Abstract
The purpose of this study is to see the feasibility of the newly developed 2D dosimetry system using phosphor screen for helical tomotherapy. The cylindrical water phantom was fabricated with phosphor screen to emit the visible light during irradiation. There are three types of virtual target, one is one spot target, another is C-shaped target, and the other is multiple targets. Each target was planned to be treated at 10 Gy by treatment planning system (TPS) of tomotherapy. The cylindrical phantom was placed on the tomotherapy table and irradiated as calculations of the TPS. Every frame which acquired by CCD camera was integrated and the doses were calculated in pixel by pixel. The dose distributions from the fluorescent images were compared with the calculated dose distribution from the TPS. The discrepancies were evaluated as gamma index for each treatment. The curve for dose rate versus pixel value was not saturated until 900 MU/min. The 2D dosimetry using the phosphor screen and the CCD camera is respected to be useful to verify the dose distribution of the tomotherapy if the linearity correction of the phosphor screen improved.
Go to : 
References
1. Welsh JS, Patel RR, Ritter MA, et al. Helical tomotherapy: an innovative technology and approach to radiation therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 1(4):311–316. 2002.

2. Langen KM, Papanikolaou N, Balog J, et al. QA for helical tomotherapy: Report of the AAPM Task Group 148. Med Phys. 37(9):4817–4853. 2010.
3. Langen KM, Meeks SL, Poole DO, et al. Evaluation of a diode array for QA measurements on a helical tomotherapy unit. Med Phys. 32(11):3424–3430. 2005.

4. Geurts M, Gonzalez J, Serrano-Ojeda P. Longitudinal study using a diode phantom for helical tomotherapy IMRT QA. Med Phys. 36(11):4977–4983. 2009.

5. Feygelman V, Opp D, Javedan K, et al. Evaluation of a 3D diode array dosimeter for helical tomotherapy delivery QA. Med Dosim. 35(4):324–329. 2010.

6. Pavoni JF, Pike TL, Snow J, DeWerd L, Baffa O. Tomotherapy dose distribution verification using MAGIC-f polymer gel dosimetry. Med Phys. 39(5):2877–2883. 2012.
