Abstract
As image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) has been commonly used for more accurate patient setup and monitoring tumor movement during radiation therapy, the necessity for management of imaging dose is increased. However, it has not been an interest issue to radiation therapy communities because the imaging dose is much lower than the therapeutic dose. However, since the cumulative dose from 4DCT and repeated imaging for daily setup verificationin would not be ignorable, appropriate dose management based on ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle is required. In this study, we aimed that (1) survey on imaging equipments and modalities used for IGRT, (2) estimation of IGRT imaging dose depending on treatment types and equipments, (3) collecting data of effective dose on treatment sites from each equipment and imaging protocol, and thus finally provide guideline for imaging dose reduction and optimization.
Go to : 
References
1. Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography: an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med. 357(22):2277–2284. 2007.
2. Berrington de González A, Mahesh M, Kim KP, et al. Projected cancer risks from computed tomographic scans per – formed in the United State s in 2007. Arch Intern Med. 169(22):2071–2077. 2009.
3. Koenig TR, Wolff D, Mettler FA, Wagner LK. Skin injuries from fluoroscopically guided procedures: part 1, characteristics of radiation injury. A J R Am J Roe ntgenol. 177:3–20. 2001.
4. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm185898.htm,SafetyInvestigationofCTBrainPerfusionScans:Update11/9/2010
5. http://www.imagegently.org
6. http://www.imagewisely.org
7. Aird EGA. Second cancer risk, concomitant exposures, and IRMER2000. Br J Radiol. 77:983–985. 2004.

9. Followill D, Geis P, Boyer A. Estimates of whole-body dose equivalent produced by beam intensitymodulated conformal therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 38:667–672. 1997.
10. Hall EJ, Wuu CS. Radiation-induced second cancers: The impact of 3D-CRT and IMRT. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 56:83–88. 2003.

11. Brenner D. Induced cancers after prostate-cancer radiotherapy: No cause for concern? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 65:637–639. 2006.
12. BEIR: Committee on the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiations BEIR V, National, Research Council, Health effects of exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation: BEIR V National Academy Press. Washington, DC (. 1990.
13. Brenner DJ. Estimating cancer risks from pediatric CT: Going from the qualitative to the quantitative. Pediatr Radiol. 32:228–231. 2002.

14. NCRP: Medical x-ray, electron beam and gamma-ray protection for energies up to 50 MeV Equipment design, performance and use. NCRP Report 102 (. 1989.
15. Tremains MR, Georgiadis GM, Dennis MJ. Radiation exposure with use of the inverted C-arm technique in upper-extremity surgery. J Bone Jt Surg. 83A:674–768. 2001.
16. Chu RYL, Fisher J, Archer BR, et al. Standardized methods for measuring diagnostic x-ray exposures. AAPM Report 31 (. 1990.
18. Jacobi W. The concept of effective dose: A proposal for the combination of organ doses. J Radiat Environ Biophys. 12:101–109. 1975.
19. Perkins CL, Fox T, Elder E, Kooby DA, Staley III CA, Landry J. Image-guided radiation therapy IGRT in gastrointestinal tumors. JOP: Journal of the Pancreas Online. 7:372–381. 2006.
20. Nagel HD. Radiation Exposure in Computed Tomography. CTB Publications, Hamburg, Germany (. 2002.
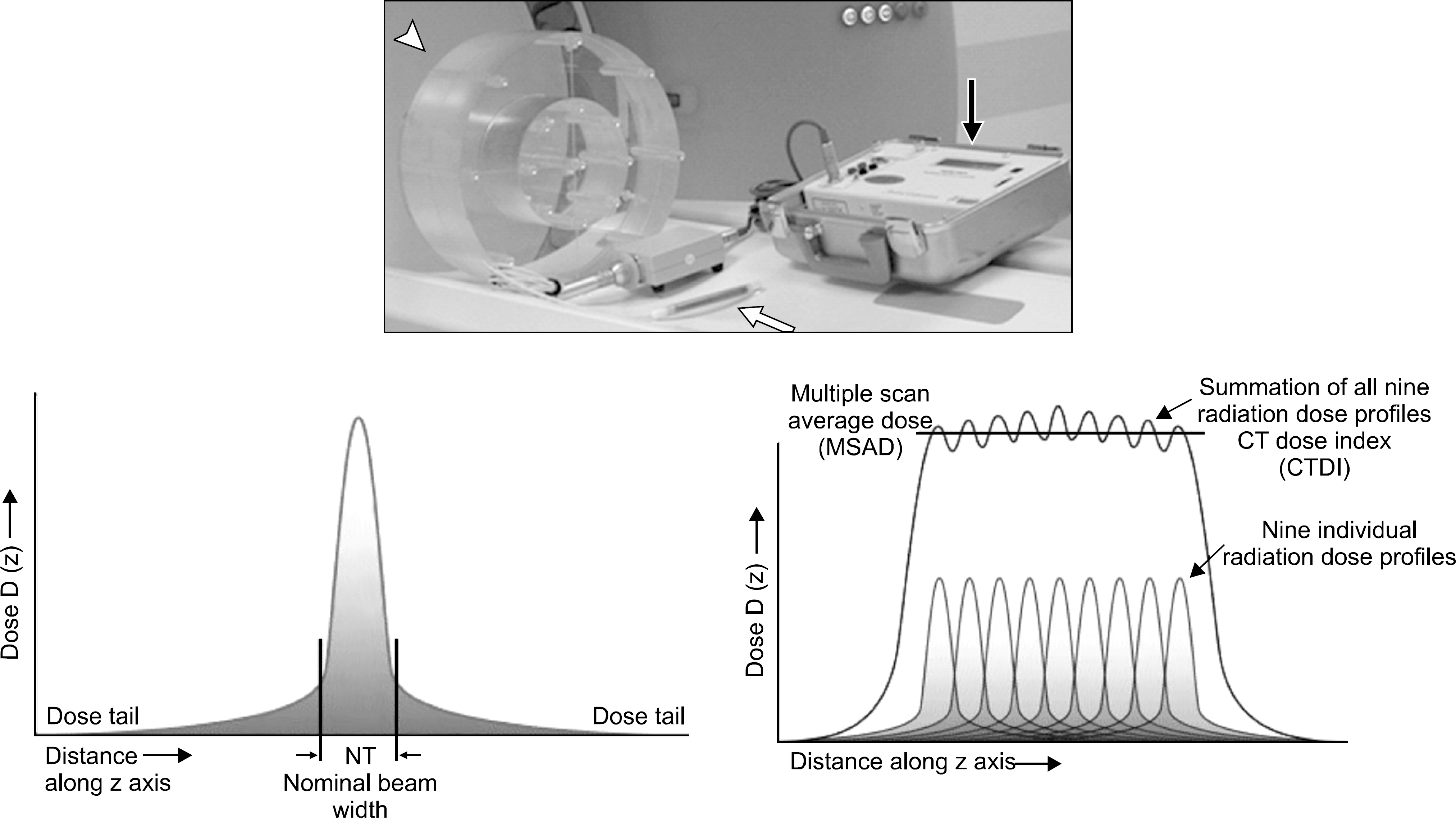
21. McCollough C, Leng S, Yu L, Cody D, Boone J, Gray M. CT dose index and patient dose: they are not the same thing. Radiology. 259(2):311–316. 2011.
22. 보건복지부, 방사선안전관리시리즈 No.19: CT 엑스선검사에서 의 환자선량 권고량 가이드라인. 2009.
23. Low DA, Nystrom M, Kalinin E, et al. A method for the reconstruction of four-dimensional synchronized CT scans acquired during free breathing. Med Phys. 30:1254–1263. 2003.

