초록
Purpose
To determine whether the tumor size associtates with aggressive clinicopathologic features and tumor recurrence in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC) who had undergone thyroidectomy. Clinical significance of tumor size in patients with PTMC is still controversial.
Methods
A search of PubMed, MEDLINE, and EMBASE identified the clinical studies that examined the association of subgroups classified by tumor size (5 mm) in surgical specimens with aggressive clinicopathologic features, and clinical outcomes between 1976 and 2017.
Seven hundred twenty relevant studies were searched, and the authors selected 34 studies, including 12,134 PTMC cases. Random effects meta-analyses were performed using odds ratios (ORs) or relative risks (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
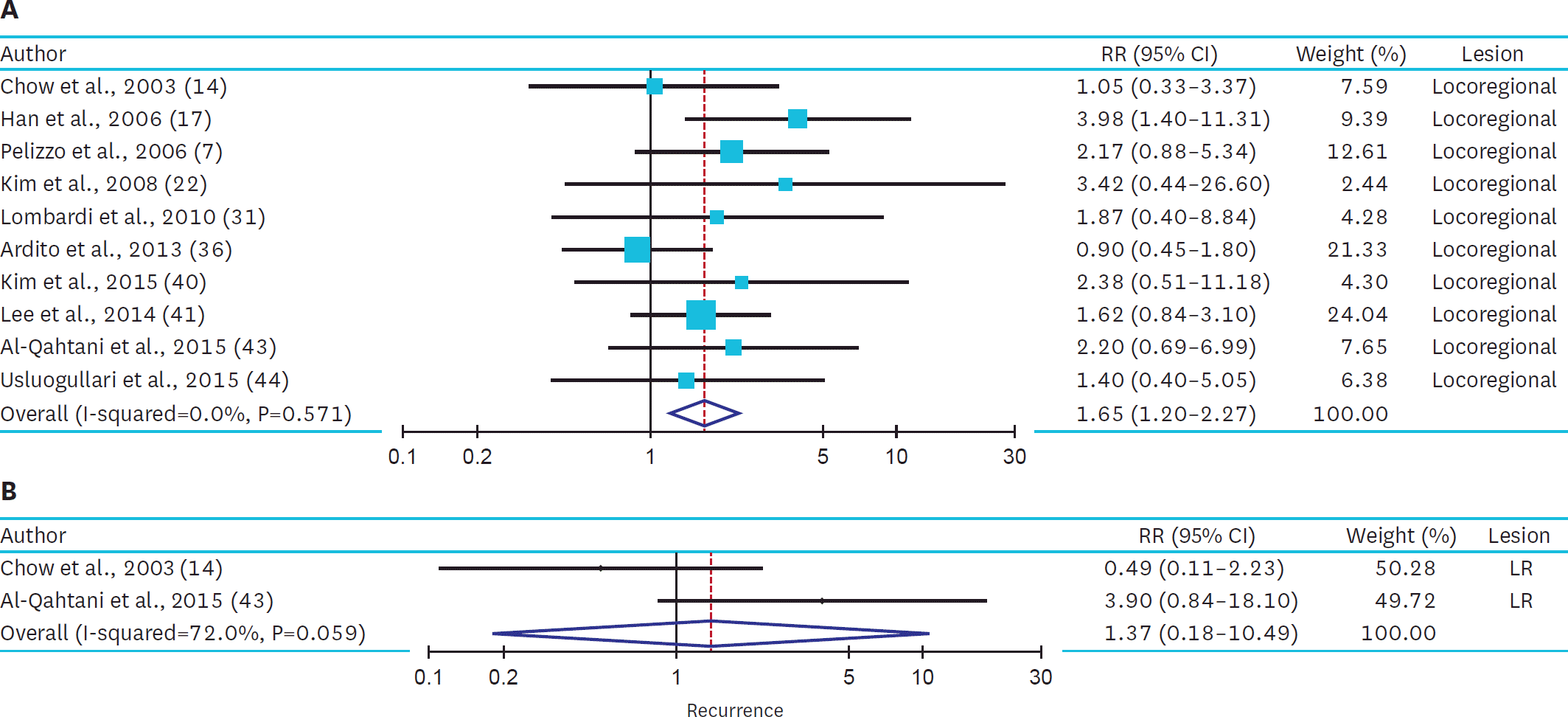
In 34 studies, compared with the patients with small PTMC, the patients with large PTMC had a higher risk of multifocality (OR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.61–2.40; I2, 40.7%), extrathyroidal extension (OR, 3.42; 95% CI, 2.46–4.75; I2, 64.9%), and lymph node metastasis (OR, 2.45; 95% CI, 1.79–3.37; I2, 80.5%). In 10 studies, patient with large PTMC had 1.65-fold increased risk of locoregional recurrence (95% CI, 1.20–2.27; I2, 0.0%).
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Hedinger CE., Williams ED., Sobin LH. Histological Typing of Thyroid Tumours. 2nd ed.Berlin: Springer-Verlag;1988.
2.Ito Y., Tomoda C., Uruno T., Takamura Y., Miya A., Kobayashi K, et al. Clinical significance of metastasis to the central compartment from papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroid. World J Surg. 2006. 30:91–9.

