Abstract
An inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a rare disease that can occur in a variety of locations, including the lung, orbit, parotid, pleura, and stomach. Despite multiple reports in various organs, a duodenal IMT is rare with limited case reports. We encountered a case of a 49-year-old male with a duodenal IMT. The patient underwent a laparoscopic wedge resection under the impression of a duodenal mesenchymal tumor, such as gastrointestinal stromal tumor, but the final diagnosis was a duodenal IMT. The patient was treated successfully with an oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug for the residual lesions. He was free of recurrence during the 12 month follow-up period.
References
1. Petrovic I, Augustin G, Hlupic L, Nedic A, Romic I, Skegro M. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the duodenum. Asian J Surg. 2016; 39:247–252.

2. Symmers D. Primary hemangiolymphoma of the hemal nodes: an unusual variety of malignant tumor. Arch of Intern Med (Chic). 1921; 28:467–474.

3. Coffin CM, Watterson J, Priest JR, Dehner LP. Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor). A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 84 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995; 19:859–872.

4. Kim HY, Moon SB, Jung SE, Lee SC, Park KW, Kim WK. Abdominal inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in children. J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2008; 14:153–163.

5. Fong SS, Zhao C, Yap WM, Loke SC, Lim KH. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour of the duodenum. Singapore Med J. 2012; 53:e28–e31.
6. Woo HJ, Bae CH, Kim YD. A case of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of nasal cavity in an 8 year-old girl. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2008; 51:481–483.
7. Butrynski JE, D'adamo DR, Hornick JL, et al. Crizotinib in ALK-re-arranged inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1727–1733.
8. Stringer MD, Ramani P, Yeung CK, Capps SN, Kiely EM, Spitz L. Abdominal inflammatory myofibroblastic tumours in children. Br J Surg. 1992; 79:1357–1360.

9. Mattei P, Barnaby K. Rapid regression of duodenal inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor after intravenous ketorolac: case report and review of the literature. J Pediatr Surg. 2008; 43:1196–1199.

10. Wynn GR, Giles A, Steger AS, Wilkinson ML. Case report: inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the duodenum. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2008; 39:79–81.

11. Kim SJ, Kim WS, Cheon JE, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the abdomen as mimickers of malignancy: imaging features in nine children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:1419–1424.

12. Kwak JW, Paik CN, Jung SH, et al. An inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the ampulla of vater successfully managed with endoscopic papillectomy: report of a case. Gut liver. 2010; 4:419–422.

13. Mirshemirani A, Tabari AK, Sadeghian N, Shariat-Torbaghan S, Pourafkari M, Mohajerzadeh L. Abdominal inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: report on four cases and review of literature. Iran J Pediatr. 2011; 21:543–548.
14. Xiang J, Liu X, Wu S, Lv Y, Wang H. Multiple inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the duodenum: case report and literature review. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012; 16:1442–1445.

15. González MG, Vela D, Álvarez M, Caramés J. Inflammatory myofibroblastic duodenal tumor: a rare cause of massive intestinal bleeding. Cancer Biomark. 2016; 16:555–557.

16. Sinha L, Hasan A, Singh AK, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor involving liver, gallbladder, pylorus & duodenum: a rare case presentation. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2017; 31:27–29.
17. Karnak I, Senocak ME, Ciftci AO, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in children: diagnosis and treatment. J Pediatr Surg. 2001; 36:908–912.

18. Han BD, Lee JW, Kim MK, Kim JK. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the parotid gland. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2012; 55:664–667.

