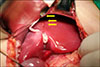
Abstract
A 6-year-old male who lived with a mother in a single-parent family was referred to the emergency room with multiple traumas. There was no specific finding on CT scan of the other hospital performed 55 days before admission. However, CT scan at the time of admission showed common bile duct (CBD) stenosis, proximal biliary dilatation and bile lake formation at the segment II and III. Endoscopic retrograde biliary drainage was performed, but the tube had slipped off spontaneously 36 days later, and follow-up CT scan showed aggravated proximal biliary dilatation above the stricture site. He underwent excision of the CBD including the stricture site, and the bile duct was reconstructed with Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy. Pathologic report of the resected specimen revealed that the evidence of trauma as a cause of bile duct stricture. While non-iatrogenic extrahepatic biliary trauma is uncommon, a level of suspicion is necessary to identify injuries to the extrahepatic bile duct. The role of the physicians who treat the abused children should encompass being suspicious for potential abdominal injury as well as identifying visible injuries.
Figures and Tables
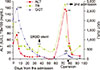
Fig. 1
Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan. (A) CT scan taken two months before admission shows no visible bile duct dilatation or bile lake in the upper abdomen. (B) CT scan taken at the admission shows stenosis at proximal common bile duct with common hepatic duct dilatation and a bile lake at S2/3 of the liver.
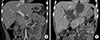
Fig. 2
Timeline plot of clinical course. CBD, common bile duct; ERBD, endoscopic retrograde biliary drainage.
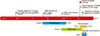
Fig. 3
The changes and trends of each liver function tests. TB, total bilirubin; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; ERBD, endoscopic retrograde biliary drainage.
References
1. National Child Protection Agency. 2015 National Children's Abuse Status Report. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Bureau of childcare policye;2016.
2. Ledbetter DJ, Hatch EI Jr, Feldman KW, Fligner CL, Tapper D. Diagnostic and surgical implications of child abuse. Arch Surg. 1988; 123:1101–1105.

4. Takamizawa S, Nozaki N, Aoyama N, Nishijima E, Muraji T. Endoscopic retrograde biliary drainage for posttraumatic intrapancreatic biliary stenosis in a child. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44:e25–e28.

5. McDonald KC. Child abuse: approach and management. Am Fam Physician. 2007; 75:221–228.
6. Kellogg ND. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect. Evaluation of suspected child physical abuse. Pediatrics. 2007; 119:1232–1241.

7. Park DH, Kim MH, Kim TN, Son HY, Lee TY, Kwon S, et al. Endoscopic treatment for suprapancreatic biliary stricture following blunt abdominal trauma. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:544–549.

8. Yoon KH, Ha HK, Kim MH, Seo DW, Kim CG, Bang SW, et al. Biliary stricture caused by blunt abdominal trauma: clinical and radiologic features in five patients. Radiology. 1998; 207:737–741.

9. Mullady DK, Carr-Locke DL. Traumatic biliary stricture. Medscape J Med. 2008; 10:114.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download