Abstract
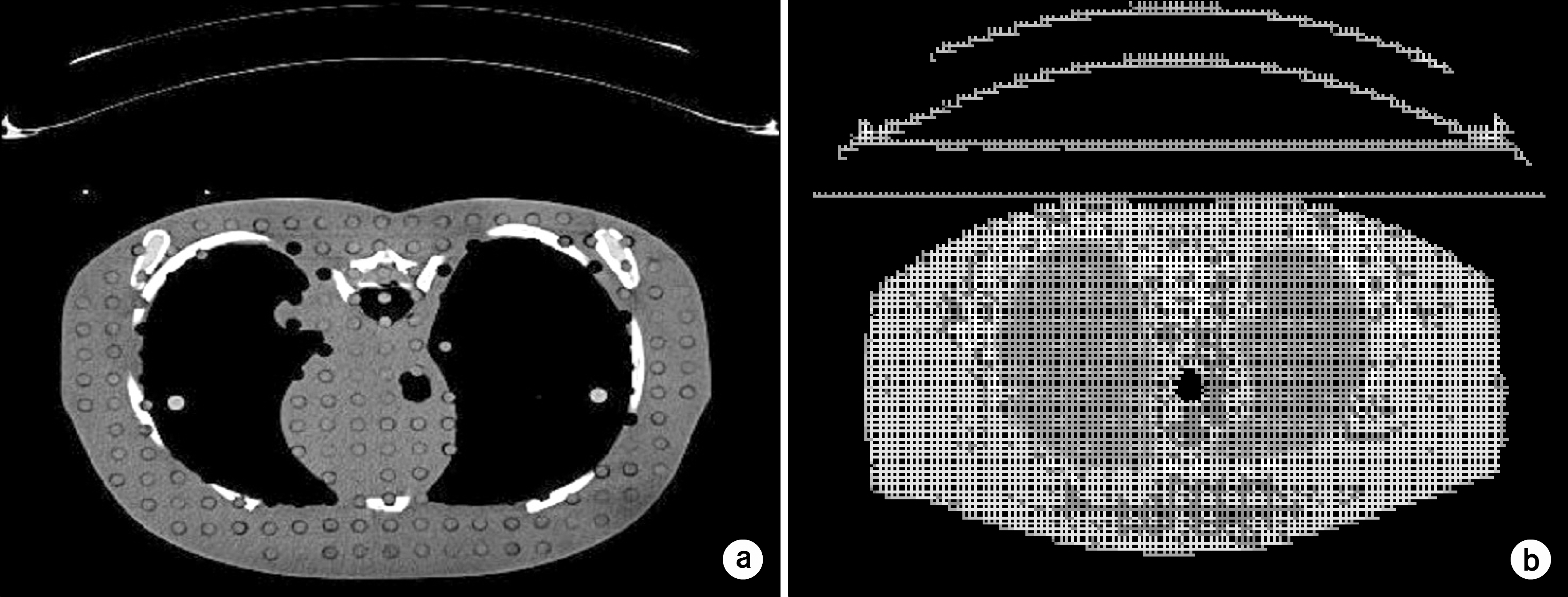
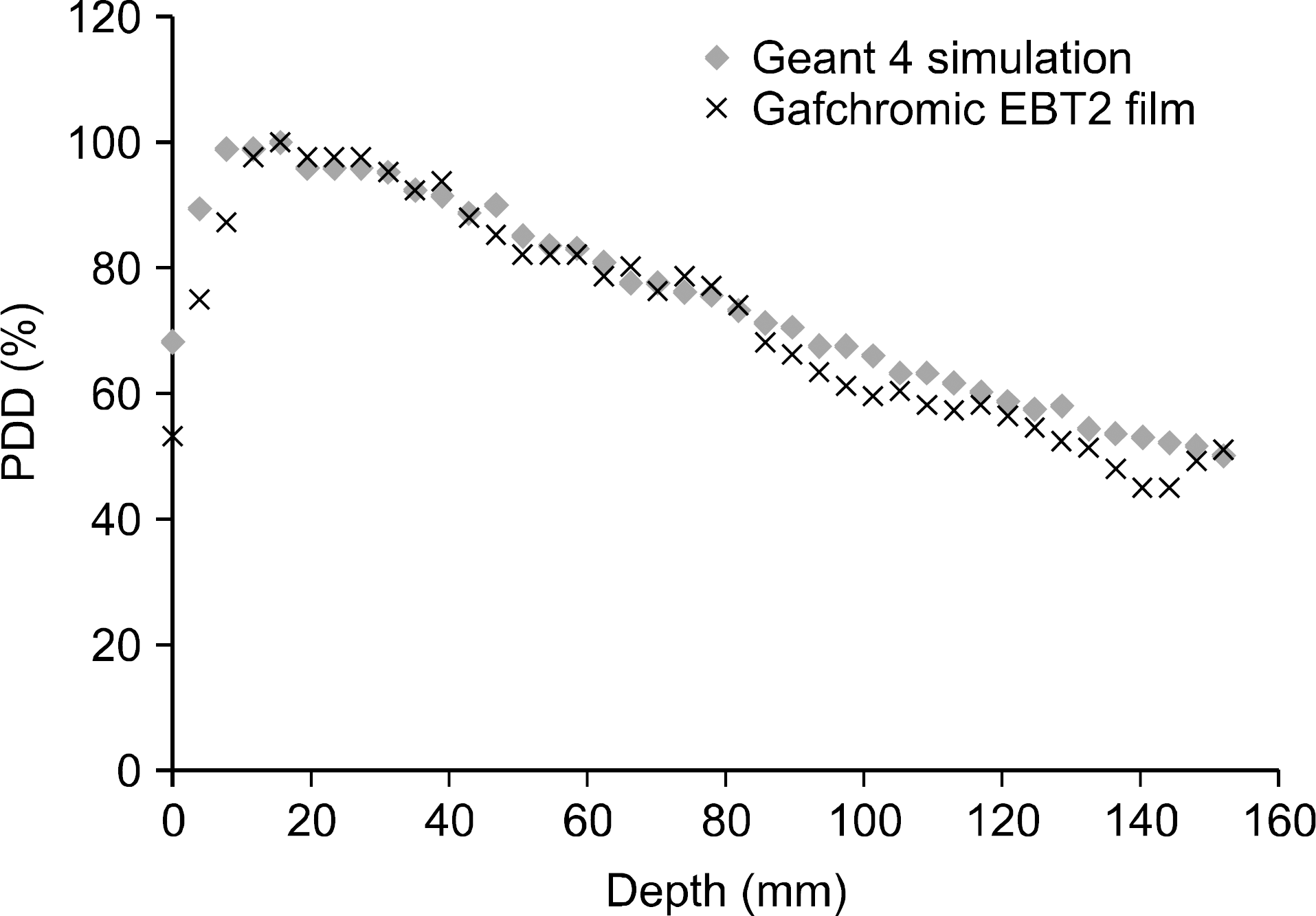
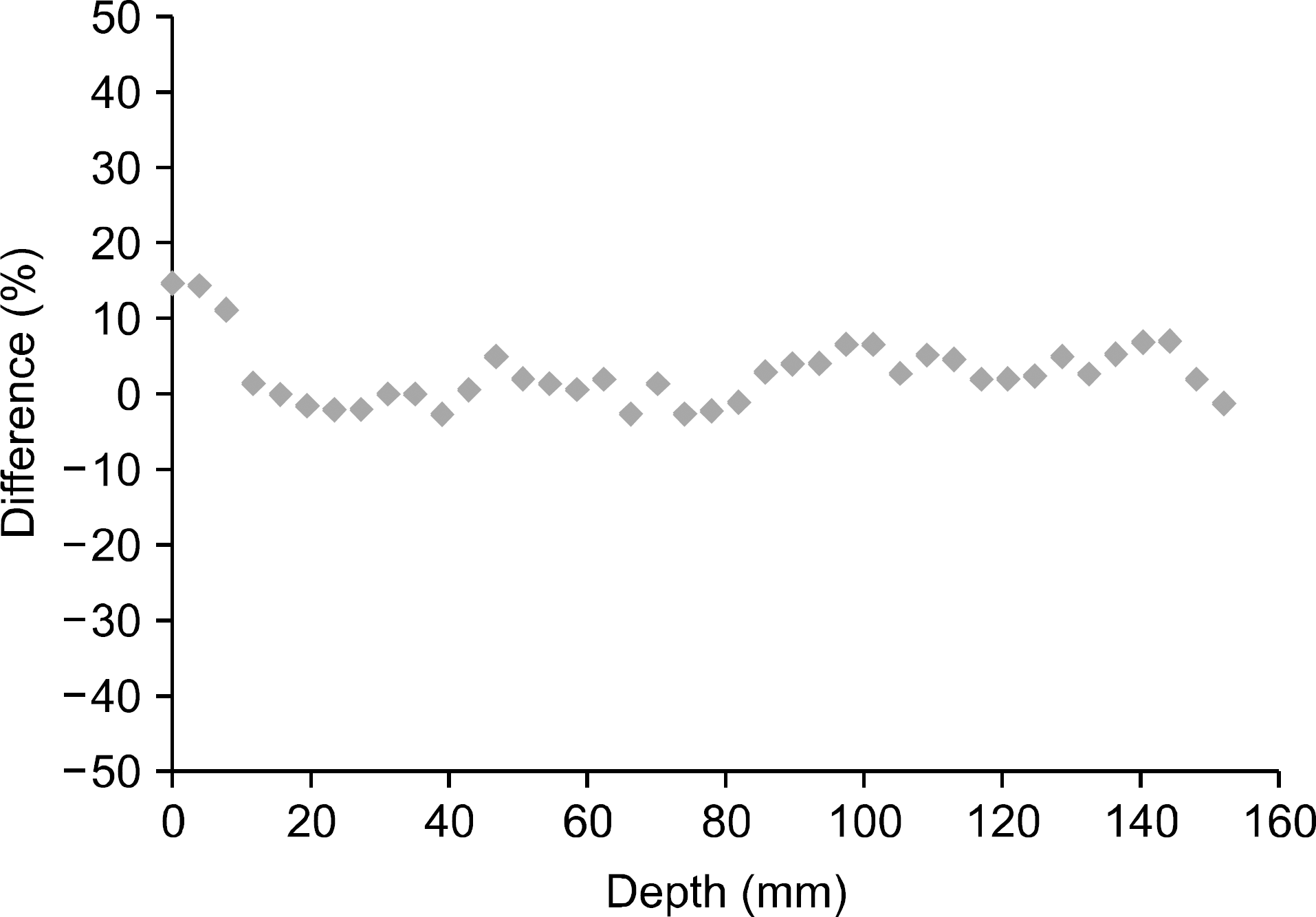
Monte Carlo method has been known as the most accurate method for calculating absorbed dose in the human body, and an anthropomorphic phantom has been mainly used as a method of simulating internal organs for using such a calculation method. However, various efforts are made to extract data on several internal organs in the human body directly from CT DICOM files in recent Monte Carlo calculation using Geant4 code and to use by converting them into the geometry necessary for simulation. Such a function makes it possible to calculate the internal absorbed dose accurately while duplicating the actual human anatomical structure. Thus, this study calculated the absorbed dose in the human body by using Geant4 associating with DICOM files, and aimed to confirm the usefulness by compare the result with the measured dose using a Gafchromic EBT2 film. This study compared the dose calculated using simulation and the measured dose in beam central axis using the EBT2 film. The results showed that the range of difference was an average of 3.75% except for a build-up region, in which the dose rapidly changed from skin surface to the depth of maximum dose. In addition, this study made it easy to confirm the target absorbed