3.Jacquot-Laperrière S., Timoshenko AP., Dumollard JM., Peoc'h M., Estour B., Martin C, et al. Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: incidence and prognostic factors. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007. 264:935–9.

4.Roti E., degli Uberti EC., Bondanelli M., Braverman LE. Thyroid papillary microcarcinoma: a descriptive and meta-analysis study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008. 159:659–73.

5.Noguchi S., Yamashita H., Uchino S., Watanabe S. Papillary microcarcinoma. World J Surg. 2008. 32:747–53.

7.Pelizzo MR., Boschin IM., Toniato A., Piotto A., Bernante P., Pagetta C, et al. Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC): prognostic factors, management and outcome in 403 patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2006. 32:1144–8.

8.Zhao Q., Ming J., Liu C., Shi L., Xu X., Nie X, et al. Multifocality and total tumor diameter predict central neck lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013. 20:746–52.

9.Kim SY., Park JE., Lee YJ., Seo HJ., Sheen SS., Hahn S, et al. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013. 66:408–14.

10.McDonald JH. The Handbook of biological statistics [Internet]. Baltimore (MA): Sparky House Publishing;2007. [cited 2011 Mar 2]. Available from. http://udel.edu/~mcdonald/statpermissions.html.
11.Higgins JP., Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002. 21:1539–58.

12.Egger M., Davey Smith G., Schneider M., Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997. 315:629–34.

13.Yoon KS., Oh SS., Park SG., Chung ES. Diagnosis and treatment of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Korean J Head Neck Oncol. 1998. 14:228–35.
14.Chow SM., Law SC., Au SK., Mang O., Yau S., Yuen KT, et al. Changes in clinical presentation, management and outcome in 1348 patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma: experience in a single institute in Hong Kong, 1960–2000. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2003. 15:329–36.

15.Wada N., Duh QY., Sugino K., Iwasaki H., Kameyama K., Mimura T, et al. Lymph node metastasis from 259 papillary thyroid microcarcinomas: frequency, pattern of occurrence and recurrence, and optimal strategy for neck dissection. Ann Surg. 2003. 237:399–407.
16.Cho B., Choi J., Kim JH. A clinical review of papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroid. Korean J Endocr Surg. 2006. 6:87–93.

17.Han IW., Choe JH., Han W., Noh DY., Oh SK., Youn YK. Papillary thyroid microcarcinomas: experience at a single institute. Korean J Endocr Surg. 2006. 6:63–7.

18.Lee J., Rhee Y., Lee S., Ahn CW., Cha BS., Kim KR, et al. Frequent, aggressive behaviors of thyroid microcarcinomas in Korean patients. Endocr J. 2006. 53:627–32.