24. Islam MK, Purdie TG, Norrlinger BD, et al. Patient dose from kilovoltage cone beam computed tomography imaging in radiation therapy. Med Phys. 33:1573–1582. 2006.

25. Amer A, Marchant T, Sykes J, et al. Doses from cone beam CT integrated to a radiotherapy treatment machine. United Kingdom Radiation Oncology Conference (. 2005.
26. Song W, Kamath S, Ozawa S, et al. A dose comparison study between XVI and OBI CBCT systems. Med Phys. 35(2):480–486. 2008.
27. Ding G, Munro P, Pawlowski J, et al. Reducing radiation exposure to patients from kV-CBCT imaging. Radiother Oncol. 97:585–592. 2010.

28. Chen J, Morin O, Aubin M, Bucci MK, Chuang CF, Pouliot J. Dose-guided radiation therapy with megavoltage cone-beam CT. Br J Radiol. 79:S87–S98. 2006.

29. Winston JP, Gilley DB. Patient Exposure and Dose Guide 2003, Conference of Radiation Control Program Directors. CRCPD publication E-03–2 (. 2003.
30. http://www.cyberknife.com.tr/images/yayin/Imaging_Whitepaper.pdf,EstimationoftheimagingdosefortheCyberkniferoboticradiosurgerysystem
31. Shrimpton PC, Hillier MC, Lewis MA, Dunn M. National survey of doses from CT in the UK: 2003. Br J Radiol. 79:968–980. 2006.

32. Huda W, Ogden MK, Khorasani M. Converting dose-length product to effective dose at CT. Radiology. 248:995–1003. 2008.

33. Winslow JF, Hyer DE, Fisher RF, Tien CJ, Hintenlang DE. Construction of anthropomorphic phantoms for use in dosimetry studies. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 10:195–204. 2009.

34. Hyer DE, Fisher RF, Hintenlang DE. Characterization of a water-equivalent fiberoptic coupled dosimeter for use in diagnostic radiology. Med Phys. 36:1711–1716. 2009.

35. Hyer DE, Serago CF, Kim S, Li JG, Hintenlang DE. An organ and effective dose study of XVI and OBI cone-beam CT systems. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 11:181–197. 2010.

36. Hyera DE, Hintenlang DE. Estimation of organ doses from kilovoltage cone-beam CT imaging used during radiotherapy patient position verification. Med Phys. 37:4620–4626. 2010.
37. Waddington SP, McKensie AL. Assessment of effective dose from concomitant exposures required in verification of the target volume in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 77:557–561. 2004.

38. CEP10071. X-ray tomographic image guided radiotherapy systems. Purchasing and Supply Agency (. 2010.
39. Shah AP, Langen KM, Ruchala KJ, Cox A, Kupelian PA, Meeks SK. Patient dose from megavoltage computed tomography imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 70:1579–1587. 2008.

40. Morin O, Gillis A, Descovich M, et al. Patient dose considerations for routine megavoltage cone-beam CT imaging. Med Phys. 34:1819–1827. 2007.

41. Siewerdsen JH, Jaffray DA. Cone-beam computed tomography with a flat-panel imager: Magnitude and effects of x-ray scatter. Med Phys. 28:220–231. 2001.

42. Wong JW, Sharpe M, Jaffray D, et al. The use of active breathing control ABC to reduce margin for breathing motion. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 44:911–919. 1999.