dose by internal organ and organ through the output of the calculated value of dose by CT slice and the dose value of each voxel in each slice. Thus, the method that outputs dose value by slice and voxel through the use of CT DICOM, which is actual image data of human body, instead of the anthropomorphic phantom enables accurate dose calculations of various regions. Therefore, it is considered that it will be useful for dose calculation of radiotherapy planning system in the future. Moreover, it is applicable for currently-used several energy ranges in current use, so it is considered that it will be effectively used in order to check the radiation absorbed dose in the human body.
References
1. 강상구, 안성환, 김종일: 몬테카를로 방법에 의한 6MV 선형가 속기의 광자 흡수선량 분포 평가에 관한 연구. 방사선기술과 학. 34(1):43–49. 2011.
2. Agostinelli S, Allison J, Amoko K, et al. GEANT4-a simulation toolkit. NIMPRA. 506(3):250–303. 2003.
3. Pia MG. The Geant4 Toolkit: simulation capabilities and application results. NPB (Proc. Suppl). 125:60–68. 2003.
4. Agostinelli S, Allison J, Amoko K, et al. Geant4 developments and applications. TNS. 53(1):270–278. 2006.
5. http://medical.nema.orgDICOMHomepage
6. Kimura A, Tanaka S, Aso T, et al. DICOM interface and visualization tool for geant4-based dose calculation. Nuclear science symposium conference record, 2005. IEEE. 2:981–984. 2005.

