Abstract
Ectopic varices are rare among patients with portal hypertension, especially in the ascending colon. It is difficult to evaluate massive lower gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis by colonoscopy due to hemodynamic instability and poor bowel preparation. In Korea, there has only been one case report about ascending colon variceal bleeding, in which hemostasis was performed by venous coil embolization. We report another rare case of ascending colon variceal bleeding in a patient with alcoholic cirrhosis, who was successfully treated via two sessions of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate injection through colonoscopy. This case suggests that the careful endoscopic approach and hemostasis with glue injection might be an option for treating massive bleeding in the lower gastrointestinal varix.
Go to : 
References
1. Ko BS, Kim WT, Chang SS, et al. A case of ascending colon variceal bleeding treated with venous coil embolization. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:311–315.

3. Watanabe N, Toyonaga A, Kojima S, et al. Current status of ectopic varices in Japan: results of a survey by the Japan Society for Portal Hypertension. Hepatol Res. 2010; 40:763–776.

4. Misra SP, Dwivedi M. Ligation of a bleeding colonic varix using an upper gastrointestinal endoscope. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:657.

5. Chevallier P, Motamedi JP, Demuth N, Caroli-Bosc FX, Oddo F, Padovani B. Ascending colonic variceal bleeding: utility of phase-contrast MR portography in diagnosis and follow-up after treatment with TIPS and variceal embolization. Eur Radiol. 2000; 10:1280–1283.

6. Chen WC, Hou MC, Lin HC, Chang FY, Lee SD. An endoscopic injection with N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate used for colonic variceal bleeding: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:540–542.

7. Vangeli M, Patch D, Terreni N, et al. Bleeding ectopic varices– treatment with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) and embolisation. J Hepatol. 2004; 41:560–566.
8. Wiegand N, Pfiffner R, Bauerfeind P. Ascending colonic variceal bleeding. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:1073–1074. discussion 1074.

9. Christian KE, McCurdy MT, Potosky DR. Massive hematochezia from ascending colonic varices. West J Emerg Med. 2015; 16:577–578.

10. Kim HU, Her KH, Kim SH, et al. A case of variceal bleeding of the ascending colon associated with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Korean J Med. 2008; 75:215–220.
11. Bernard AC, Hagihara PF, Burke VJ, Kugelmas M. Endoscopic localization and management of colonic bleeding in patients with portal hypertension. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2001; 11:195–198.

12. Anan A, Irie M, Watanabe H, et al. Colonic varices treated by balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration in a cirrhotic patient with encephalopathy: a case report. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:880–884.

13. Sato T, Yamazaki K, Akaike J, et al. Transverse colonic varices successfully treated with endoscopic procedure. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2008; 1:52–55.

14. Sohn W, Lee HL, Lee KN. Variceal hemorrhage of ascending colon. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:A24.

15. Jha AK, Goenka U, Goenka MK. Endoscopic glue injection for acute colonic variceal bleed. Dig Endosc. 2012; 24:478.

16. Ko BS, Kim WT, Chang SS, et al. A case of ascending colon variceal bleeding treated with venous coil embolization. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:311–315.

16. Sousa M, Ribeiro I, Proenca L, Silva J, Ponte A, Rodrigues J. Histoacryl injection for treatment of varices in the ascending colon. Endoscopy. 2016; 48(Suppl 1):E285.