43. Kubo HD, Hill BC. Respiration gated radiotherapy treatment: A technical study. Phys Med Biol. 41:83–91. 1996.

44. Schweikard A, Glosser G, Bodduluri M, Murphy M, Adler JR. R obotic motion compensation for respiratory movement during radiosurgery. Comput Aided Surg. 5:263–277. 2000.
45. Siewerdsen JH, Moseley DJ, Burch S, et al. Volume CT with a f l a t -pa ne l detector on a mobile, isoce ntric C -ar m: Pre-clinical investigation in guidance of minimally invasive surgery. Med Phys. 32:241–254. 2005.
46. Murphy MJ, Chang SD, Gibbs IC. Patte rns of pa tient movement during fra meless imageguided radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Onc ol Biol P hys. 55:1400–l408. 2003.
Go to : 
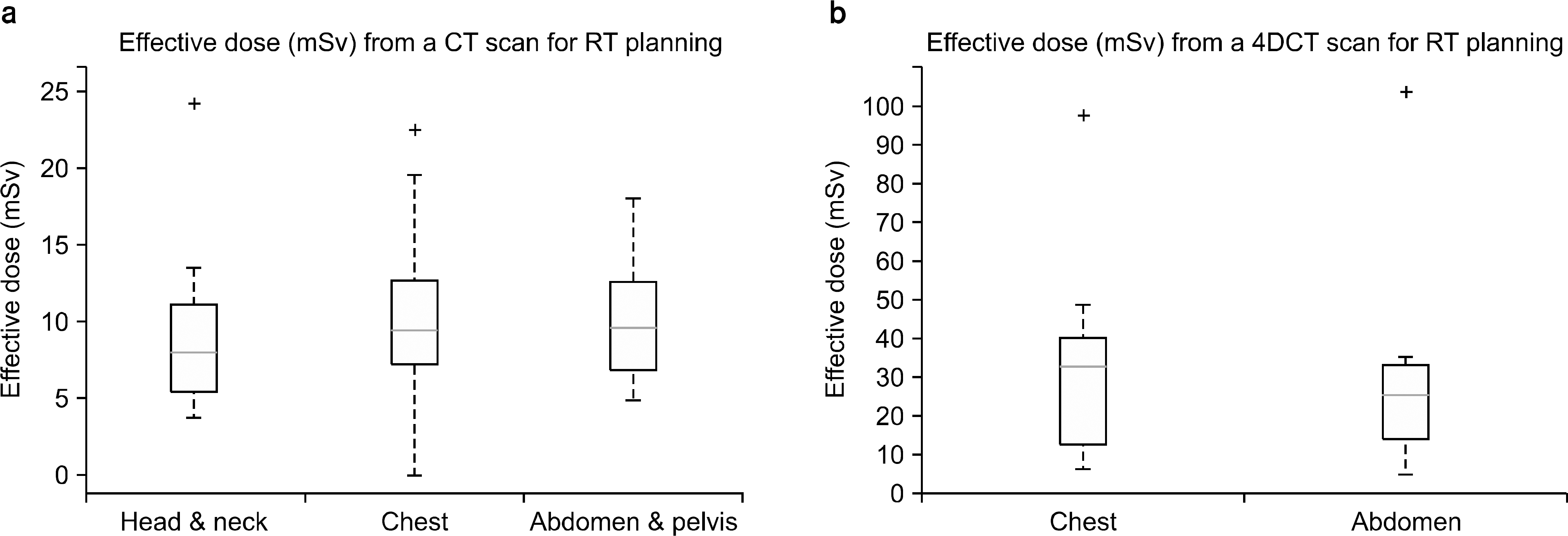
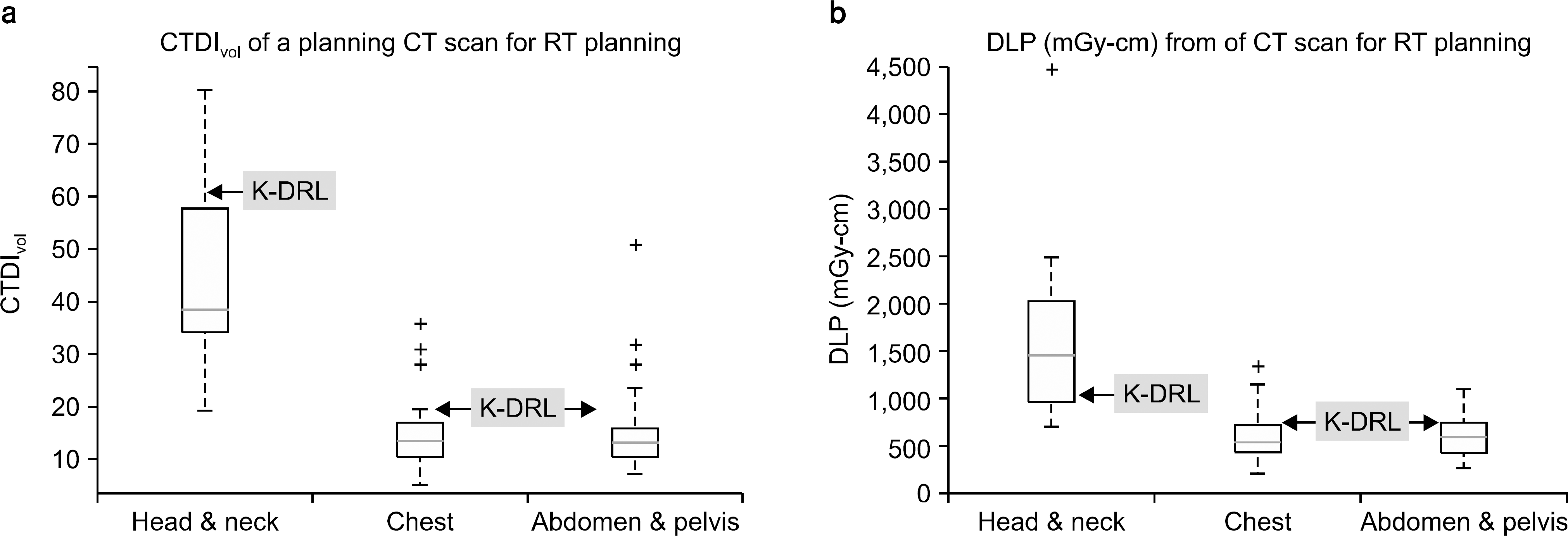 | Fig. 6.치료계획용 CT의 임상선량 현황 boxplot. CTDIvol (a) 및 DLP (b). 2009년 CT 엑스선검사에 환자선량 권고량 식약청 가이드라 인(K-DRL)과 비교하였음. |
Table 1.
CT 엑스선검사에서의 환자선량 권고량과 외국 환자선량 권고량과의 비교(DLP).
Table 2.
국내 영상유도 방사선치료용 영상장비 보유 현황.
Table 3.
치료 부위별, 장비별 영상유도 방사선 치료시행 현황.
Table 4.
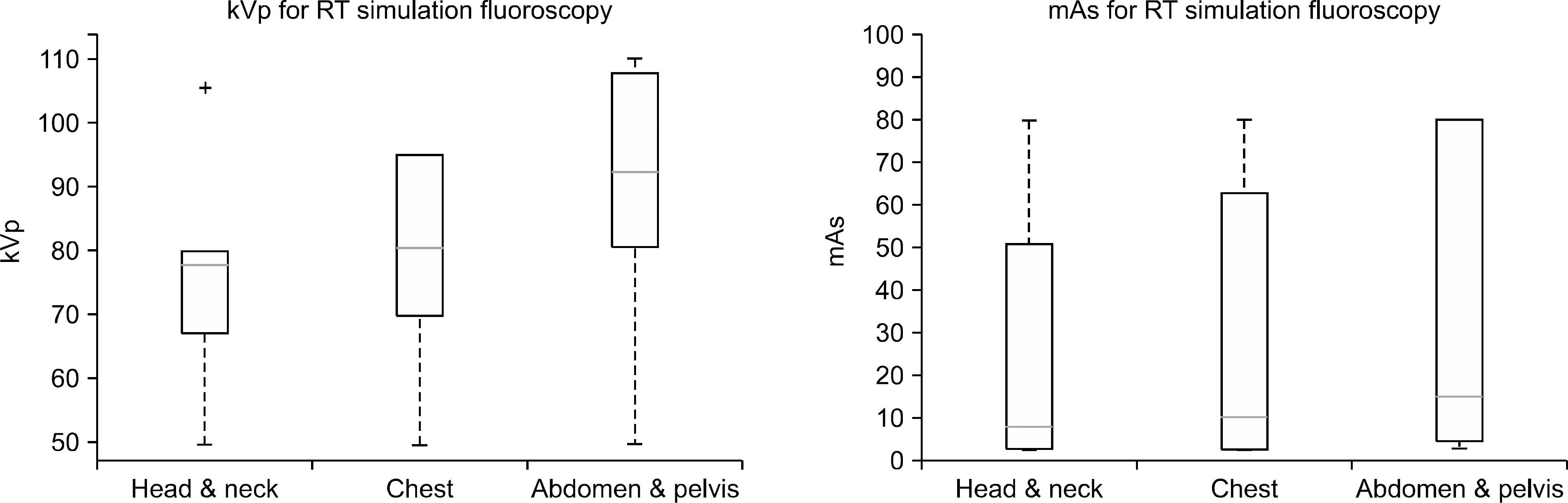
치료계획용 투시장치의 부위별 임상 촬영조건 현황.
Table 5.
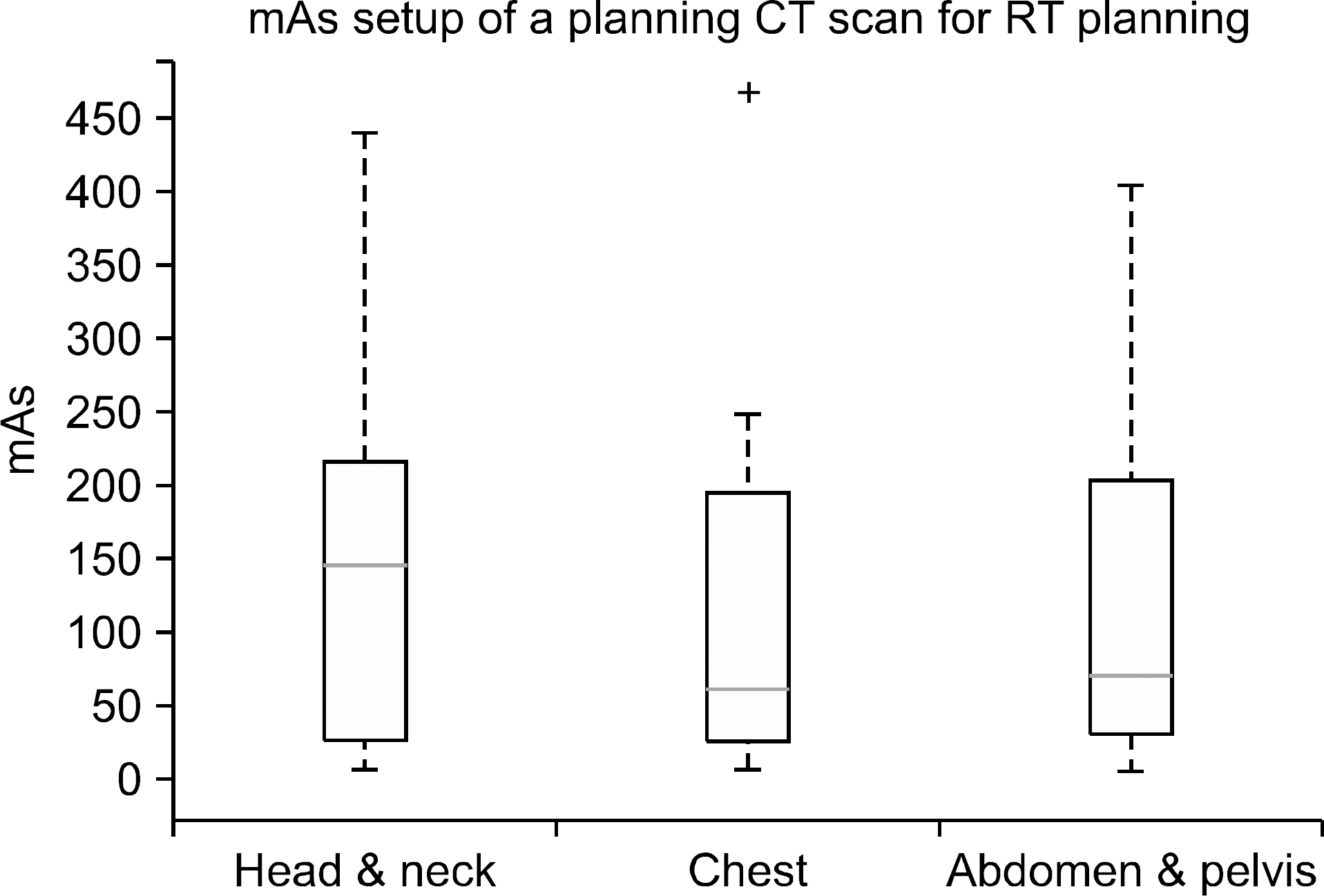
치료계획용 CT 임상 관전류 촬영조건 분포 현황.