19.Roti E., Rossi R., Trasforini G., Bertelli F., Ambrosio MR., Busutti L, et al. Clinical and histological characteristics of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: results of a retrospective study in 243 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006. 91:2171–8.

20.Park HL., Kwak JY., Kang SS., Kim DY., Kang HG., Shim JY, et al. The analysis of tumor aggressiveness according to tumor size in occult papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007. 73:470–5.
21.Pakdaman MN., Rochon L., Gologan O., Tamilia M., Garfield N., Hier MP, et al. Incidence and histopathological behavior of papillary microcarcinomas: study of 429 cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008. 139:718–22.

22.Kim KM., Cho MS., Choi YH., Bae KS., Kang SJ. The prognostic factors and therapeutic strategy for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Korean J Endocr Surg. 2008. 8:177–82.

23.Kim TY., Hong SJ., Kim JM., Kim WG., Gong G., Ryu JS, et al. Prognostic parameters for recurrence of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2008. 8:296.

24.Lee SH., Lee SS., Jin SM., Kim JH., Rho YS. Predictive factors for central compartment lymph node metastasis in thyroid papillary microcarcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2008. 118:659–62.

25.Tae K., Chung JH., Lee YS., Choi YY., Park YS., Kim DS, et al. Characteristics of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma according to tumor size. J Korean Thyroid Assoc. 2008. 1:142–7.
26.Yoo YS., Kim SS., Mun SP., Kim KJ., Chang JH., Min YD, et al. Clinicopathologic findings of micropapillary carcinomas, according to tumor size. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009. 76:348–54.

27.Kim YW., Wang SG., Lee JC., Lee BJ., Lee JW., Kim YK, et al. Clinically related factors and features of central compartment neck lymph nodes in thyroid micropapillary carcinoma. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2009. 52:232–6.

28.Friguglietti CU., Dutenhefner SE., Brandao LG., Kulcsar MA. Classification of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma according to size and fine-needle aspiration cytology: behavior and therapeutic implications. Head Neck. 2011. 33:696–701.

29.Kim JW., Lee DY., Cho YU., Kim CH., Oh YS., Kim YM. Clinical characteristics of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2010. 53:166–71.

30.Lee NS., Bae JS., Jeong SR., Jung CK., Lim DJ., Park WC, et al. Risk factors of lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. J Korean Surg Soc. 2010. 78:82–6.

31.Lombardi CP., Bellantone R., De Crea C., Paladino NC., Fadda G., Salvatori M, et al. Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: extrathyroidal extension, lymph node metastases, and risk factors for recurrence in a high prevalence of goiter area. World J Surg. 2010. 34:1214–21.

32.Lee KJ., Cho YJ., Kim SJ., Lee SC., Kim JG., Ahn CJ, et al. Analysis of the clinicopathologic features of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma based on 7-mm tumor size. World J Surg. 2011. 35:318–23.

33.Buffet C., Golmard JL., Hoang C., Trésallet C., Du Pasquier Fédiaevsky L., Fierrard H, et al. Scoring system for predicting recurrences in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012. 167:267–75.

34.Vasileiadis I., Karakostas E., Charitoudis G., Stavrianaki A., Kapetanakis S., Kouraklis G, et al. Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: clinicopathological characteristics and implications for treatment in 276 patients. Eur J Clin Invest. 2012. 42:657–64.

35.Zhou YL., Gao EL., Zhang W., Yang H., Guo GL., Zhang XH, et al. Factors predictive of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma with bilateral involvement and central lymph node metastasis: a retrospective study. World J Surg Oncol. 2012. 10:67.

