Abstract
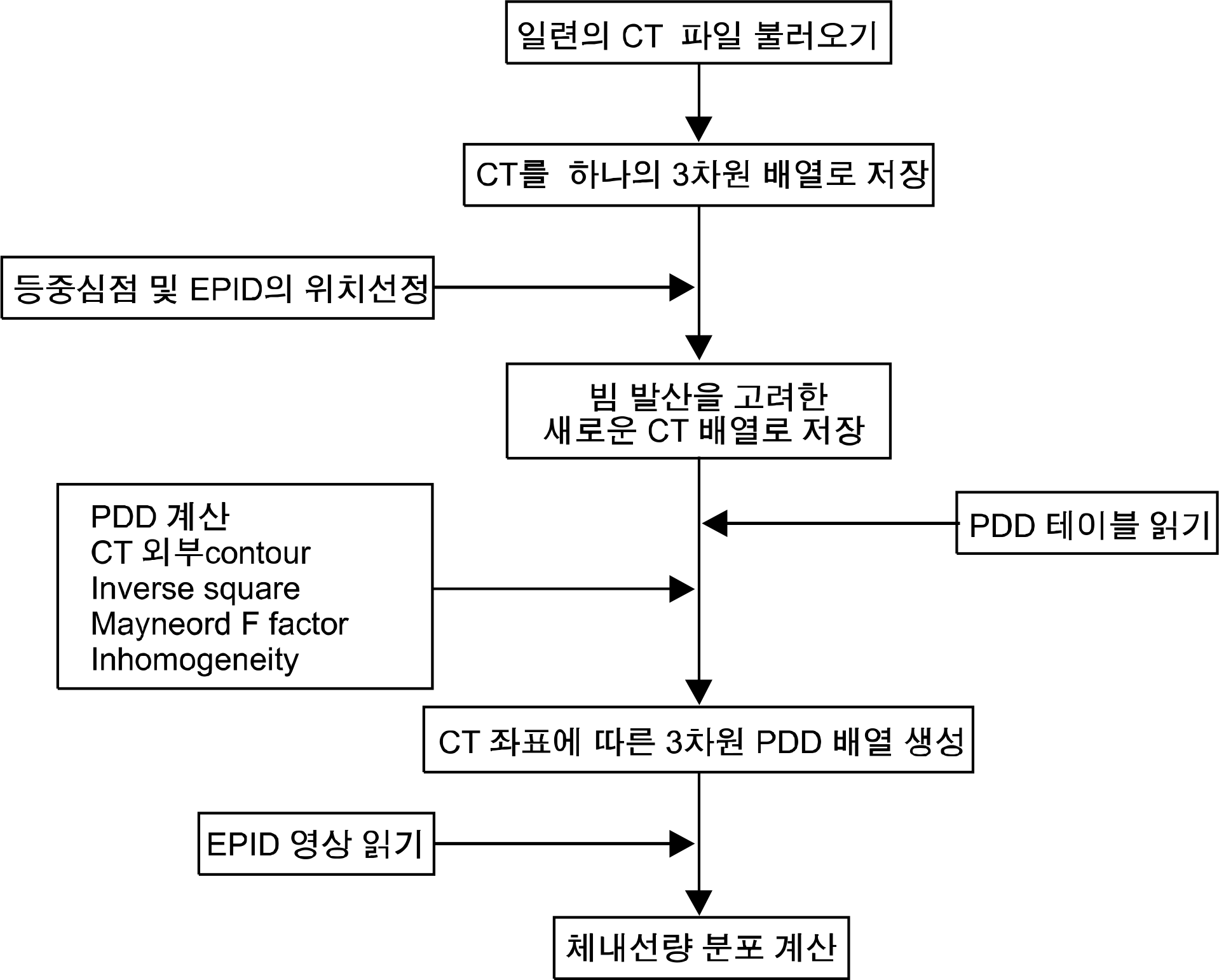
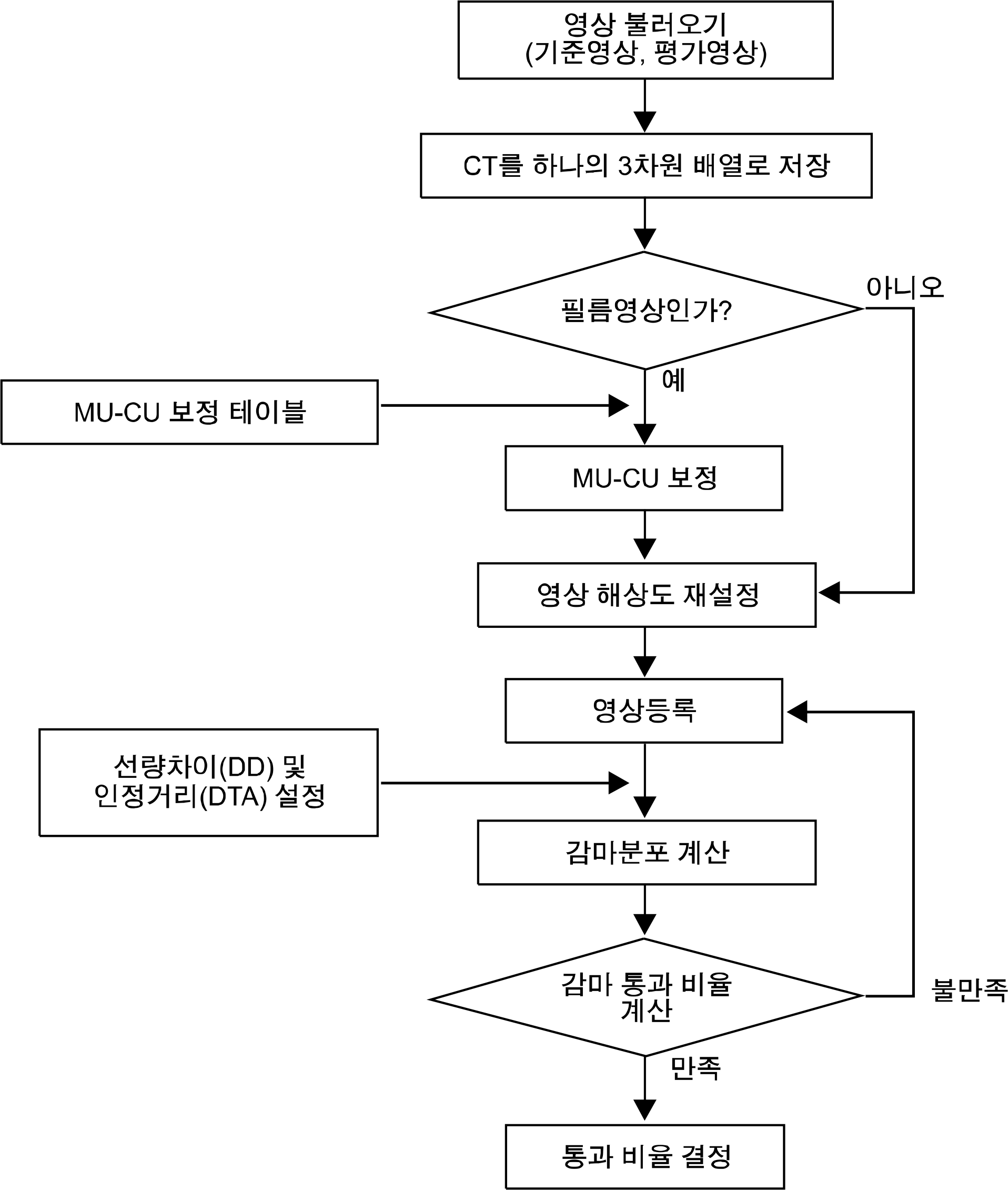
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the developed dose verification program for in vivo dosimetry based on transit dose in radiotherapy. Five intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) plans of lung cancer patients were used in the irradiation of a homogeneous solid water phantom and anthropomorphic phantom. Transit dose distribution was measured using electronic portal imaging device (EPID) and used for the calculation of in vivo dose in patient. The average passing rate compared with treatment planning system based on a gamma index with a 3% dose and a 3 mm distance-to-dose agreement tolerance limit was 95% for the in vivo dose with the homogeneous phantom, but was reduced to 81.8% for the in vivo dose with the anthropomorphic phantom. This feasibility study suggested that transit dose-based in vivo dosimetry can provide information about the actual dose delivery to patients in the treatment room.
REFERENCES
1. Boellaard R. M., van Herk , Mijnheer BJ. A convolution model to convert transmission dose images to exit dose distributions. Medical Physics. 24:189–200. 1997.

2. Boellaard Ronald, Essers Marion, Herk Marcel van, Mijnheer Ben J.New method to obtain the midplane dose using portal in vivo dosimetry. Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys. 41(2):465–474. 1998.

3. Louwe RJW, Damen EMF, van Herk M., Minken AWH, Torzsok O, Mijnheer BJ. 3D dose reconstruction of breast cancer treatment using portal imaging. Medical Physics. 30:2376–2398. 2003.
