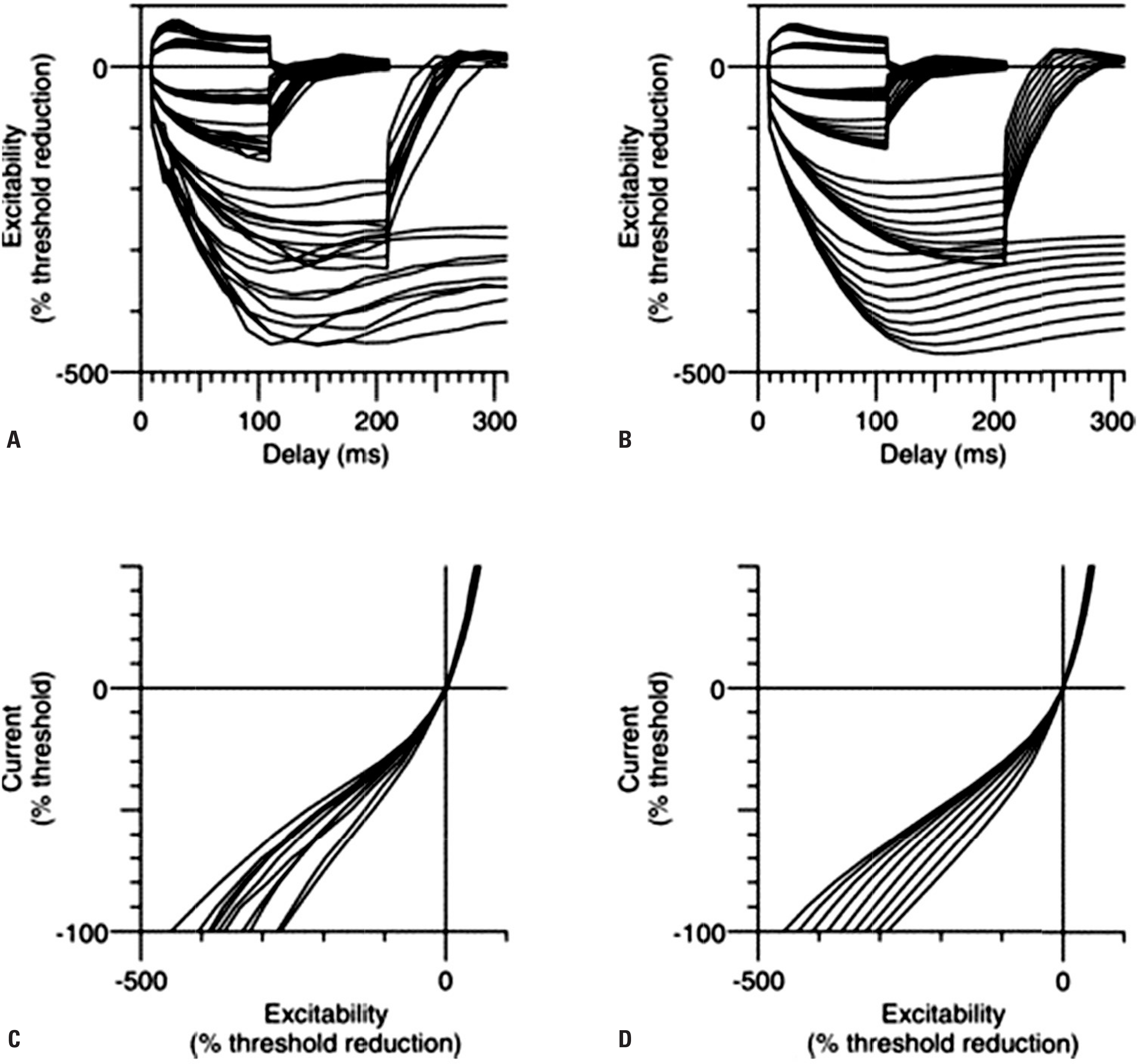
Fig. 4.
Activity-dependent hyperpolarisation of motor axons due to voluntary contraction. The median nerve was stimulated at the wrist and a 70% CMAP was tracked over the thenar muscles, using increments and decrements in stimulus intensity of 2%. In each panel, maximal voluntary contractions were performed 5 min after the onset of the traces. The increase in the normalised threshold represents the increase in current required to produce the control CMAP, and this reflects the axonal hyperpolarisation. The extent of hyperpolarisation and its duration depend on the duration of contraction (i.e., the impulse load). In A, B and C, the contractions lasted 15, 30 and 60 s, respectively. Each trace represents mean data for six subjects. Reused from reference23 with permission. CMAP, compound muscle action potential; MVC, maximal voluntary contraction.