| Sites | Avg. | SD | 25th percentiles | 75th percentiles | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HN | 157.4 | 140.1 | 30.0 | 220.0 | 10.0 | 440.0 |
| Chest | 121.1 | 125.9 | 30.0 | 200.0 | 10.0 | 469.0 |
| Pelvis | 121.4 | 114.7 | 40.0 | 205.0 | 10.0 | 407.0 |
Table 6.
치료계획용 kV 투시장치의 임상 촬영 조건별 일반촬영 선량.
| Radiograph mode | ESDa) | Eff doseb) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kVp | mA | ms | mAs | mGy | mSv | ||
| Head | AP | 80 | 100 | 400 | 40 | 2.90 | 0.015 |
| & neck | LAT | 0.019 | |||||
| Chest | AP | 80 | 100 | 400 | 40 | 2.90 | 0.589 |
| LAT | 0.121 | ||||||
| Pelvis | AP | 90 | 200 | 400 | 80 | 7.33 | 0.398 |
| LAT | 0.0354 | ||||||
Table 7.
진단 방사선 검사에서의 성인 환자의 권고 선량(IAEA BSS No.115).
| 부위 | 조사방향 | ESD/radiograph (mGy) |
|---|---|---|
| Head & neck | PA | 5 |
| LAT | 3 | |
| Chest | PA | 0.4 |
| LAT | 1.5 | |
| Abdomen/Pelvis | AP | 10 |
| 투시촬영 | Normal | 25 mGy/min |
| High level | 100 mGy/min (IVR) |
Table 8.
치료계획용 kV 투시장치의 임상 촬영 조건별 투시촬영 선량율.
| Fluoroscopy mode (continuous) | ESD/min | Eff dose ratea) (mSv/min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kVp | mA | mA-min | mGy/min | (AP/LAT) | |
| Head & neck | 70 | 3 | 180 | 8.0 | 0.337 (0.148/0.189) |
