Abstract
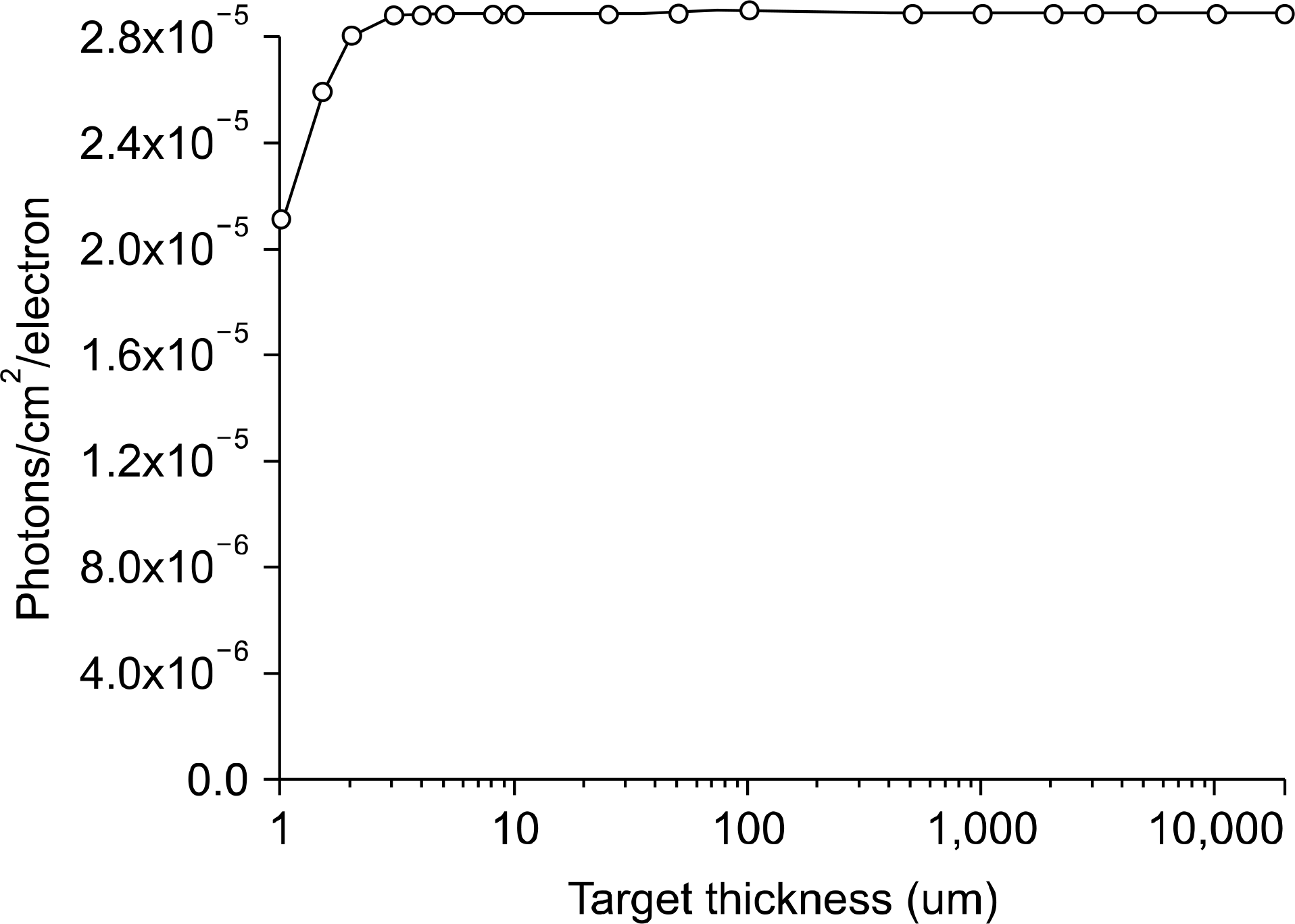
To investigate the optimum x-ray tube design for the dental radiology, factors affecting x-ray beam characteristics such as tungsten target thickness and anode angle were evaluated. Another goal of the study was to addresses the anode heel effect and off-axis spectra for different target angles. MCNPX has been utilized to simulate the diagnostic x-ray tube with the aim of predicting optimum target angle and angular distribution of x-ray intensity around the x-ray target. For simulation of x-ray spectra, MCNPX was run in photon and electron using default values for PHYS:P and PHYS:E cards to enable full electron and photon transport. The x-ray tube consists of an evacuated 1 mm alumina envelope containing a tungsten anode embedded in a copper part. The envelope is encased in lead shield with an opening window. MCNPX simulations were run for x-ray tube potentials of 70 kV. A monoenergetic electron source at the distance of 2 cm from the anode surface was considered. The electron beam diameter was 0.3 mm striking on the focal spot. In this work, the optimum thickness of tungsten target was 3 μm for the 70 kV electron potential. To determine the angle with the highest photon intensity per initial electron striking on the target, the x-ray intensity per initial electron was calculated for different tungsten target angles. The optimum anode angle based only on x-ray beam flatness was 35 degree. It should be mentioned that there is a considerable trade-off between anode angle which determines the focal spot size and geometric penumbra. The optimized thickness of a target material was calculated to maximize the x-ray intensity produced from a tungsten target materials for a 70 keV electron energy. Our results also showed that the anode angle has an influencing effect on heel effect and beam intensity across the beam.