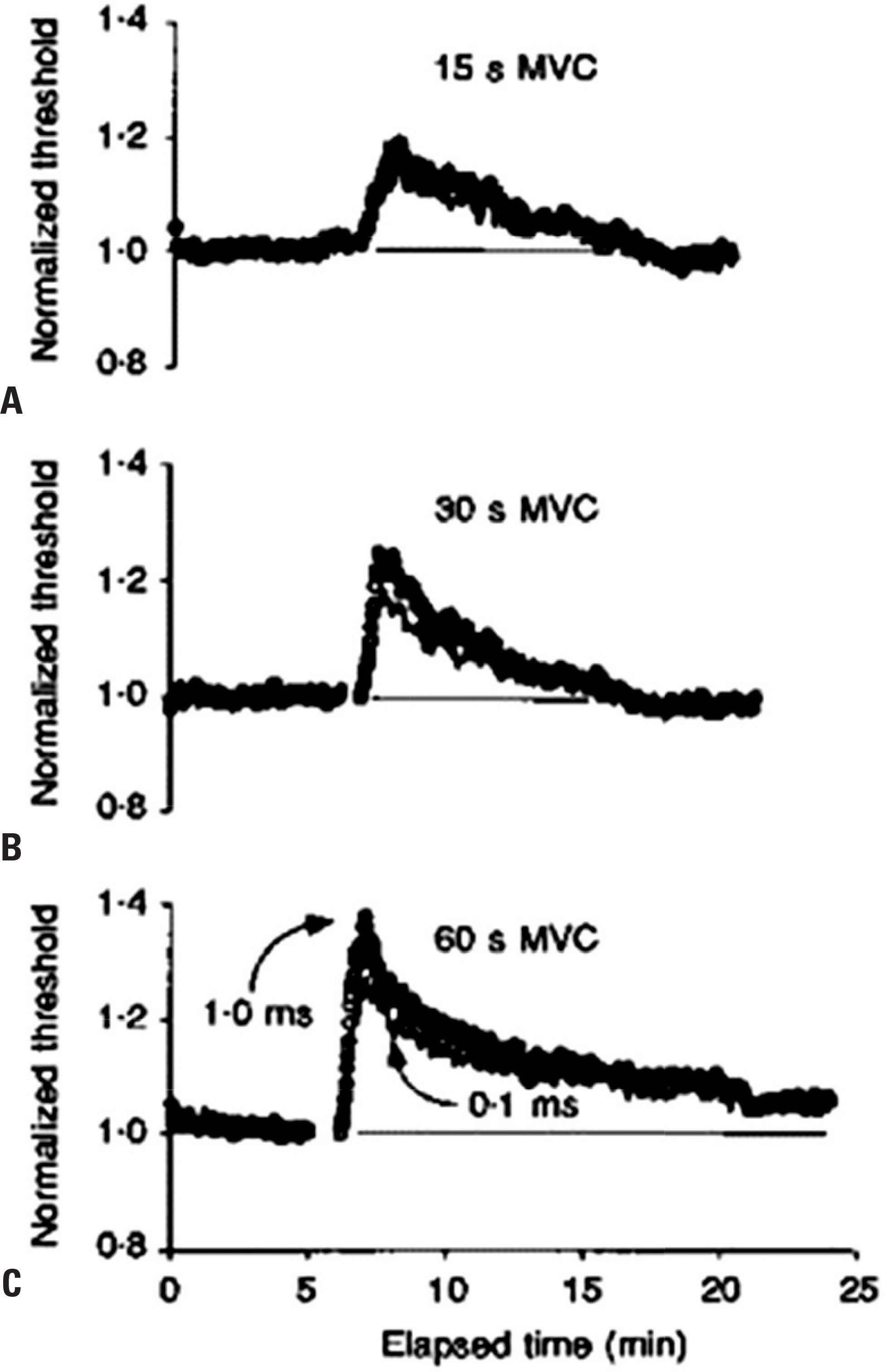
Fig. 5.
Activity-dependent changes in threshold for motor and sensory axons. Mean changes in threshold (± SEM) recorded for 9 subjects following repetitive stimulation of the median nerve at the wrist at 8 Hz for 10 min. Changes are shown for motor (A) and sensory axons (B) using test stimuli of 0.1 and 1 ms duration. Immediately following cessation of impulse trains, axons became less excitable, with a prominent increase in threshold, significantly greater for motor axons when compared to sensory. Reused from reference24 with permission. SEM, standard error of the mean.
Fig. 6.