| Chest | 70 | 5 | 300 | 13.5 | 5.12 (3.87/1.25) |
| Pelvis | 90 | 15 | 900 | 69.0 | 5.10 (4.68/0.417) |
Table 9.
치료확인용 kV 투시장치(Varian OBI)의 임상 촬영 조건별 일반촬영 선량.
Table 10.
치료확인용 kV 투시장치(Elekta XVI)의 임상 촬영 조건별 일반촬영 선량.
Table 11.
치료확인용 kV 투시장치(Cyberknife)의 임상 촬영 조건별 일반촬영 선량.
| Site | kV | mA | ms | mAs | ESD per image (mGy) | ED (mSv) per image pair |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head | 110 | 100 | 100 | 10 | 0.50 | 0.009 |
| Chest | 110 | 150 | 100 | 15 | 0.53 | 0.054 |
| Prostate | 120 | 150 | 100 | 15 | 0.64 | 0.07 |
Table 12.
Cyberknife 조건별 선량 참고문헌30) 비교치.
| Anatomy | kVp | mAs | ESD/image (mGy) | A (cm2) | F (mSv/mGy -cm2×10−5) | ED (mSv) per image pair |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head | 115 | 10 | 0.22 | 225 | 4.5 | 0.0045 |
| Chest | 120 | 11.5 | 0.28 | 225 | 20.5 | 0.0258 |
| Pelvis | 124 | 34.5 | 0.91 | 225 | 19.9 | 0.0815 |
Table 13.
치료확인용 kV 투시장치(Exactrac)의 임상 촬영 조건별 일반촬영 선량.
| Site | kV | mA | ms | mAs | s ESD per image (mGy) | ED (mSv) per image pair |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head & neck | 100 | 80 | 80 | 6.4 | 0.39 | 0.011 |
| Chest | 120 | 160 | 160 | 25.6 | 0.90 | 0.214 |