REFERENCES
1. Cheng Y, Zhang J, Lee YZ, Gao B, Dike S, Lin W, et al. Dynamic radiography using a carbon-nanotube-based field- emission x-ray source. Review of scientific instruments. 75(10):3264–3267. 2004.
2. Knoll GF. Radiation detection and measurement. John Wiley & Sons. 2010.
3. Ay MR, Shahriari M, Sarkar S, Adib M, Zaidi H. Monte Carlo simulation of x-ray spectra in diagnostic radiology and mammography using MCNP4C. Physics in medicine and biology. 49(21):4897–4917. 2004.

4. Acosta E, Llovet X, Coleoni E, Riveros J, Salvat F. Monte Carlo simulation of x-ray emission by kilovolt electron bombardment. Journal of applied physics. 83(11):6038–6049. 1998.

5. Pelowitz DB. MCNPX user's manual version 2.5. 0. Los Alamos National Laboratory. 2005.
6. Kulkarni R. Supe S. Monte Carlo calculations of mammographic x-ray spectra. Physics in medicine and biology. 29(2):185. 1984.
7. Briesmeister J. A General Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code, MCNP. Los Alamos National Laboratory, ORNL-13221, Oak Ridge, TN, USA. 2000.
Fig. 1.
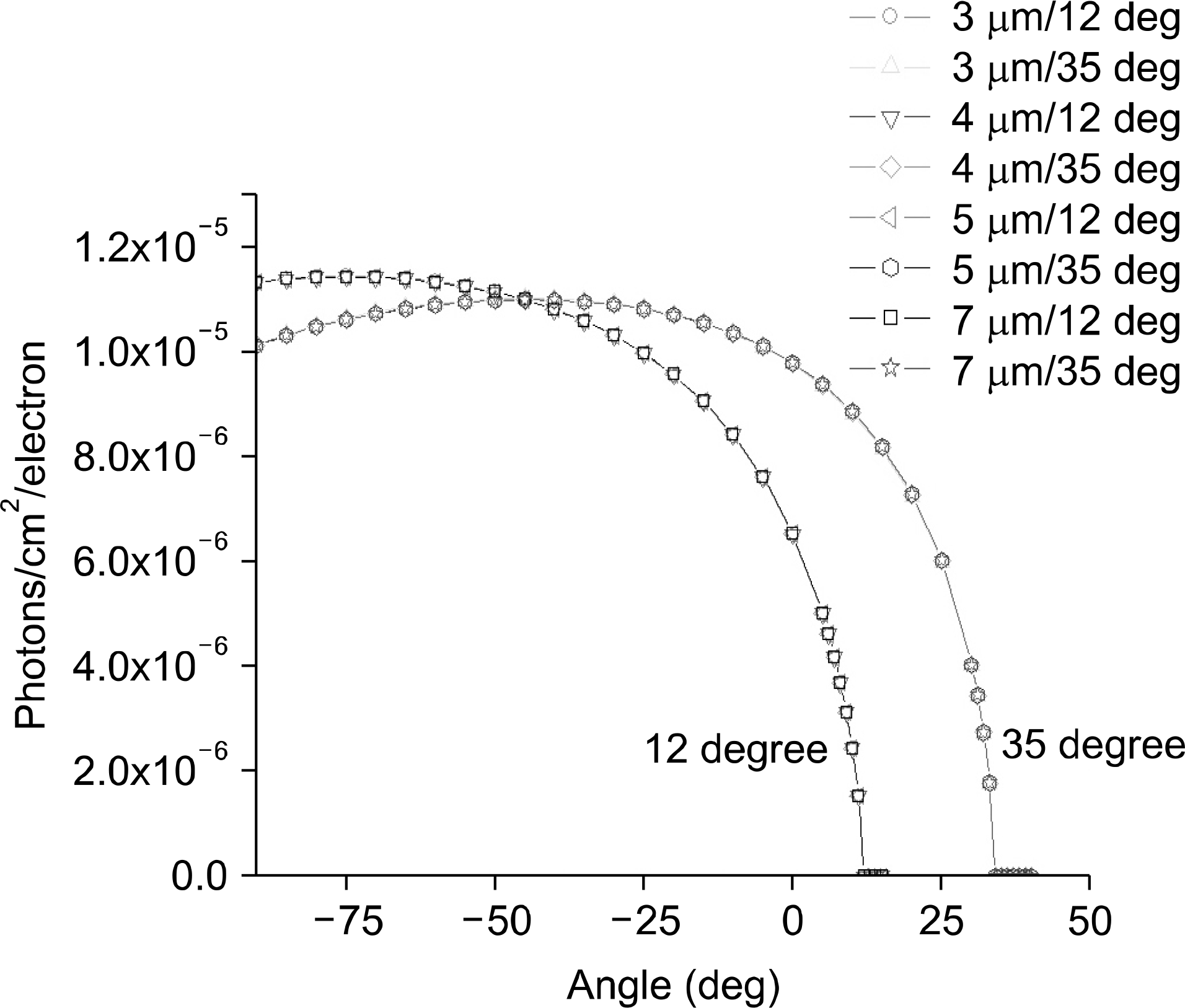
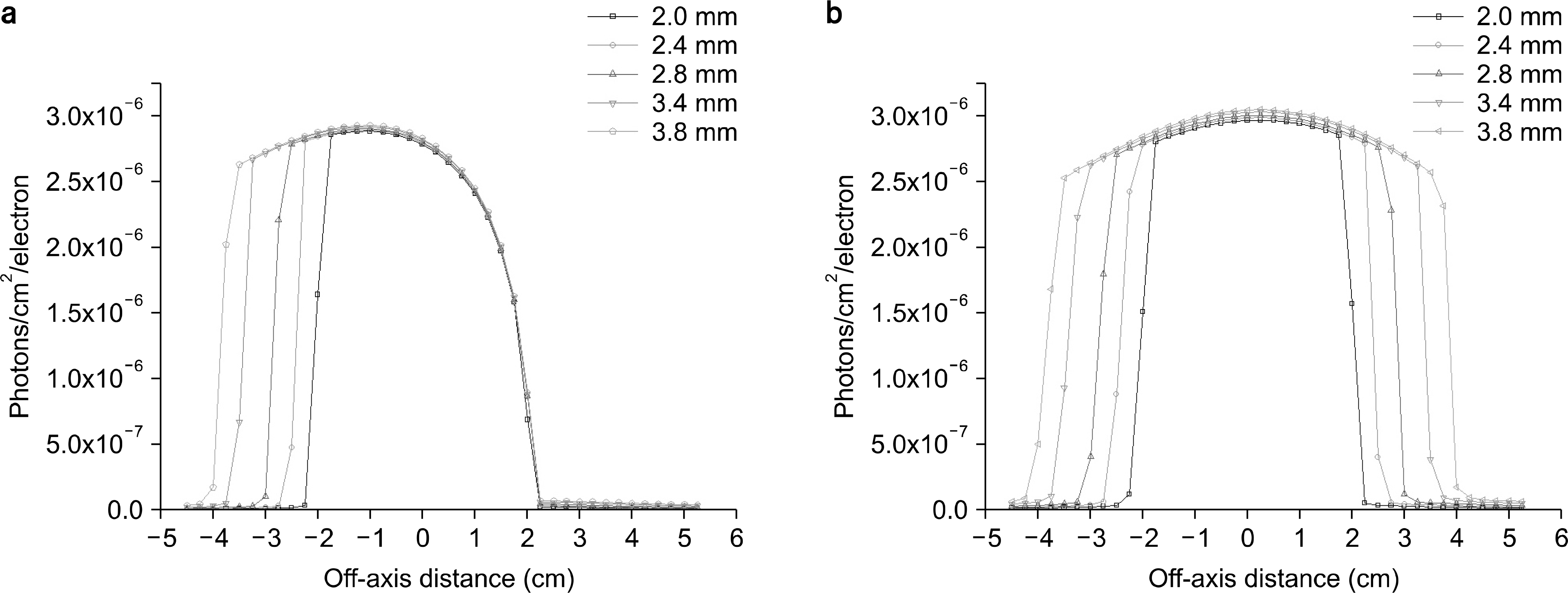
Geometry for Monte Carlo simulation of x-ray intensity and assessment of anode heel effect. The position of detectors for calculation of x-ray beam intensity is also shown.