4. WJC van Elmpt. Nijsten SMJJG, Mijnheer BJ, Minken AWH. Experimental verificaiton of a portal dose prediction model. Medical Physics. 32:2805–2818. 2005.
5. Wendling Markus, Louwe Robert J. W., McDermott Leah N., Sonke Jan-Jakob, Herk Marcel van, Mijnheer Ben J.Accurate two-dimensional IMRT verification using a back-projection EPID dosimetry method. Medical Physics. 33(2):259–336. 2006.

6. van Elmpt Wouter J. C., Nijsten Sebastiaan M. J. J. G., Robert FH, et al. Monte Carlo based 3D dose reconstruction method derived from portal dose images. Medical Physics. 33(7):2426–2478. 2006.
7. Louwe RJW, Wendling M, Herk MB van, Mijnheer BJ. 3D heart dose reconstruction to estimate normal tissue complication probability after breast irradiation using portal dosimetry. Medical Physics. 34(4):1354–1371. 2007.
8. Wendling Markus, McDermott Leah N., Mans Anton, Sonke Jan-Jakob, Herk Marcel van, Mijnheer Ben J.Simple backprojection algorithm for 3D in vivo EPID dosimetry of IMRT treatments. Medical Physics. 36(7):3310–3321. 2009.
9. Khan Faiz M.The Physics of Radiation Therapy. 4th ed. Williams & Wilkins;Baltimore, MD: 2010. ), pp.p. 146–148.
10. Dempsey James F.Evaluation of the gamma dose distribution comparison method. Medical Physics. 30(9):2455–2464. 2003.
Fig. 5.
Gamma distribution evaluated between dose distributions calculated from the EPID and given from the treatment planning system. (a) homogeneous solid phantom, (b) inhomogeneous humanoid phantom.
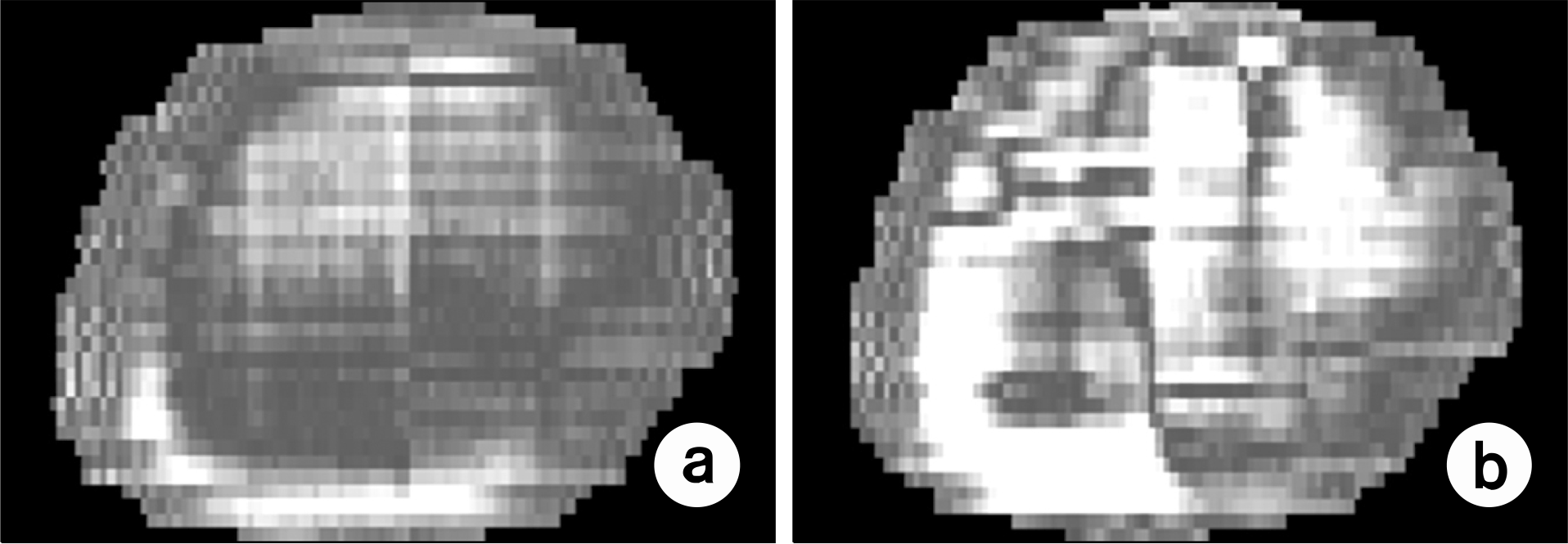
Fig. 6.