17. Rawal KK. Colorectal variceal bleeding managed by endoscopic therapy in patients with cirrhosis. J Assoc Physicians India. 2016; 64:88–89.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.At proximal ascending colon, there was dilated vascular structure with shallow erosion (A). The endoscopic variceal obturation with N-butyl-2-acyanoacrylate was performed through colonoscopy (B). |
 | Fig. 2.Second session of endoscopic variceal obturation was done targeting the remnant dilated varix one week after 1st session (A). After 2nd injection, bloated varix with sclerosant was noted (B). |
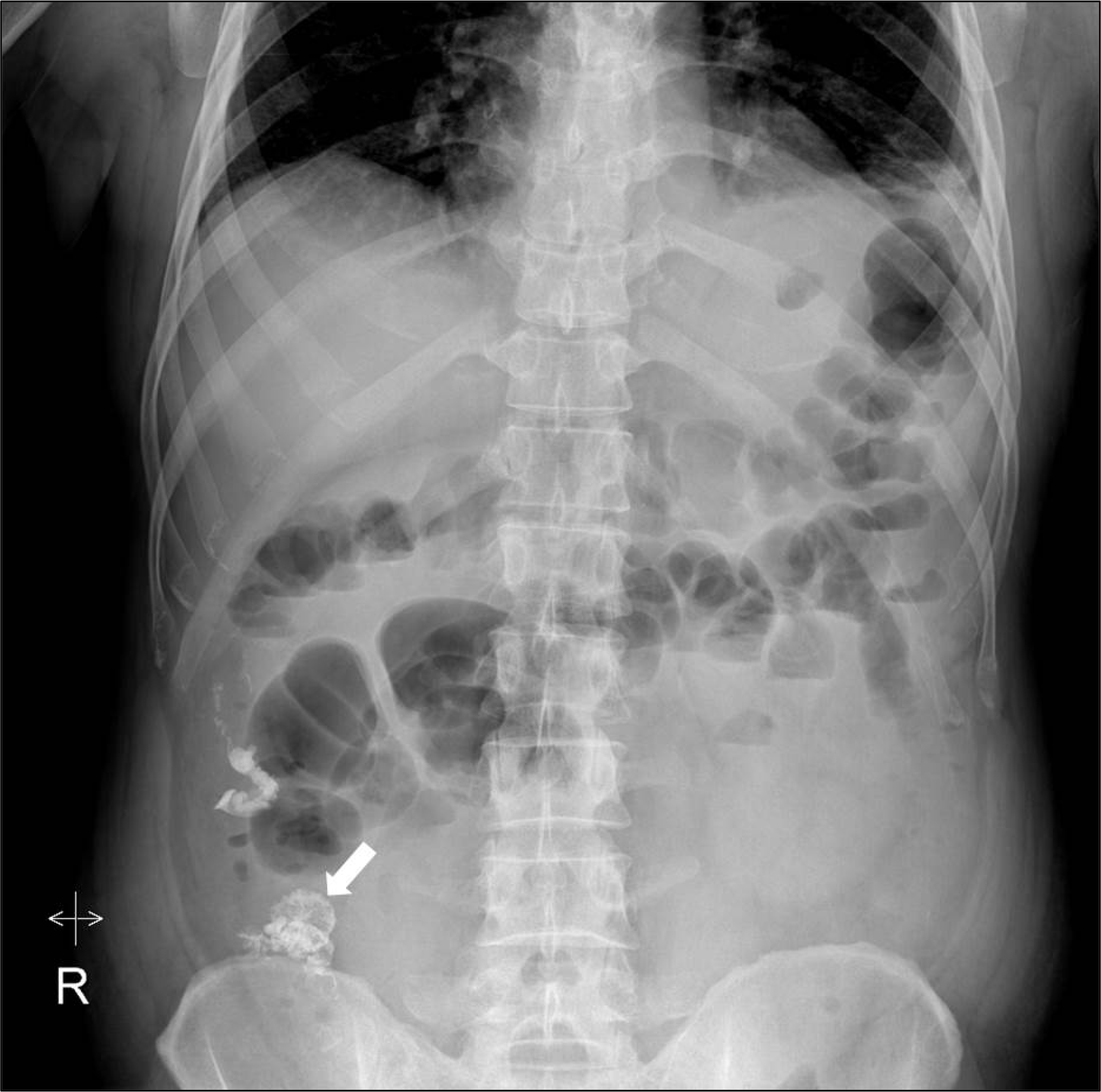 | Fig. 3.Simple abdomen after 2nd endoscopic variceal obturation (white arrow: lipiodol in the ascending colon varix). |
 | Fig. 4.A radiopague lipiodol attenuation with N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate in the ascending varix was shown after hemostatic procedure (white arrow). The liver shows surface nodularity and blunting edge. |
Table 1.
Previously Reported Colon Varices Presenting Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding except Rectal Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Portal Hypertension since 2000
| Author (year) | Age/gender | Cause | Location | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chevallier et al. (2000)5 | 44/F | Alcoholic LC | Ascending colon | EVO, then rebleeding |
| TIPS and embolization | ||||
| Chen et al. (2000)6 | 64/M | HBV LC | Sigmoid colon | EVO, then rebleeding |
| Bernard et al. (2001)11 | 40/M | HCV LC | Transverse colon | EIS with epinephrine and |
| morrhuate, then rebleeding | ||||
| Vangeli et al. (2004)7 | 37/F | Alcoholic LC | Cecum | TIPS & embolization |
| Vangeli et al. (2004)7 | 19/M | Autoimmune hepatitis | Non-specified colon | TIPS & embolization |
| Wiegand et al. (2006)8 | 43/M | Alcoholic LC | Ascending colon | TIPS, then rebleeding |
| EVO & embolization | ||||
| Anan et al. (2006)12 | 62/F | HCV LC | Splenic flexure | BRTO |
| Misra and Dwivedi (2006)4 | 32/M | HBV LC | Descending colon | EVL |
| Kim et al. (2008)10 | 43/M | Alcoholic LC | Ascending colon | Right hemicolectomy |
| Sato et al. (2008)13 | 75/F | HCV LC | Transverse colon | EIS with ethanolamine oleate |
| Watanabe et al. (2010)3 | − | −a | Non-specified | BRTO |
| Watanabe et al. (2010)3 | − | −a | Non-specified | PTO |
| Sohn et al. (2012)14 | 33/F | IVC occlusion by APS | Ascending colon | Octreotide and β-blocker |
| Jha et al. (2012)15 | 59/M | Alcoholic liver disease | Sigmoid colon | EVO |
| Ko et al. (2013)1 | 38/F | Alcoholic LC | Ascending colon | Venous embolization |
| Christian et al. (2015)9 | 54/M | Alcoholic liver disease | Ascending colon | TIPS and embolization |
| Sousa et al. (2016)16 | 50/F | Alcoholic LC | Ascending colon | EVO |
| Rawal (2016)17 | 42/M | Alcoholic liver disease | Cecum | EVO |
| Zhou et al. (2017)18 | 38/M | HBV LC | Ascending colon | TIPS |
| Jindal and Philips (2017)19 | 58/M | LC | Sigmoid colon | Conservative therapy |
F, female; LC, liver cirrhosis; EVO, endoscopic variceal obturation by N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate; TIPS, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; M, male; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; EIS, endoscopic injection sclerotharpy; BRTO, balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration; EVL, endoscopic variceal ligation; PTO, percutaneous transhepatic obliteration; IVC, inferior vena cava; APS, antiphospholipid syndrome.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download