36.Ardito G., Revelli L., Giustozzi E., Salvatori M., Fadda G., Ardito F, et al. Aggressive papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: prognostic factors and therapeutic strategy. Clin Nucl Med. 2013. 38:25–8.
37.Kim KE., Kim EK., Yoon JH., Han KH., Moon HJ., Kwak JY. Preoperative prediction of central lymph node metastasis in thyroid papillary microcarcinoma using clinicopathologic and sonographic features. World J Surg. 2013. 37:385–91.

38.Zheng X., Wei S., Han Y., Li Y., Yu Y., Yun X, et al. Papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroid: clinical characteristics and BRAF(V600E) mutational status of 977 cases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013. 20:2266–73.

39.Karatzas T., Vasileiadis I., Charitoudis G., Karakostas E., Tseleni-Balafouta S., Kouraklis G. Bilateral versus unilateral papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: predictive factors and associated histopathological findings following total thyroidectomy. Hormones (Athens). 2013. 12:529–36.

40.Kim E., Choi JY. Koo DH, Lee KE, Youn YK. Differences in the characteristics of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma ≤5 mm and >5 mm in diameter. Head Neck. 2015. 37:694–7.
41.Lee J., Song Y., Soh EY. Central lymph node metastasis is an important prognostic factor in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. J Korean Med Sci. 2014. 29:48–52.

42.Zeng RC., Zhang W., Gao EL., Cheng P., Huang GL., Zhang XH, et al. Number of central lymph node metastasis for predicting lateral lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Head Neck. 2014. 36:101–6.

43.Al-Qahtani KH., Al Asiri M., Tunio MA., Aljohani NJ., Bayoumi Y., Fatani H, et al. Adjuvant Radioactive iodine 131 ablation in papillary microcarcinoma of thyroid: Saudi Arabian experience. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015. 44:51.