Fig. 3.
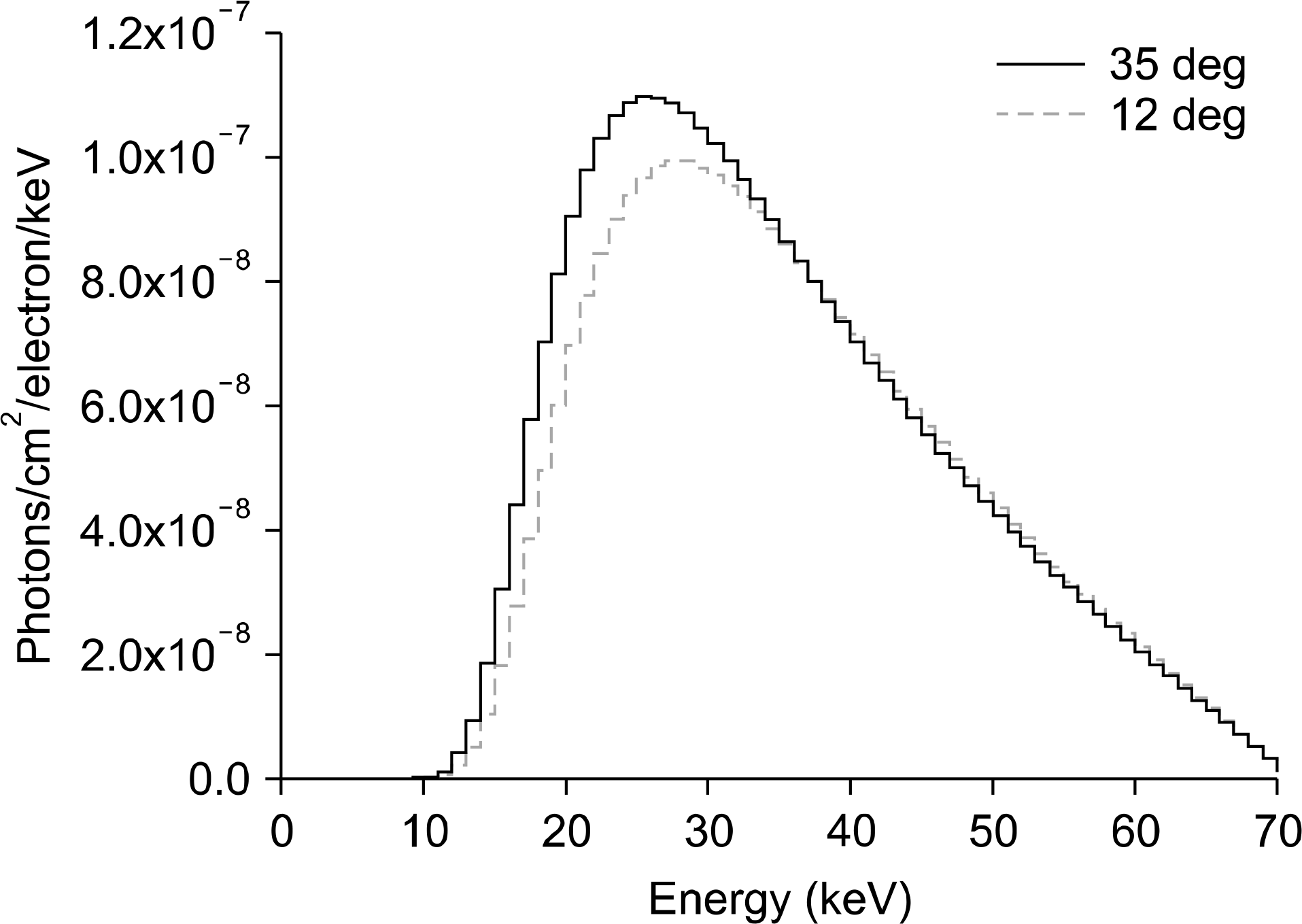
The x-ray spectrum without Alumina envelope for target angle 12 degree at 10 cm distance from the target position.