7. Lim S, Yeo IJ, Kim DY, Ahn YC, Huh SJ. Application of an imaging plate to relative dosimetry of clinical x-ray beams. Kor J Med Phys. 11(2):117–122. 2000.
8. Lim S, Yi BY, Ko YE, et al. Feasibility study of the real-time IMRT dosimetry using a scintillation screen. J Korean Soc Ther Radiol Oncol. 22(1):64–68. 2004.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.Custom made cylindrical water phantom for tomotherapy: The phosphor screen placed axially in the phantom and the CCD camera captures the visible light from the phosphor screen during the irradiation. The LCD monitor is used to check the focus and the setup of the phantom and the CCD camera. |
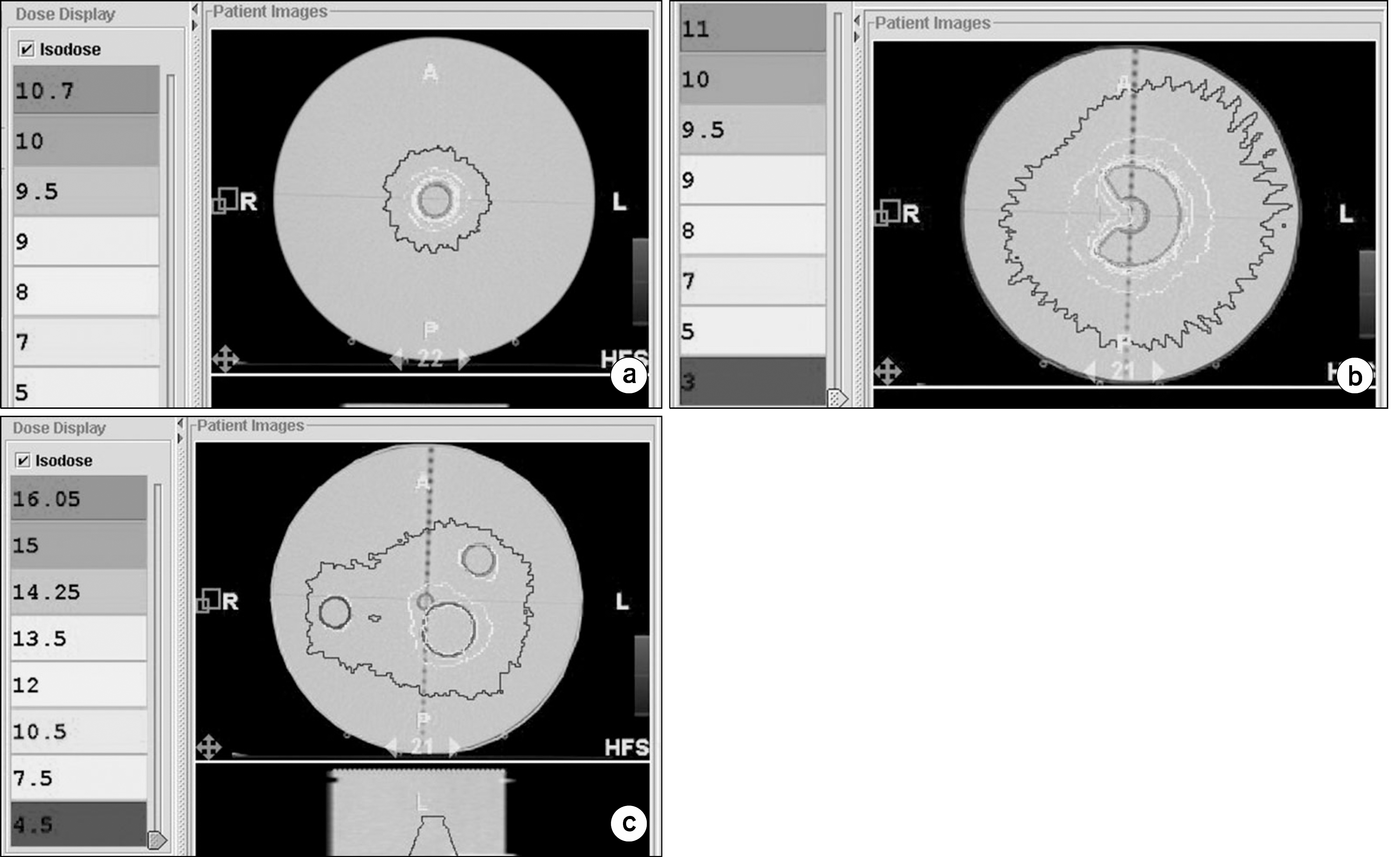 | Fig. 2.Dose distributions from treatment planning for three types of virtual targets in the cylindrical water phantom; there are single (a), C-shaped (b), and multiple targets (c). 10 Gy was to be delivered to each target with dose rate of 900 MU/min. |
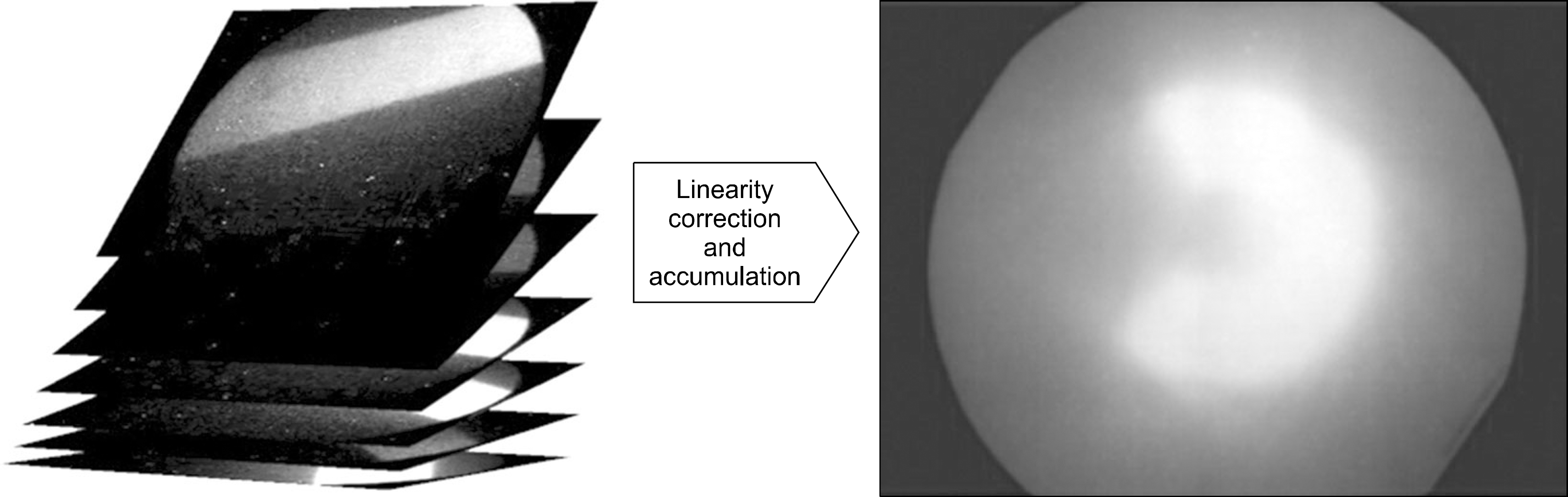 | Fig. 3.Every frame were calibrated and cumulated. Right picture shows example of reconstructed dose map for C-shaped virtual target. |