44.Usluogullari CA., Onal ED., Ozdemir E., Ucler R., Kiyak G., Ersoy PE, et al. A retrospective analysis of prognostic factors predictive of lymph-node metastasis and recurrence in thyroid papillary microcarcinoma. Minerva Endocrinol. 2015. 40:15–22.
Go to : 
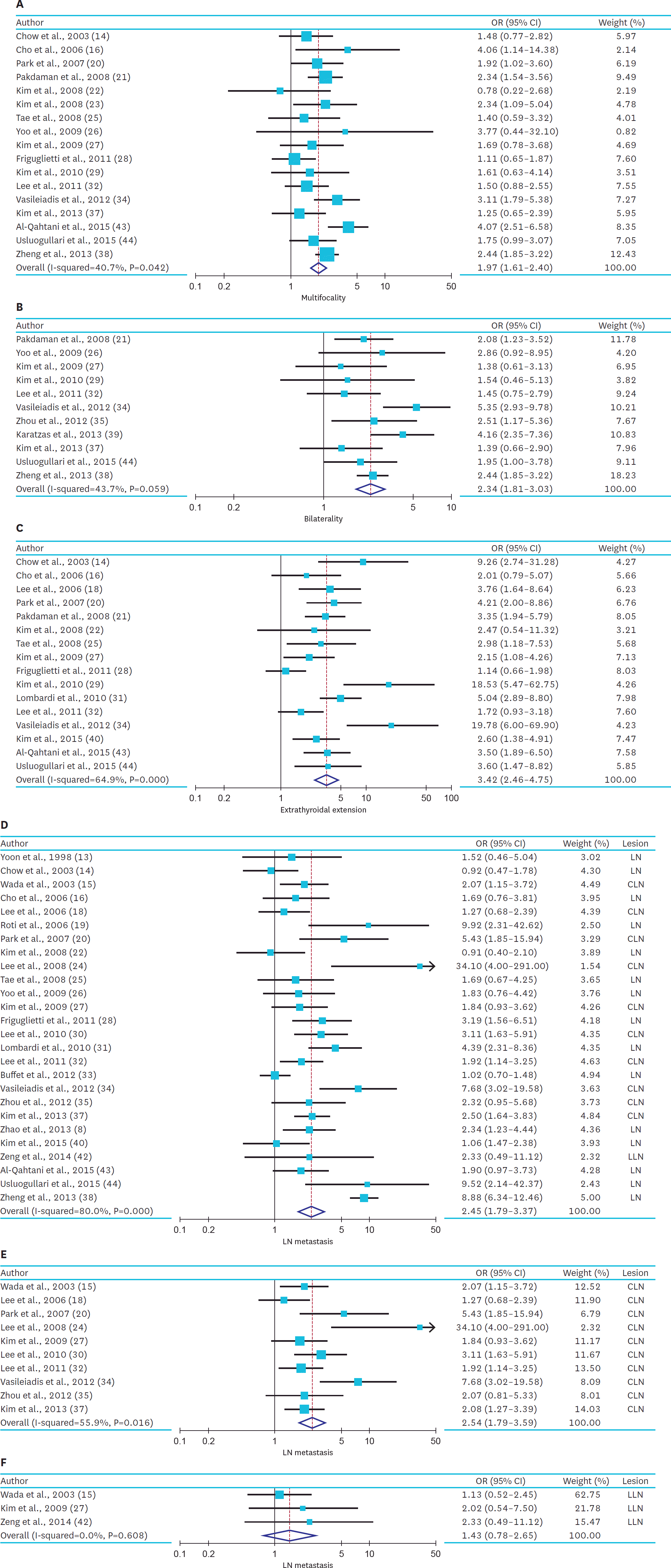 | Fig. 2.Summarized statistics and corresponding forest plot on the association of large PTMC (size >5 mm) with the high-risk factors: (A) multifocality, (B) bilaterality, (C) extrathyroidal extension, (D) LN metastasis, (E) CLN metastasis, and (F) LLN metastasis. PTMC = papillary thyroid microcarcinoma; LN = lymph node; CLN = central lymph node; LLN = lateral lymph node; OR = odds ratio; CI = confidence interval. |
 | Fig. 2.(Continued) Summarized statistics and corresponding forest plot on the association of large PTMC (size >5 mm) with the high-risk factors: (A) multifocality, (B) bilaterality, (C) extrathyroidal extension, (D) LN metastasis, (E) CLN metastasis, and (F) LLN metastasis. PTMC = papillary thyroid microcarcinoma; LN = lymph node; CLN = central lymph node; LLN = lateral lymph node; OR = odds ratio; CI = confidence interval. |
 | Fig. 3.Summarized statistics and corresponding forest plot on the association of large PTMC (size >5 mm) with the risk of tumor recurrence: (A) LR and (B) DM recurrence. PTMC = papillary thyroid microcarcinoma; LR = locoregional recurrence; DM = distant metastasis; RR = relative risk; CI = confidence interval. |
Table 1.
Characteristics of the 34 studies included in the meta-analysis
| Study | No. of patients∗ | Gender (M/F) | Age, mean | Period of study | Multifocal tumors∗ | Bilateral tumors∗ | Extrathyroidal extension∗ | LN metastasis∗ | Recurrence∗ | Country | Incidence (ASR)† | Study quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yoon et al., 1998 (13) | 72 (32/40) | 10/62 | 45.0 | 1985–1995 | − | − | 7/16 | − | Korea | 35.4 | 11 | |
| Chow et al., 2003 (14) | 203 (70/133) | 27/176 | 46.8 | 1960–1999 | 18/45 | − | 3/39 | 18/32 | 4/8 (LR), 0/3 (DM) | Hong Kong | 1.4 | 13 |
| Wada et al., 2003 (15) | 259 (61/198) | 29/230 | 48.0 | 1988–1998 | − | − | 34/146 | − | Japan | 3.1 | 13 | |
| Cho et al., 2006 (16) | 134 (39/95) | 11/123 | − | 2003–2006 | 3/24 | − | 7/29 | 11/38 | − | Korea | 35.4 | 13 |