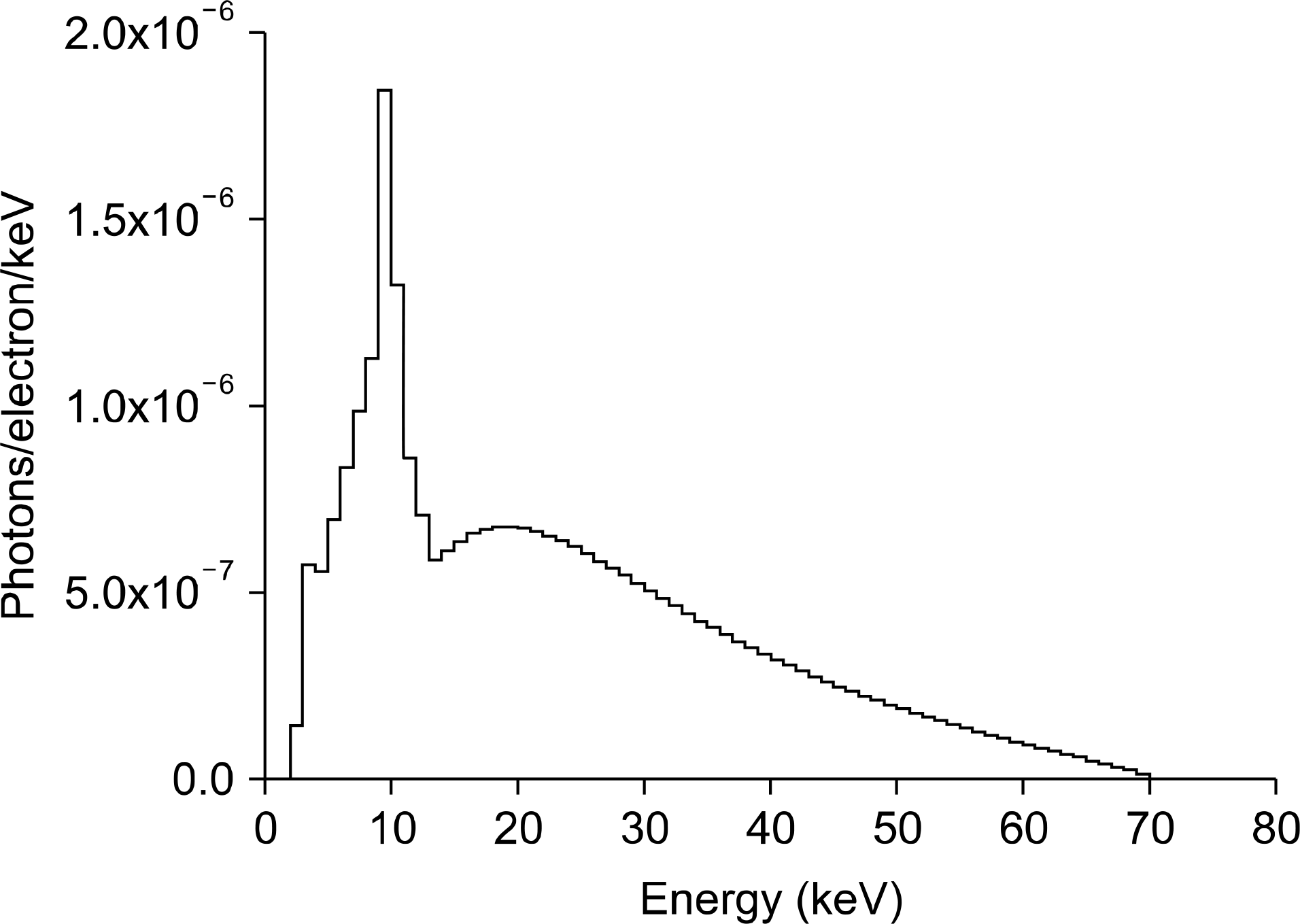