Fig. 1.
(A) Endoscopic finding. Endoscopy reveals a 2-cm-sized subepithelial tumor with central ulcer in the second portion of the duodenum.(B) Endoscopic ultrasonography. On endoscopic ultrasonography, the tumor is a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass with unclear border, originating from the deep mucosal and submucosal layers.
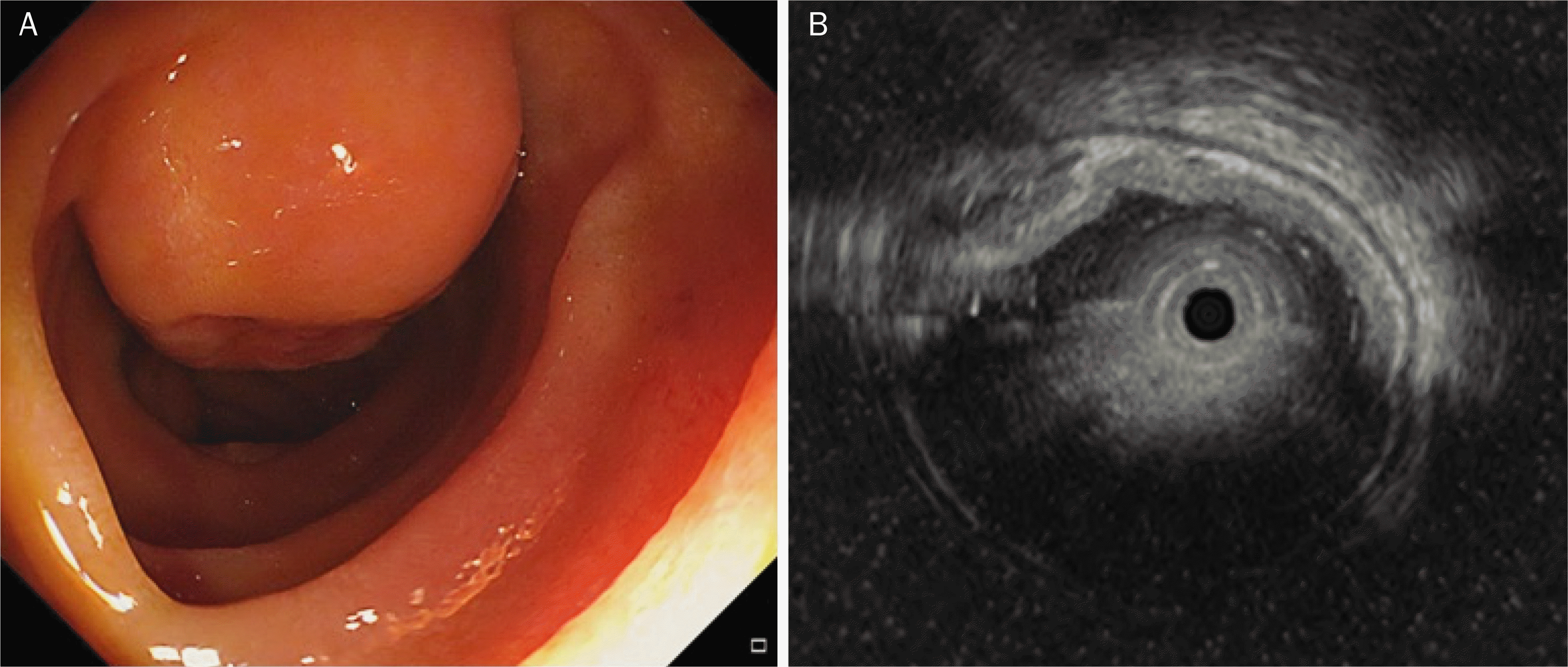
Fig. 2.
Abdominal computed tomography (CT) reveals a 1.7-cm-sized hypervascular solid mass in the second portion of the duodenum (red arrows). (A) CT transverse view. (B) CT coronal view.
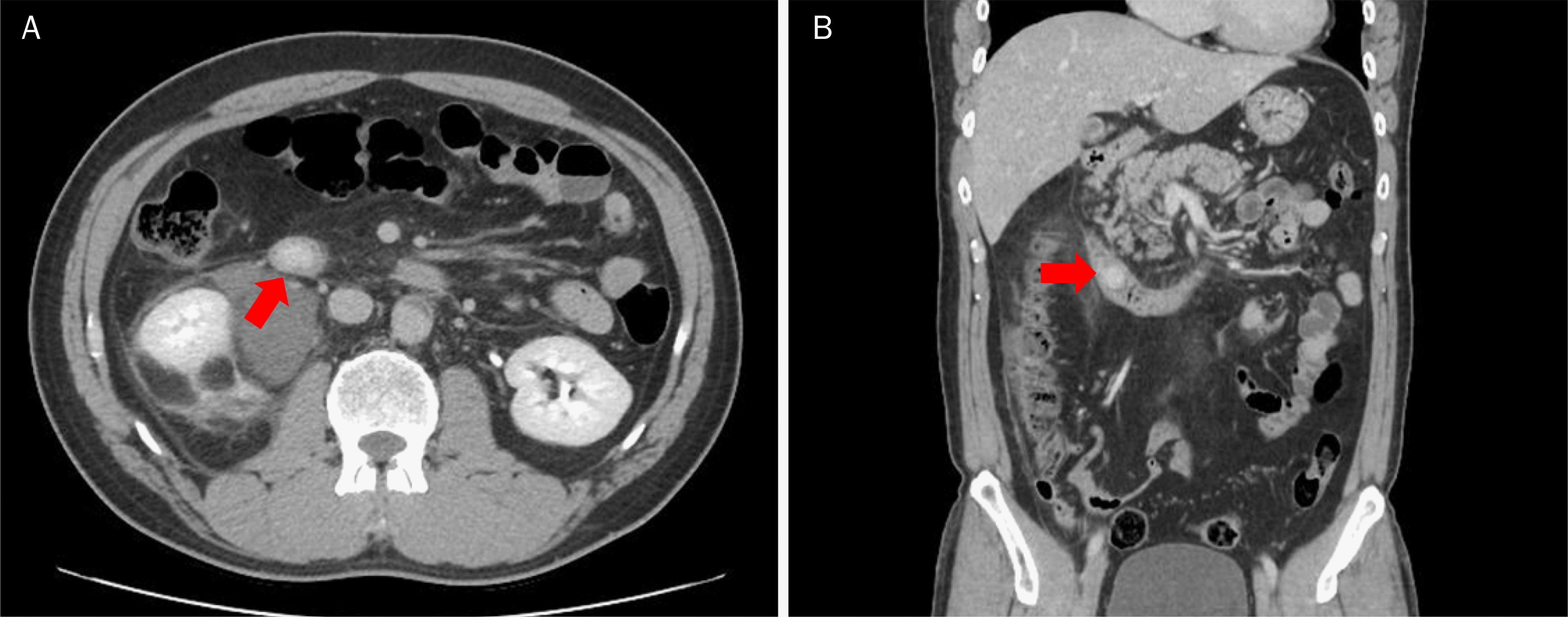
Fig. 3.
(A) Gross finding. Resected specimen shows a relatively well-defined, yellowing subepithelial mass. (B) Microscopic finding reveals spindle cell tumors (red arrows), scattered inflammatory cells (blue arrows), epithelial cells (yellow arrows), and stellate cells (green arrow)(H&E,×400). (C-F) Immunohistochemical stain. Positive for SMA (C, ×400), and negative for S-100 (D, ×100), C-kit (E, ×400), ALK (F, ×200). SMA, smooth muscle actin; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase.
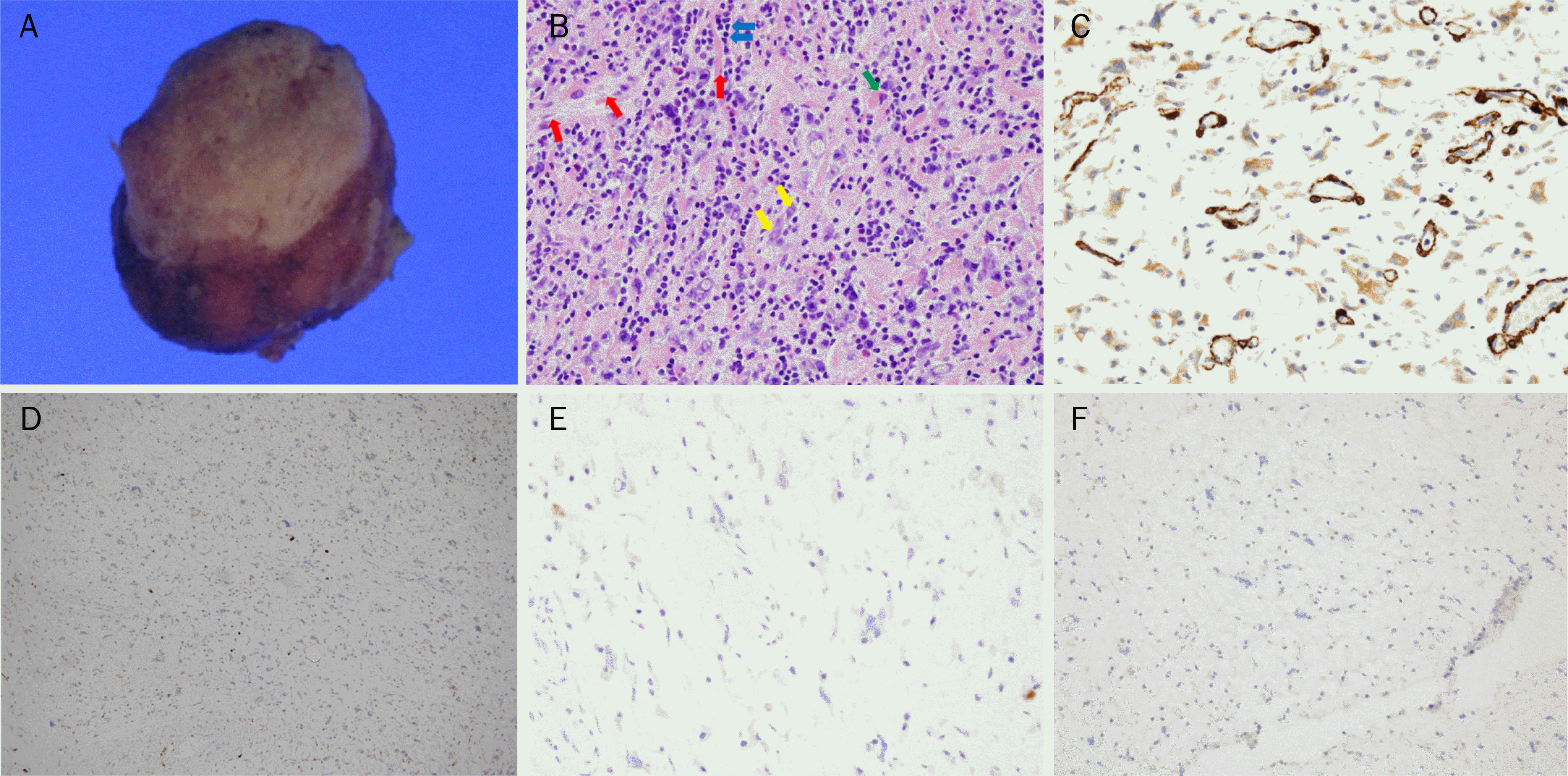
Table 1.
Summary of Previous Reported Cases of Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumors in the Duodenum
| Authors (publish year) | Sex | Age (yr) | Symptoms | Segment of duodenum | Size a (cm) | Treatment | Recurrence | 2nd treatment/2nd recurrence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stringer et al. (1992)8 | F | 5 | Vomiting | Second | 7.0 | Resection | None | − |
| Mattei et al. (2008)9 | M | 13 | Asymptomatic | First, second | − | NSAIDs/Resection | None | − |
| Kim et al. (2008)4 | M | 9 | − | Multiple | − | Mass partial excision | − | − |
| M | 14 | − | Multiple | − | No operation | − | − | |
| Wynn et al. (2008)10 | M | 16 | Epigastric pain | First | 6.0 | Resection | Recurrence | Steroid and azathioprine/none |
| Kim et al. (2009)11 | M | 10 | Abdominal pain | Multiple | 6.0 | Open biopsy | − | |
| M | 15 | Abdominal pain | Multiple | 9.8 | − | − | ||
| Kwak et al. (2010)12 | F | 65 | Epigastric pain | Ampulla of vater | 2.3 | Endoscopic papillectomy | None | − |
| Mirshemirani et al. (2011)13 | M | 13 | Weight loss | First | − | Resection | − | − |
| Fong et al. (2012)5 | F | 57 | Obstruction | Second, third | 3.6 | Resection | None | − |
| Xiang et al. (2012)14 | M | 20 | Epigastric pain | Multiple | 7.0 | Resection | None | − |
| Petrovic et al. (2016)1 | M | 58 | Epigastric pain | Fourth | 15.5 | Resection | None | − |
| González et al. (2016)15 | F | 14 | Epigastric pain | Third | − | Resection | − | − |
| Sinha et al. (2017)16 | F | 36 | Abdominal bloating | Multiple | − | Resection | − | − |
| Present case | M | 49 | Asymptomatic | Second | 2.7 | Resection | None | NSAIDs due to incomplete resection |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download