| Abdomen | 120 | 160 | 130 | 20.8 | 0.77 | 0.058 |
Table 14.
치료확인용 kV 투시장치 (Varian OBI, Elekta XVI)의 투시촬영 선량율.
| kV | mA | ms | mAs | Frame | mGy/mAs-frame- | mGy/min | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Varian | AP | 74 | 50 | 50 | 2.5 | 90 | 0.02 | 4.5 |
| OBI | ||||||||
| Elekta | AP | 120 | 25 | 40 | 1 | 150 | 0.12 | 18 |
| XVI |
Table 15.
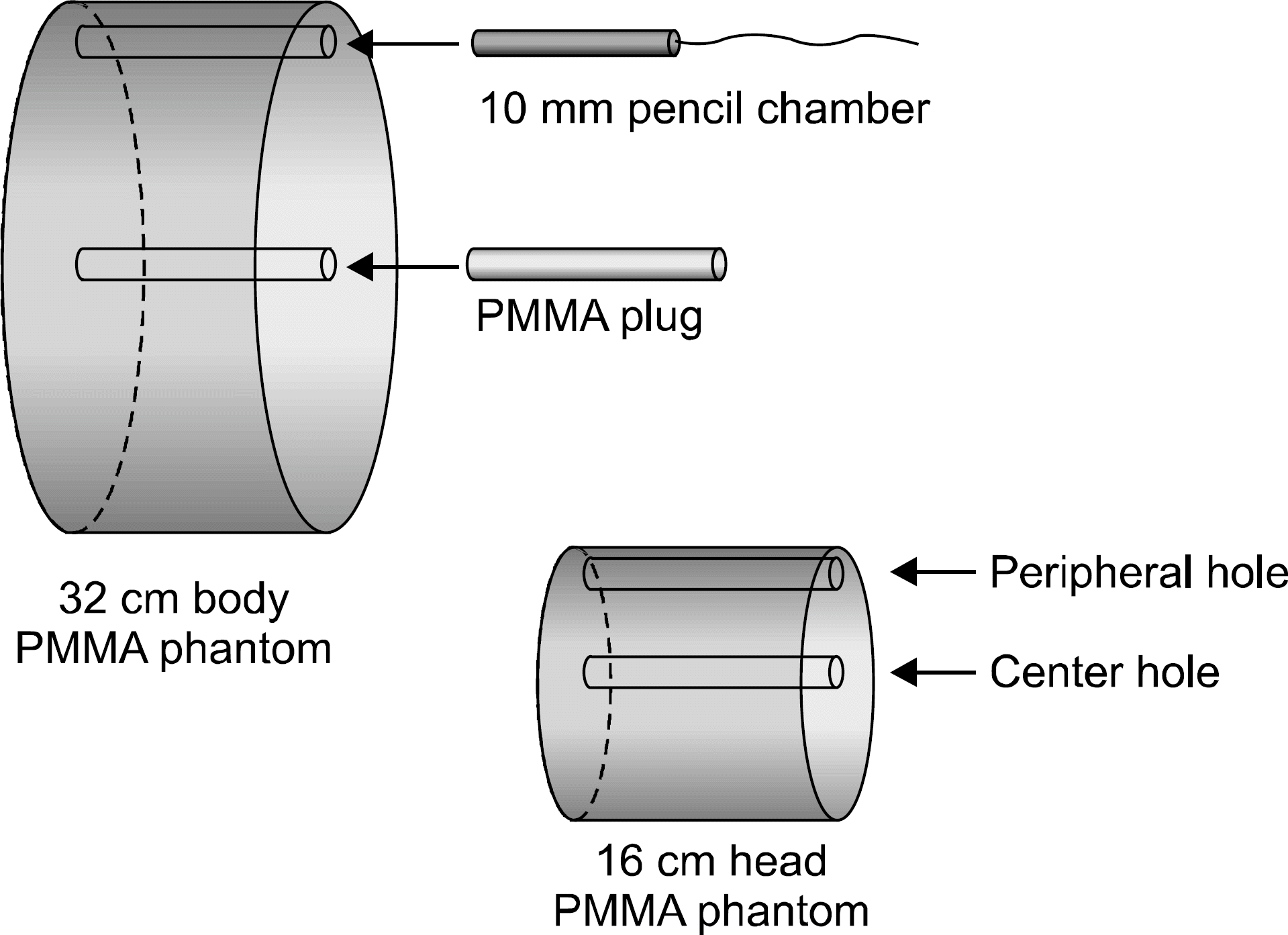
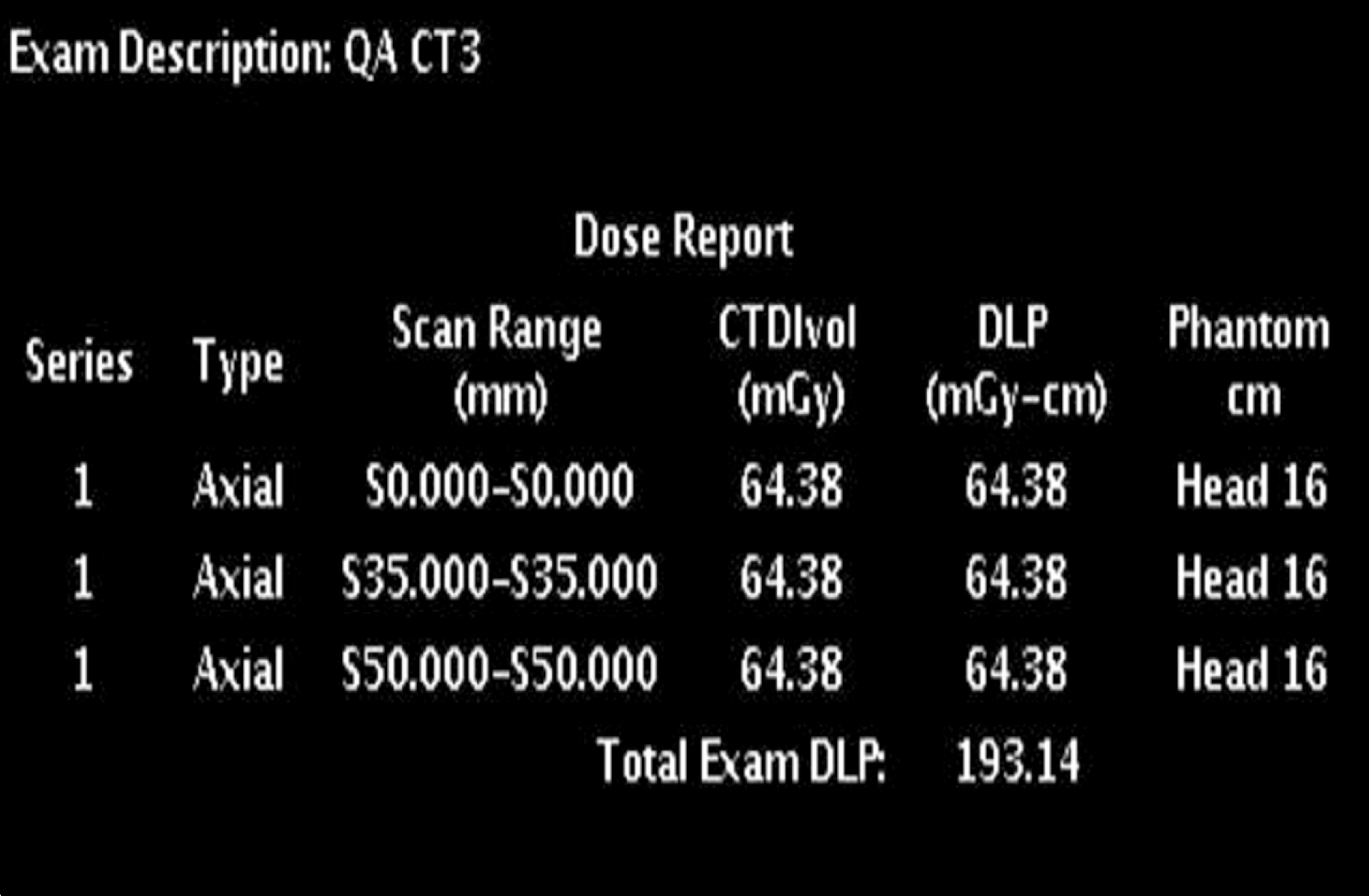
치료계획용 kV CT (GE Lightspeed)의 임상 촬영 조건별 CTDI 측정치.
| kVp | mA | Rot time (sec) | CTDIw | CTDIvol | %difference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head | 2.5×4i | 120 | 200 | 1 | 30 | 36.58 | 122% |
| Body | 2.5×8i | 120 | 200 | 1 | 13.2 | 14.8 | 112% |
Table 17.
치료확인용 kV CBCT의 임상 촬영 조건별 CTDI 측정치.35)
| Site | Elekta synergya) | Varian OBIa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head standard | Chest | Pelvis | Head standard | Chest | Pelvis | |
| kV Collimation | S20 | M20 | M10 | |||
| kV filter | F0 | F1 | F1 | Full bowtie | Half bowtie | Half bowtie |
| kVp | 100 | 120 | 120 | 100 | 110 | 125 |
| mA | 10 | 40 | 64 | 20 | 20 | 80 |
| ms/projection | 10 | 40 | 40 | 20 | 20 | 13 |
| No of projections | 361 | 643 | 643 | 360 | 655 | 655 |