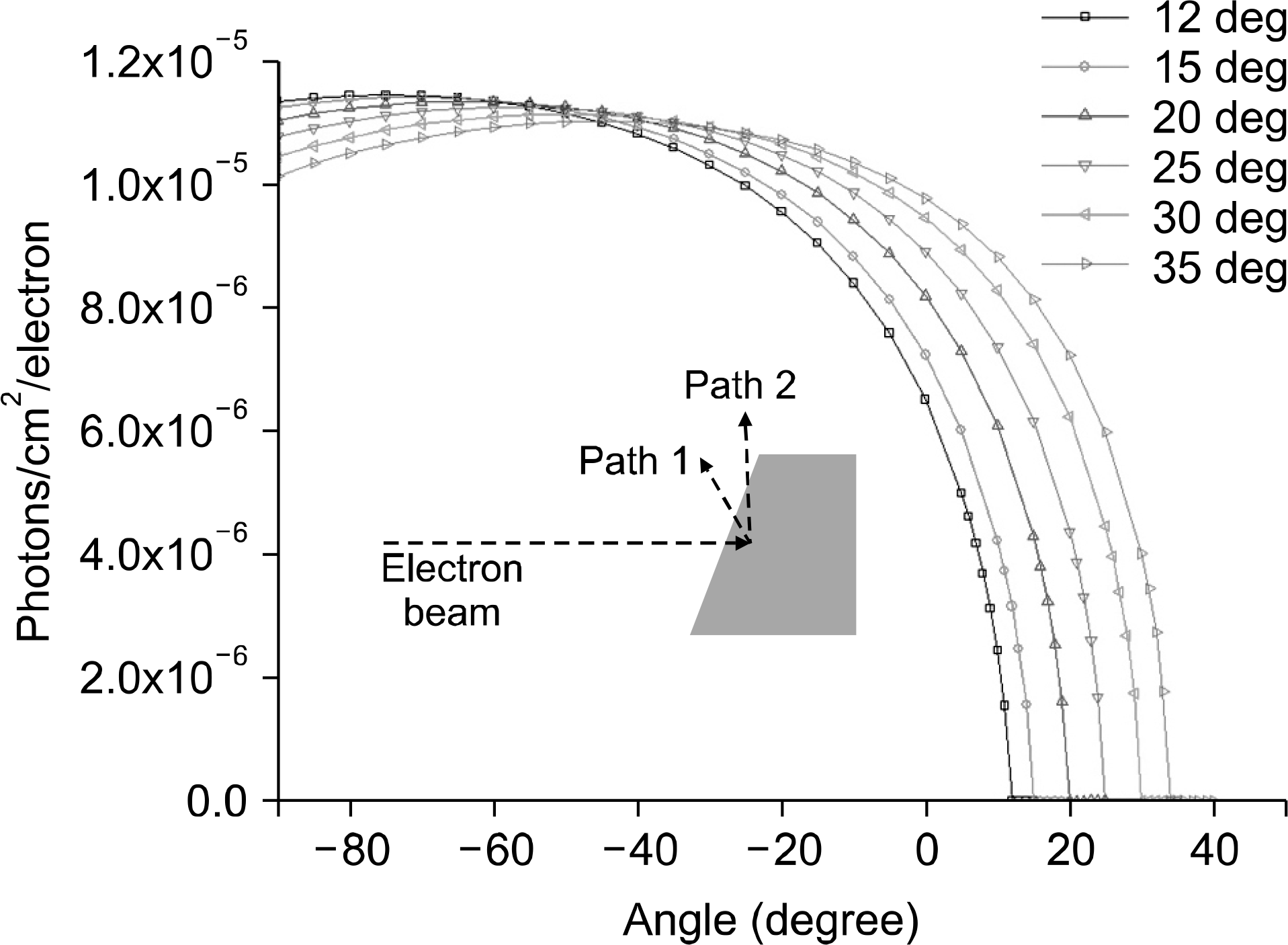
Fig. 4.
