This article has been
cited by other articles in ScienceCentral.
Abstract
This study presents a case of an oral angioleiomyoma along with its clinical diagnostic approach and laboratory confirmation. The differential diagnosis, especially from angioleiomyosarcoma, is also included. A 51-year-old patient presented with a tumor-like lesion on his upper labial mucosa. The clinical examination revealed a benign lesion that was surgically removed. Histopathological and immunohistochemical examinations confirmed the diagnosis of an oral angioleiomyoma. The post-surgical period was uneventful. No recurrence had occurred after a year of follow-up surveillance. Oral angioleiomyoma is a very rarely occurring oral lesion. Clinically, it may mimic some benign lesions, including fibroma, pyogenic granuloma or minor salivary gland tumor. Surgical excision is the treatment of choice. Histological and immunohistochemical examination can confirm the diagnosis. The differential diagnosis is crucial to rule out angioleiomyosarcoma.
Keywords: Oral angioleiomyoma, Oral vascular leiomyoma, Oral leiomyoma
I. Introduction
Angioleiomyoma is a histological type of leiomyoma that very rarely occurs in the oral mucosa. Less than 1% of all leiomyomas are found in the head and neck region due to the lack of smooth muscle in this area; oral leiomyoma accounts for only 0.06% of all leiomyomas. Three histological types have been distinguished from the oral leiomyoma: solid, angioleiomyoma (angiomyoma, vascular leiomyoma) and the rare epithelioid leiomyoma
123.
Angioleiomyoma (vascular variant) accounts for up to 65% of oral leiomyomas. This prevalence may be due to the existence of a large number of smooth muscles in blood vessel walls
23.
The oral angioleiomyoma is mainly found on the labial mucosa
345 followed by the tongue
36 the buccal mucosa
57, the hard and soft palate
38910, and the mandibular trigone
7. Rarely, it appears on the gingivae
1112, the floor of the mouth, the salivary glands, the parotid, the larynx, the uvula, and the tonsil
35.
Leiomyoma is typically found in adults and only rarely occurs in children
3. More specifically, the patient age ranges from 40 to 59 years old with a mean age of 46 years
5 and a slight predilection for males
35. It rarely is seen in infants; when it occurs in this population, it is called congenital leiomyomatous epulis, which clinically mimics a congenital granular cell tumor
3.
Angioleiomyoma is a slow-growing, painless, tumor-like lesion that may or may not exhibit an ulcerated surface. Usually, it is covered by a normal-colored oral mucosa. The color may vary from pale red to bluish, depending on its vascularity
5. Clinically, it is difficult to distinguish oral leiomyoma from other tumors of mesenchymal or salivary gland origin, such as fibromas, neurofibromas, lipomas, pleiomorphic adenomas, or overgrowths, due to chronic irritation like pyogenic granuloma
35711.
The differential diagnosis for oral leiomyosarcoma is crucial for the patient. Therefore, the histological examination should confirm the clinical diagnosis and is fundamental. Additionally, an immunohistochemical examination contributes to the correct diagnosis.
II. Case Report
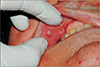
A 51-year-old patient visited our clinic regarding a swelling located on the right labial mucosa of his upper lip.(
Fig. 1) The patient reported that the lesion had developed over the past nine months. The intraoral examination revealed a well-circumscribed, red-bluish-colored overgrowth that was hard elastic in texture and painless upon palpation. The lesion was sessile, movable, approximately 8 mm in diameter, and situated on the right mucosa of the upper lip across from the first premolar. The rest of the oral cavity was evaluated as healthy. No cervical lymph nodes were detected during the extraoral examination. The medical history revealed that the patient had suffered from type 2 diabetes for the last four years and was being treated with antidiabetic medication
per os. The clinical differential diagnosis included oral fibroma, giant cell granuloma and pyogenic granuloma. Surgical excision of the lesion was chosen, and the patient's blood glucose was regulated preoperatively.
The lesion was removed
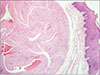
en bloc under local anesthesia. The postoperative period was uneventful. The histopathological examination revealed that the lesion was covered by stratified squamous keratinized epithelium.(
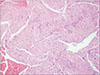
Fig. 2) Bundles of smooth muscle without mitoses, atypia or necrosis were found within it.(
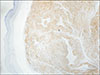
Fig. 3) Many thick-walled, congested vessels were located within these bundles of smooth muscle. No malignancy was detected. Moreover, the immunohistochemical examination revealed positivity for h-caldesmon.(
Fig. 4) The histopathological and immunohistochemical examinations confirmed the diagnosis of oral angioleiomyoma. For the year-long follow-up period after the surgical removal, no recurrence occurred.
III. Discussion
The case of a patient with an angioleiomyoma in the right upper lip region has been presented. The lesion was surgically excised, and the histopathological and immunohistochemical examinations indicated an angioleiomyoma.
The referred case is in accordance with the relative literature concerning the location (labial mucosa) sex (male) and age (middle age)
345.
The most probable histological origin of leiomyoma tends to be the smooth muscle of the tunica media of the blood vessels. Nevertheless, some authors claim that leiomyoma may derive from the remains of embryonic tissue, such as the lingual duct or circumvallate papilla of the tongue
2511. Histologically, angioleiomyoma is characterized by smooth muscle cells and numerous blood vessels that are surrounded by smooth muscle bundles, with collagen fibers exhibiting an interlacing and swirling arrangement
357.
Ossification is a very rare histopathological finding in leiomyoma that indicates tissue degeneration, which may be due to an inadequate blood supply to the lesion
13.
Of great importance concerning the histological examination is the differential diagnosis from other benign neoplasms, such as neurofibroma and neurilemmoma (Schwannoma)
357, as well as benign reactive lesions
14. For this purpose, the H&E routine stain, Masson's trichrome stain and Van Gieson's stain may be useful for detecting smooth muscle cells. Mallory's phosphotungstic acid haematoxylin is the most suitable stain because it is able to demonstrate myofibrils
35.
The immunohistochemical examination vastly contributes to an angioleiomyoma diagnosis. The positive expression of desmin along with α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) demonstrates the presence of smooth muscle cells
371115. In our case, we used the marker for smooth muscle h-caldesmon as a more specific immunohistochemical indicator for smooth muscle fibers than SMA and desmin. H-caldesmon may be used to differentiate angioleiomyoma from myopericytoma.
The use of the h-caldesmon marker for smooth muscle identification is more important than common markers like α-SMA and desmin for establishing an accurate diagnosis and avoiding a malignancy misdiagnosis.
It is crucial to differentiate an angioleiomyoma from its malignant counterpart leiomyosarcoma, which is mainly characterized by undifferentiated mesenchymal cells or fibroblast-like and myofibroblast-like cells. Immunohistochemical and molecular markers, such as proliferating cell nuclear antigen, B-cell lymphoma 2, cyclin-dependent kinase 4, p53, and mouse double minute 2 homolog, are also of great significance in identifying malignancy
15.
Surgical excision is the treatment of choice for angioleiomyoma and should lead to the minimization of recurrences and offer an excellent prognosis.
In conclusion, angioleiomyoma is the most common histologic type of oral leiomyoma, which is among the rarest of oral benign neoplasms. The histological and immunohistochemical examinations are fundamental to confirm the diagnosis and to differentiate this entity from other benign lesions as well as malignant lesions like leiomyosarcoma.









 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download