| Total mAs | 36.1 | 1,028.8 | 1,646.1 | 145 | 262 | 680 |
| Measured HVL (mm Al) | 5.9 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 5.4 | 5.7 | 6.4 |
| Acquisition angle | 350∼190 cw | 273∼269 cw | 273∼269 cw | 88∼292 cw/ccw | 88∼92 cw/ccw | 88∼92 cw/ccw |
| Acquisition time (s) | 70 | 120 | 120 | 30 | 60 | 60 |
| Axial field of view (cm) | 27 | 41 | 41 | 25 | 45 | 45 |
| Long field of view (cm) | 26 | 26 | 12.5 | 18 | 16 | 16 |
| CBDIw36) (mGy) | 0.98 | 16.62 | 24.13 | 4.6 | 5.8 | 20.28 |
| CBDIw (mGy)b) | 0.94 | 21.45 | 22.87 | 4.8 | 5.91 | 20.12 |
| Effective dose (mSv)b) | 0.13 | 9.48 | 5.43 | 0.47 | 1.61 | 6.11 |
| by ED/DLP conv29) | ||||||
| Effective dose (mSv)20) | 0.04 | 7.15 | 3.73 | 0.12 | 1.82 | 4.34 |
Table 18.
치료확인용 MV 투시의 임상 촬영 조건별 선량 평가치.
| Head & neck | Chest | Pelvis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avg dose (mGy) | 28 | 25 | 30 |
| Eff dose (mSv)a) | 2.8 | 5.1 | 5.9 |
| Conv factor (mSv/MU)37) | 0.12 | 2.15 | 0.33 |
| Eff dose (mSv) per 2MUb) | 0.5 | 8.6 | 1.35 |
Table 19.
치료확인용 kV CBCT 부위별 선량 평가치.
| Scan Mode | Head | scan | Chest | scan | Pelvis | scan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | Oral mucosa | Parotid | Lung | Heart | Bladder | Rectum |