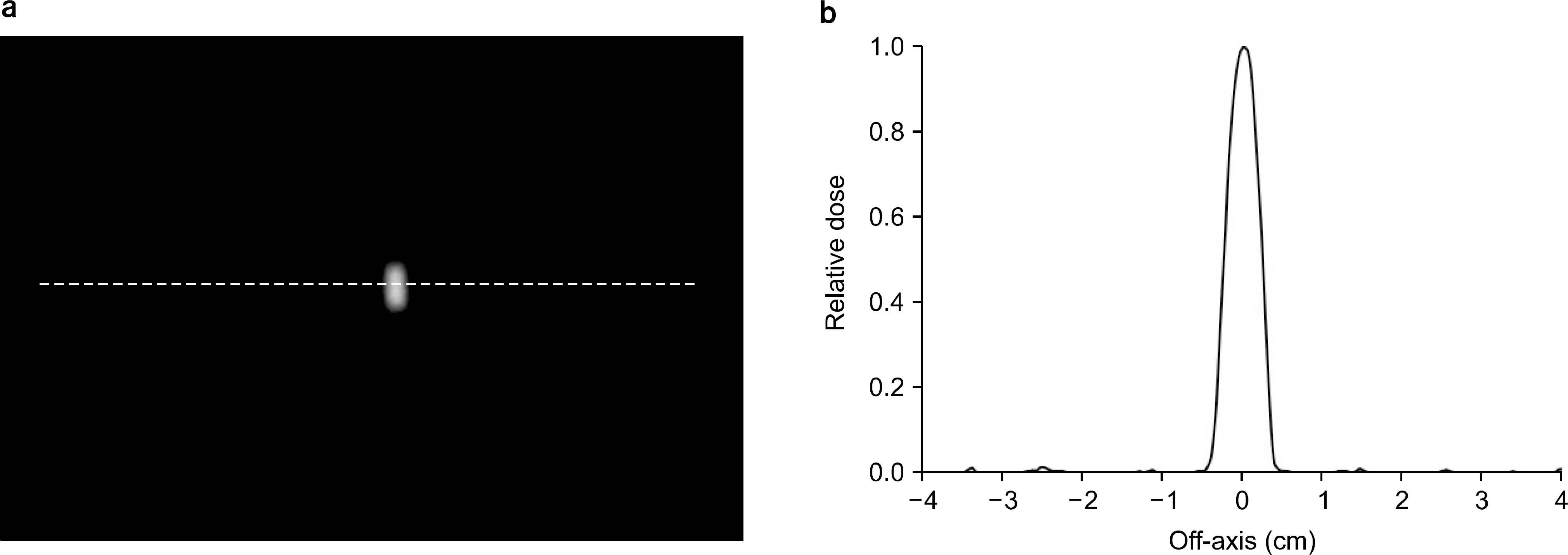 | Fig. 4.Profile of point dose from phosphor screen: (a) shows the point radiation on the phosphor screen. Blurring kernel (k) was obtained from the profile (b). |
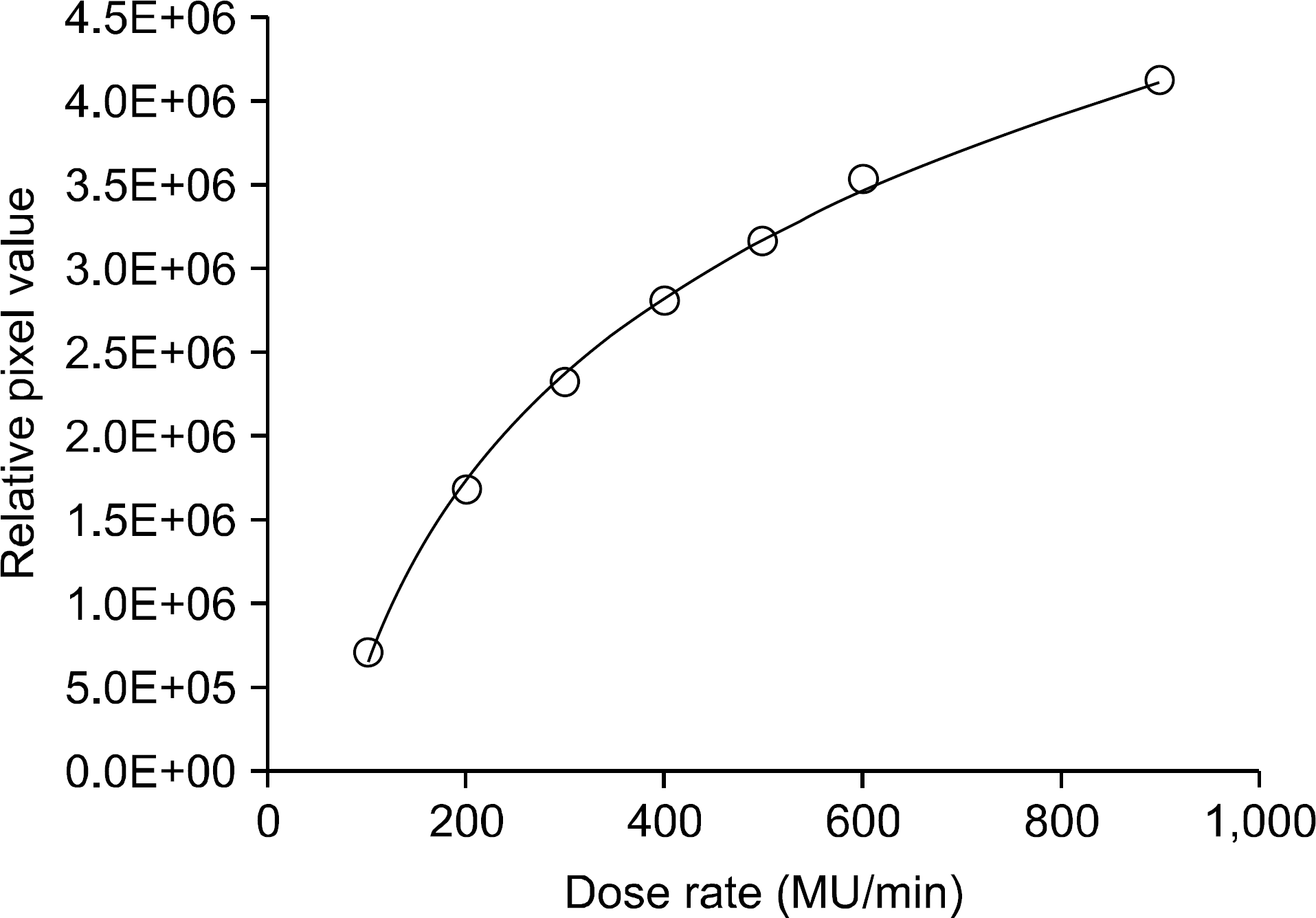 | Fig. 5.Dose rate dependency; the relative pixel values were measured versus dose rates from 100 MU/min to 900 MU/min. The solid line and the dotted line are the measurements and the fitting, respectively. |
 | Fig. 6.The dose distributions for three cases of virtual targets were analyzed. (a), (b), and (c) are cumulated gray scale images for single target, C-shpaed target, and multiple targets, respectively. (d), (e), and (f) are the gamma evaluation map between calculated and measured doses for three types of target. (d), (e), and (f) are the gamma evaluation map between calculated and measured dose distributions for three types of target. The pass rates are 84.46%, 80.38%, and 83.28%, respectively. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download