Abstract
Accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) is a new treatment delivery technique that decreases overall treatment time by using higher fractional doses than conventional fractionation. Here, a quantitative analysis study of CyberKnife-based APBI was performed on 10 patients with left-sided breast cancer who had already finished conventional treatment at the Inha University Hospital. Dosimetric parameters for four kinds of treatment plans (3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT, and CyberKnife) were analyzed and compared with constraints in the NSABP B39/RTOG 0413 protocol and a published CyberKnife-based APBI study. For the 10 patients recruited in this study, all the dosimetric parameters, including target coverage and doses to normal structures, met the NSABP B39/RTOG 0413 protocol. Compared with other treatment plans, a more conformal dose to the target and better dose sparing of critical structures were observed in CyberKnife plans. Accelerated partial breast irradiation via CyberKnife is a suitable treatment delivery technique for partial breast irradiation and offers improvements over external beam APBI techniques.
Go to : 
References
1. Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, Margolese RG, Deutsch M, Fisher ER, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1233–41.

2. Van Dongen JA, Voogd AC, Fentiman IS, Legrand C, Sylvester RJ, Tong D, et al. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing breast-conserving therapy with mastectomy: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer 10801 trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:1143–50.

3. A , Nattinger B., et al. Relation between appropriateness of primary therapy for earlystage breast carcinoma and increased use of breast-conserving surgery. Lancet. 2000; 356:1148–1153.
4. Legorreta AP, Liu X, Parker RG. Examining the use of breast-conserving treatment for women with breast cancer in a managed care environment. Am J Clin Oncol. 2000; 23:438–41.

5. Arthur DW, Vicini FA. Accelerated partial breast irradiation as a part of breast conservation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:1726–35.

6. F , Vicini A., et al. A randomized phase III study of conventional whole breast irradiation (WBI) versus partial breast irradiation (PBI) for women with stage 0, I, or II breast cancer. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group, Philadelphia, PA, protocol #0413. 2005.
7. D. W. Arthur and F. A. Vicini. Accelerated partial breast irradiation as a part of breast conservation therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005; 23:1726–1735.
8. Hepel JT, Tokita M, MacAusland SG, et al. Toxicity of three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for accelerated partial breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009; 75:1290–96.

9. Recht A, Ancukiewicz M, Alm El-Din MA, et al. Lung dose-volume parameters and the risk of pneumonitis for patients treated with accelerated partial-breast irradiation using three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:3887–93.

10. Livi L, Buonamici FB, Simontacchi G, et al. Accelerated partial breast irradiation with IMRT: New technical approach and interim analysis of acute toxicity in a phase III randomized clinical trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 77:509–15.

11. Moon SH, Shin KH, Kim TH, et al. Dosimetric comparison of four different external beam partial breast irradiation techniques: three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, intensitymodulated radiotherapy, helical tomotherapy, and proton beam therapy. Radiother Oncol. 2009; 90:66–73.