| Varian Dose (mGy) | 3.27 | 7.23 | 10.38 | 9.61 | 27.01 | 24.91 |
| CBCT ImPACTa) | 3.36 | 2.94 | 5.8 | 4.87 | 20.28 | 20.28 |
| %difference | 3% | –59% | –44% | –49% | –25% | –19% |
| Dose (mGy) Elekta | 0.43 | 1.05 | 25.8 | 24.82 | 16.52 | 15.56 |
| ImPACTa) CBCT | 0.77 | 0.8 | 19.3 | 14.65 | 19.56 | 19.56 |
| %difference | 79% | –24% | –25% | –41% | 18% | 26% |
Table 20.
치료확인용 MVCT 부위별 선량 평가치.
| Site | Head & neck | Chest | Pelvis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured organs | Oral mucosa | Parotid | Lung | Heart | Bladder | Rectum |
| 4.8 | 4.95 | 4.57 | 4.6 | 4.2 | 4.1 | |
| Average dose | 4.88 | 4.59 | 4.15 | |||
| (mGy)a) | ||||||
| DLP (25 cmscan-length) | 121.88 | 114.63 | 103.75 | |||
| ED/DLP conv. | 0.0054 | 0.017 | 0.019 | |||
| factor32) | ||||||
| (mSv/mGy∗cm) | ||||||
| Effective dose | 0.66 | 1.95 | 1.97 | |||
| (mSv) | ||||||
Table 21.
치료확인용 MV CBCT 부위별 선량 평가치.
Table 22.
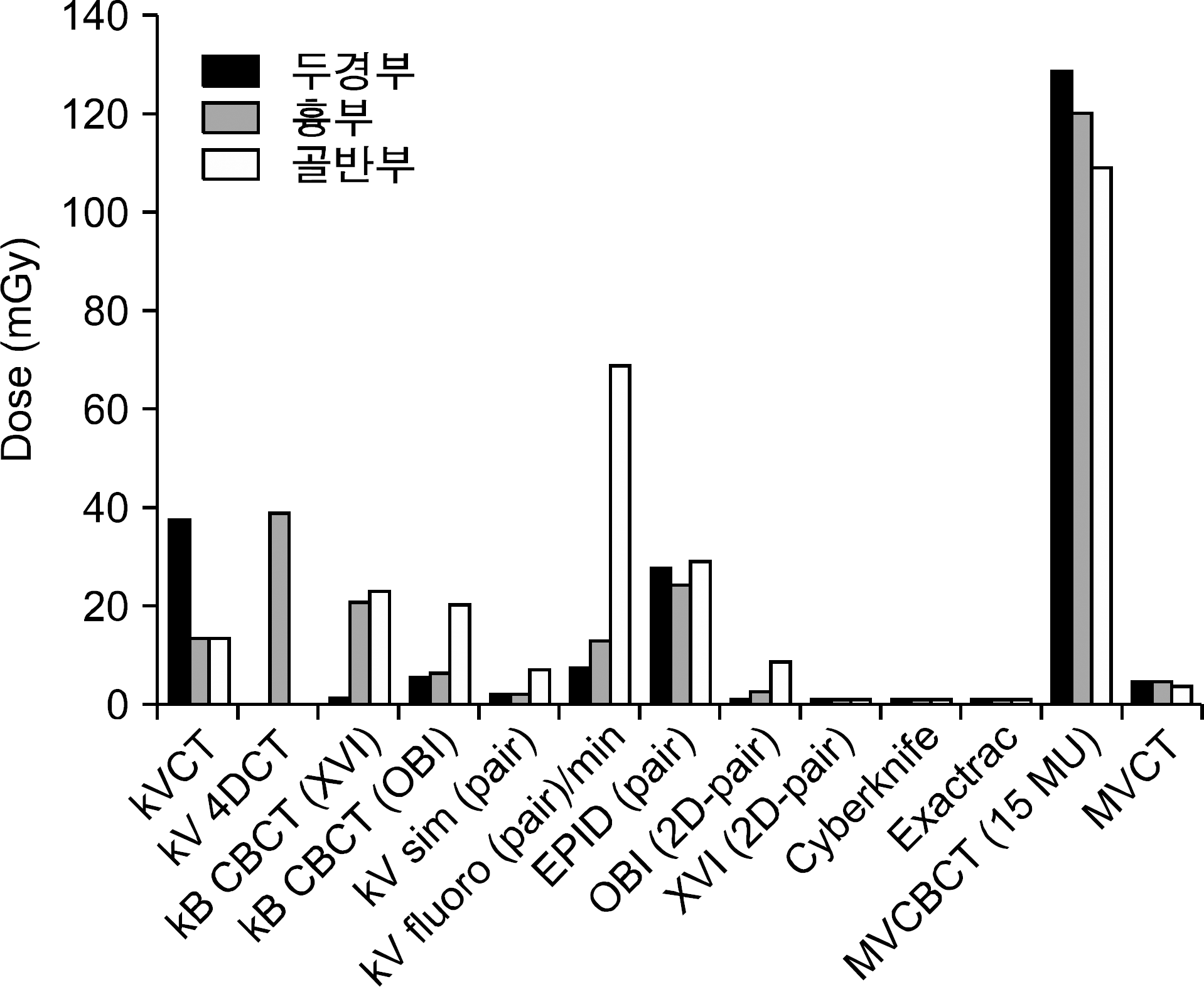
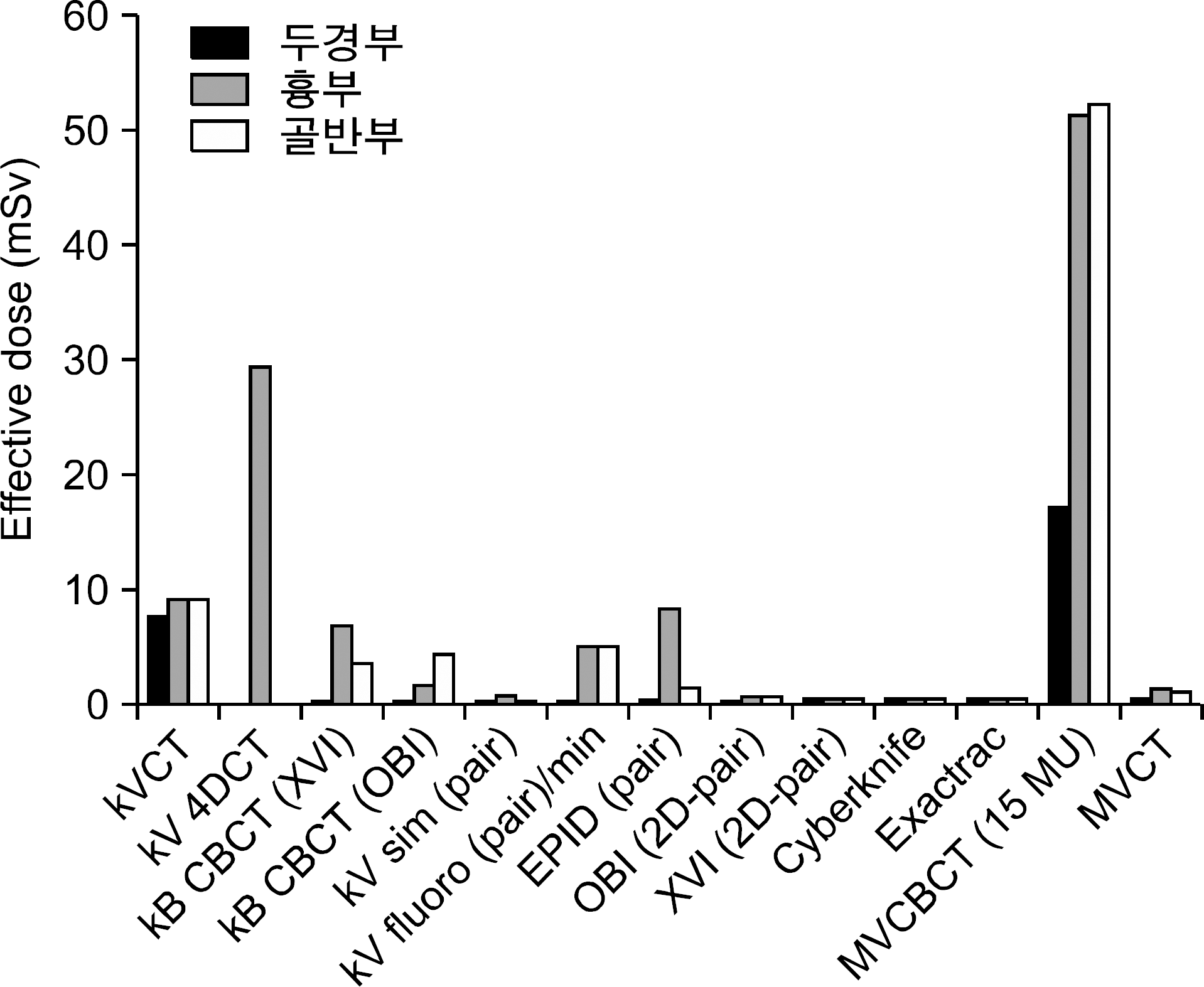
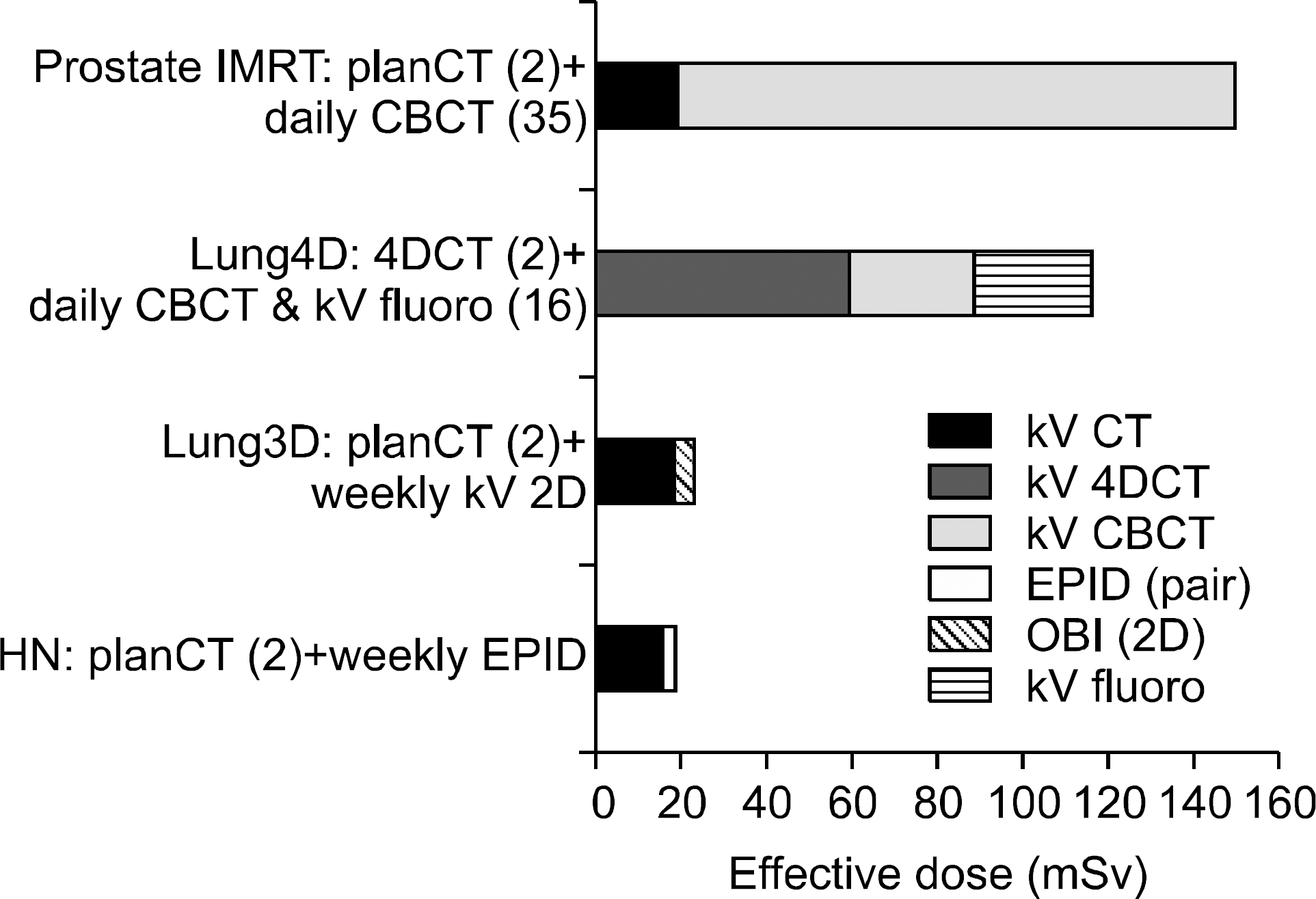
영상유도 방사선치료에 있어 영상기법별, 부위별 기준선량 권고안.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download