Box plot of gamma passing rates represented in Table 2. Average passing rate was 95% for solid phantom and 81.8% for humanoid phantom.
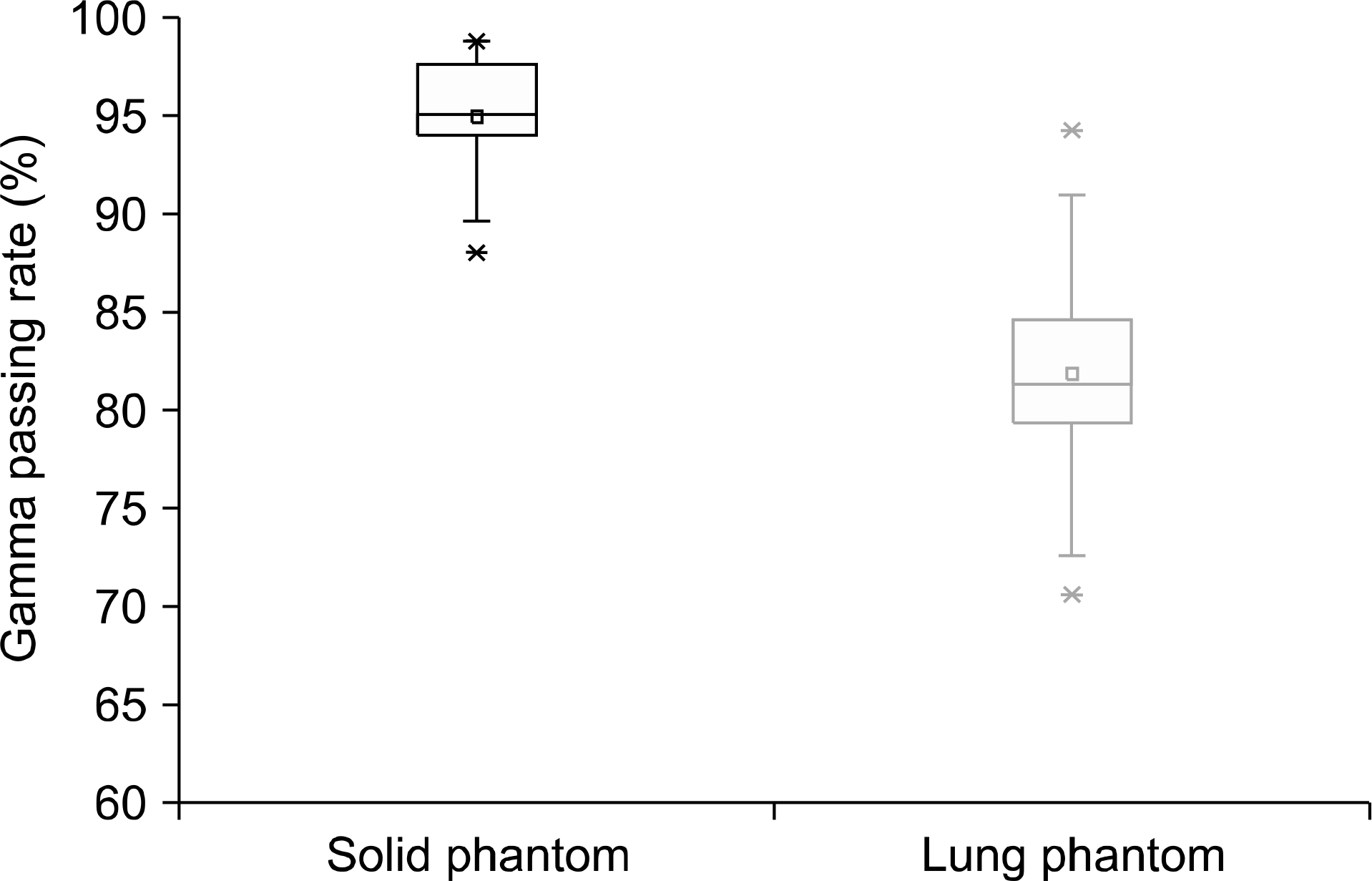
Table 1.
Patient characteristics, prescribed radiation dose and fraction size.
Table 2.
Comparison of gamma passing rates evaluated by commercial software and home-made software respectively.
Table 3.
Gamma passing rates for patient dose distribution in solid phantom and humanoid phantom respectively.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download