7. Devic S, Seuntjens J, Sham E, et al. Precise radiochromic film dosimetry using a flatbed scanner. Med Phys. 32:2245–2253. 2005.
8. Fuss M, Sturtewagen E, De Wagter C, Georg D. Dosimetric characterization of GafChromic EBT film and its implication on film dosimetry quality assurance. Phys Med Biol. 21:4211–4225. 2007.

9. Fiandra C, Ricardi U, Ragona R, et al. Clinical use of EBT model Gafchromic film in radiotherapy. Med Phys. 33:4314–4319. 2006.

10. Wilcox EE, Daskalov GM, Pavlonnis G 3rd, Shumway R, Kaplan B, VanRooy E. Dosimetric verification of intensity modulated radiation therapy of 172 patients treated for various disease sites: comparison of EBT film dosimetry, ion chamber measurements, and independent MU calculations. Med Dosim. 33:303–309. 2008.

11. Khan FM. The Physics of Radiation Therapy. 2nd ed., Williams & Wilkims, Maryland, USA (. 1984. ), pp.323–332.
12. Dong-Hyun Cho, Kyoung-Won Jang, Wook-Jae Yoo, et al. Measurement of Skin Dose and Percentage Depth Does in Build-up Region Using a Fiber-optic Dosimeter. KJOP. 21(1):16–20. 2010.
13. 장은성, 이철수: GafChromic EBT 필름을 이용한 뇌정위방사선 치료의 선량분석 가능성 평가. 대한방사선치료학회. 19(1):27–33. 2007.
Table 1.
File change with progression of simulation.
Table 2.
The calculated dose distribution table by voxe coordinate of the center slice data.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download