The development of conduction block in a human muscle spindle afferent. Raster display of action potentials of a muscle spindle afferent from extensor pollicis longus developing and recovering from conduction block. The muscle spindle afferent discharged irregularly at ~3 Hz when mild pressure was applied to the receptor. The action potential had two peaks generated at nodes of Ranvier on either side of the site of impaled internode.28 The separation of the peaks therefore reflects internodal conduction time, and its pro-longation indicates the security of transmission. When conduction across the impaled internode was blocked the recorded potential consists of only a single peak generated proximal to the site of im-palement. When the pressure was increased (Pressure on), 10 min after the onset of the recording, the discharge rate of the afferent increased to ~20 Hz, and the second positive peak became unstable and disappeared. When pressure was relaxed (Pressure off), the second peak reappeared, only to disappear 2 min later when pressure was again increased. The longest interpeak interval was 975 μs in the first episode and 1.02 ms immediately after the second episode. The illustrated sequence contains 891 consecutive action potentials. Modified from reference27 with permission.
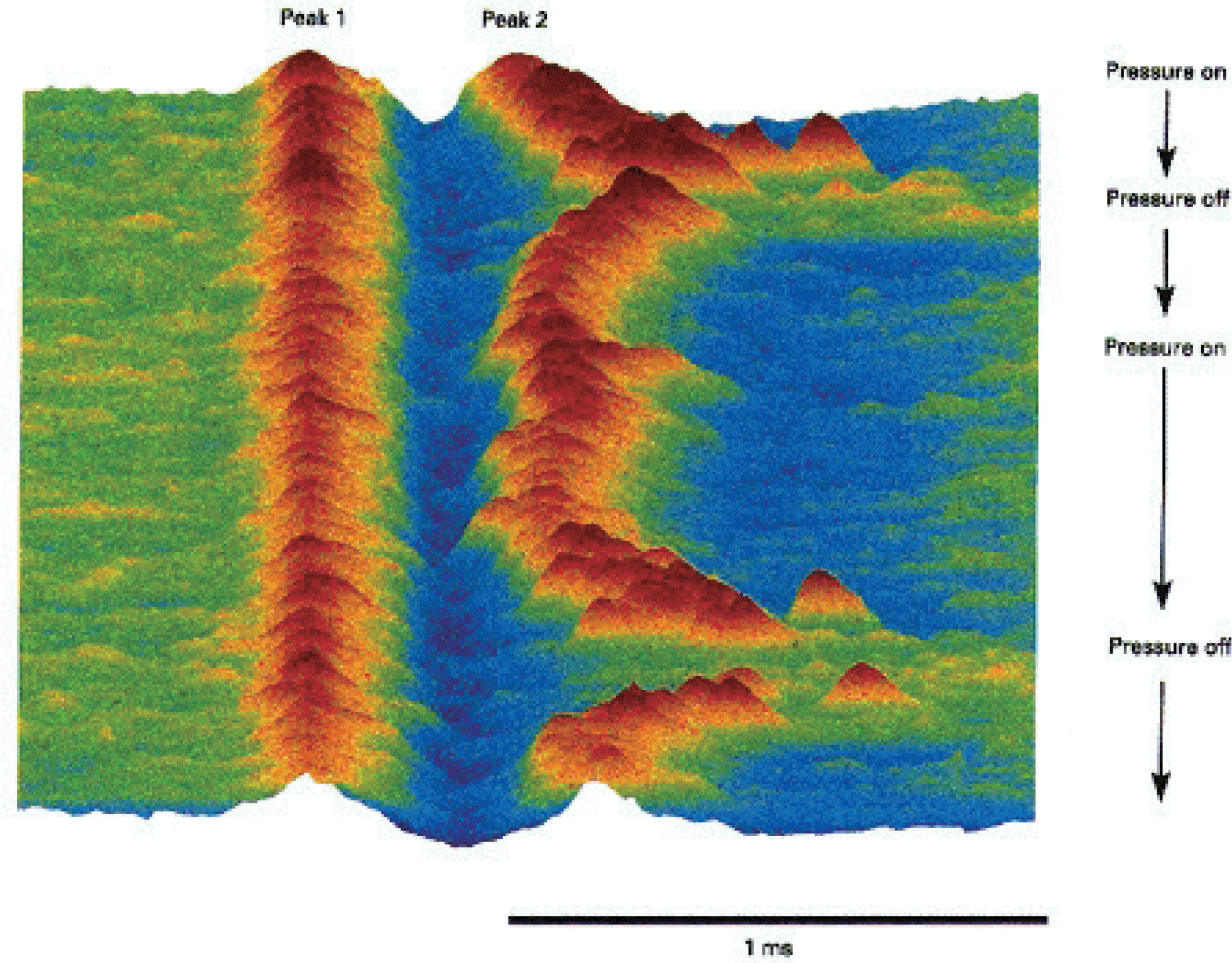
Table 2.
Physiological manoeuvres that can precipitate or worsen conduction block
Table 3.
Testing for conduction block




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download