12. Heinzerling , J.H. , Ding , C. , Ramirez , E. , Chang , K. , Anderson , J.F. , Edwards C. M., Boike, T., Rule, W., Solberg, T., and Timmerman, R.D. Comparative dose-volume analysis for CyberKnife and 3D conformal partial breast irradiation treatment of early stage breast cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010; 78:S3390.
13. Fan , J. , Hayes , S. , Freedman , G. , Anderson , P. , Li , J. , Wang , L. , Jin , L. , Price , R. , and Ma C. Planning the breast boost: dosimetric comparison of CyberKnife, photo mini tangents, IMRT, and electron techniques. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010; 78:S3306.
14. Feuvret , L. , Noel , G. , Mazeron , J. , et al. Conformity index: areview. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006; 64:333–42.
Go to : 
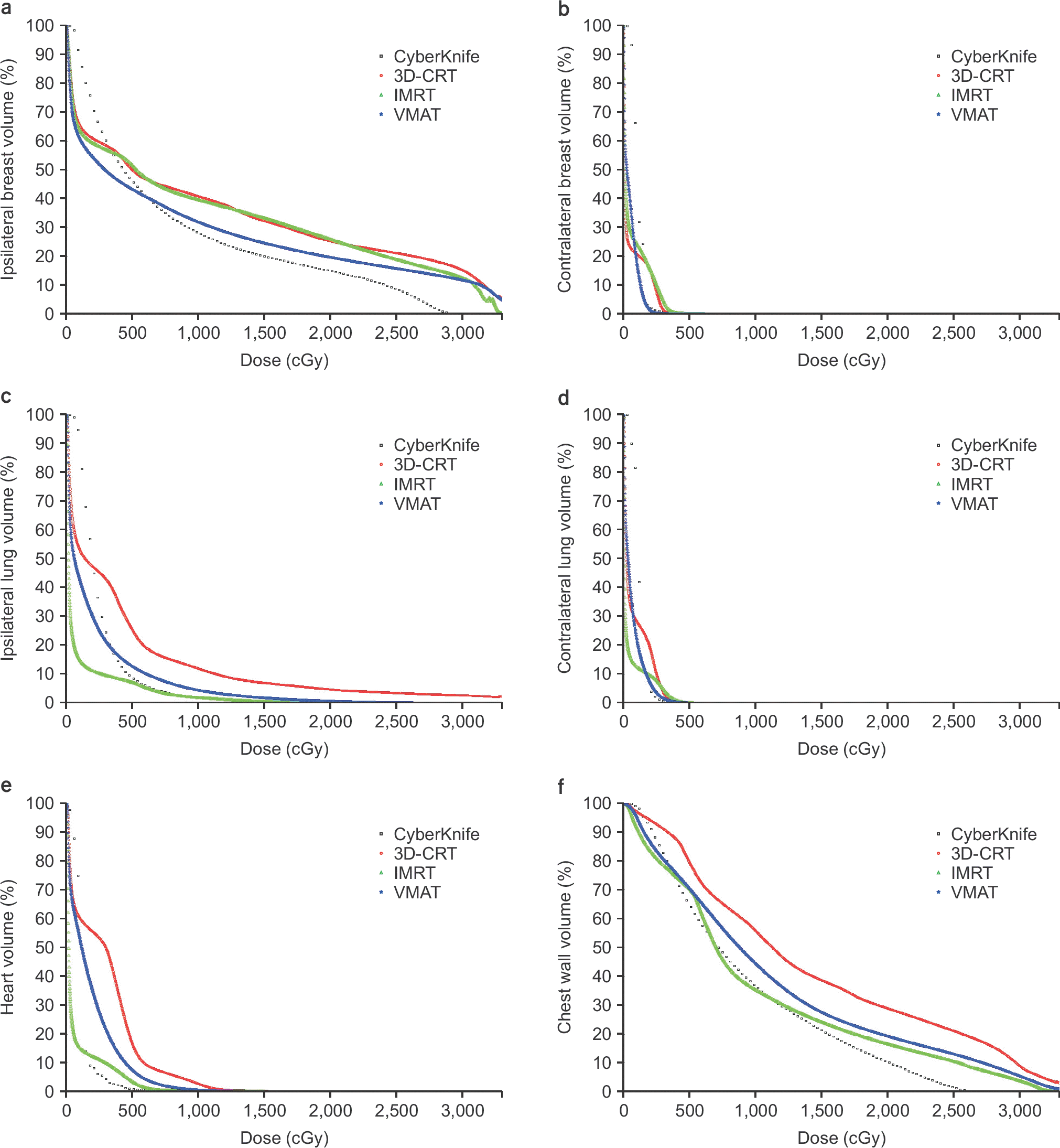 | Fig. 1.Mean DVH data for ipsilateral breast (a), contralateral breast (b), ipsilateral lung (c), contralateral lung (d), heart (e), cheat wall (f). |
Table 1.
Patient and tumor characteristics for the ten patients with ten treated tumors.
Table 2.
Constraints given by the NSABP B39/RTOG 0413 protocol for patients treated with CyberKnife SAPBI.
Table 3.
Dosimetric parmeters from plans based on the NSABP B39/RTOG 0413 protocol.
Table 4.
Comparison of our dosimetric parameters to other CyberKnife studies.
Table 5.
Comparison of our dosimetric parameters to 3D-CRT, IMRT, and VMAT plan.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download