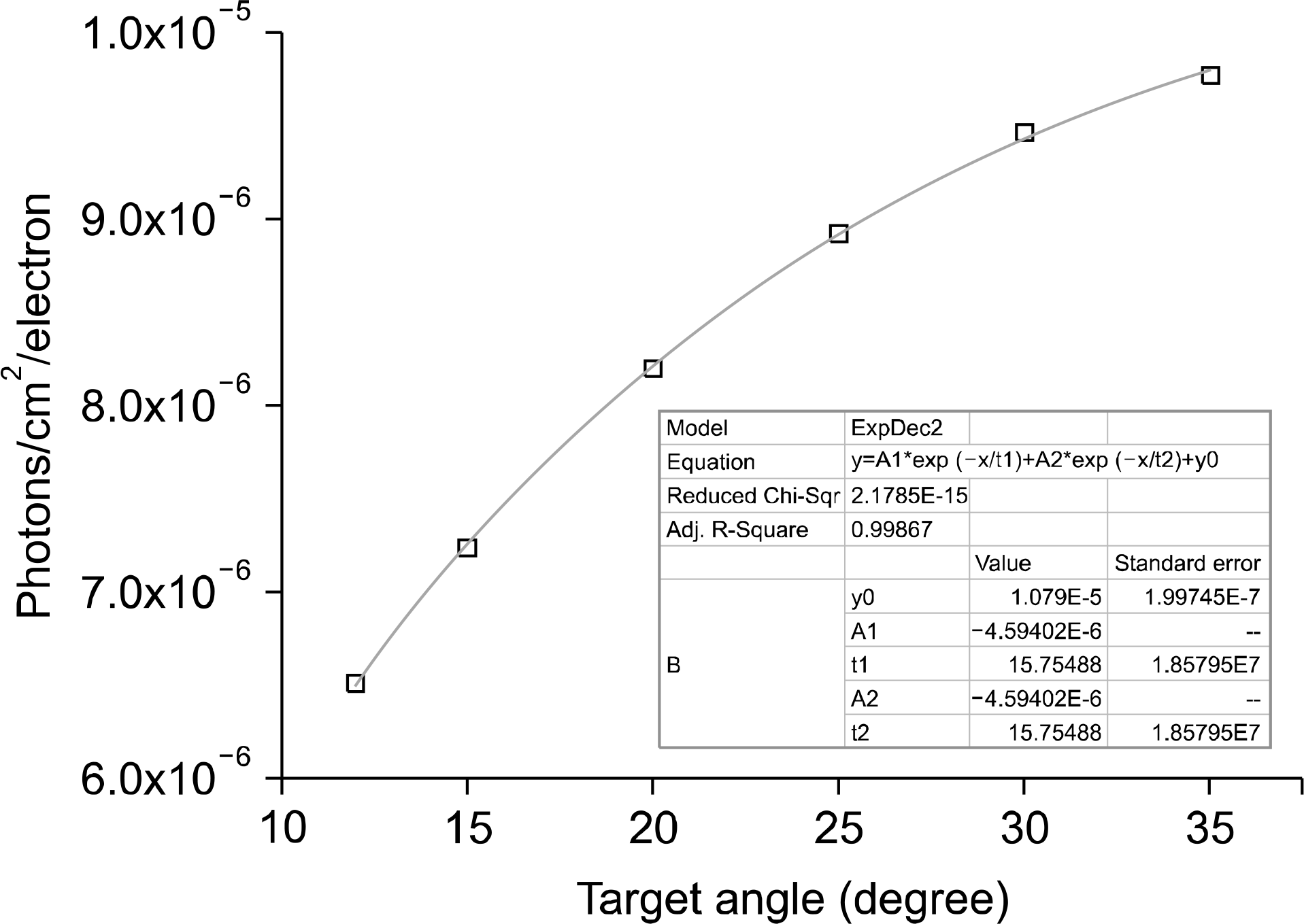
The angular distribution of the x-ray intensity emitted by the tungsten target for 3 μm target thickness.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download