| Han et al., 2006 (17) | 350 (147/203) | 54/296 | 46.5 | 1990–2004 | − | − | − | − | 4/22 | Korea | 35.4 | 13 |
| Lee et al., 2006 (18) | 300 (62/238) | 27/273 | 46.1 | 2004 | − | − | 7/77 | 16/73 | − | Korea | 35.4 | 13 |
| Pelizzo et al., 2006 (7) | 403 (169/234) | 66/337 | − | 1990–2004 | − | − | − | − | 6/18 | Italy | 9.1 | 12 |
| Roti et al., 2006 (19) | 243 (86/157) | 46/197 | 51.5 | 1993–2002 | − | − | − | 2/30 | 0/4 | Italy | 9.1 | 13 |
| Park et al., 2007 (20) | 218 (71/147) | − | − | 2001–2007 | 18/58 | 5/31 | 10/60 | 4/36 | − | Korea | 35.4 | 12 |
| Pakdaman et al., 2008 (21) | 429 (274/155) | − | − | 2002–2007 | 140/110 | 74/77 (140/110)¶ | 25/39 | − | − | Canada | 9.4 | 12 |
| Kim et al., 2008 (22) | 254 (72/182) | 41/213 | 48.1 | 1985–2002 | 4/8 | − | 2/12 | 9/21 | 1/9 | Korea | 35.4 | 13 |
| Kim et al., 2008 (23) | 307 (49/258) | 32/275 | − | 1996–2002 | 9/89 | − | − | − | − | Korea | 35.4 | 13 |
| Lee et al., 2008 (24) | 52 (26/26) | 7/45 | 47.6 | 2000–2005 | − | − | − | 1/15† | − | Korea | 35.4 | 14 |
| Tae et al., 2008 (25) | 142 (62/80) | 31/111 | 48.3 | 2000–2006 | 10/17 | − | 7/22 | 8/16 | − | Korea | 35.4 | 13 |
| Yoo et al., 2009 (26) | 165 (62/103) | 13/152 | 46.4 | 2002–2006 | 4/17 | 1/6 | − | 8/22 | 0/4 | Korea | 35.4 | 12 |
| Kim et al., 2009 (27) | 161 (52/109) | 24/137 | 48.3 | 2003–2007 | 11/34 | 10/27 | 18/58 | 19/56†; 3/12§ | - | Korea | 35.4 | 14 |
| Friguglietti et al., 2011 (28) | 448 (173/275) | 52/396 | − | 2002–2008 | 26/45 | − | 23/41 | 10/45 | − | Brazil | 2.9 | 13 |
| Kim et al., 2010 (29) | 179 (78/101) | 16/163 | 47.4 | 1996–2006 | 8/27 (29/71)¶ | 4/14 (29/71)¶ | 3/43 | − | − | Korea | 35.4 | 12 |
| Lee et al., 2010 (30) | 335 (125/220) | 41/294 | 48.0 | 2006–2008 | − | − | − | 16/72 | − | Korea | 35.4 | 14 |
| Lombardi et al., 2010 (31) | 933 (459/474) | 197/736 | − | 2002–2007 | − | − | 16/73 | 12/50 | 2/7 (100/187)¶ | Italy | 9.1 | 13 |
| Lee et al., 2011 (32) | 275 (106/169) | 13/262 | − | 2007–2009 | 29/61 | 16/40 (79/149)¶ | 18/44 | 29/71† | − | Korea | 35.4 | 13 |
| Buffet et al., 2012 (33) | 707 (138/569) | 289/418 | 47.2 | 1960–2007 | − | − | − | 56/233 | − | France | 0.7 | 15 |
| Vasileiadis et al., 2012 (34) | 276 (202/74) | 54/222 | − | 2002–2008 | 60/42 | 29/35 | 3/17 | 7/16 | − | Greece | 1.8 | 13 |
| Zhou et al., 2012 (35) | 211 (67/144) | 32/179 | 49.0 | 2010–2011 | − | 10/44 | − | 8/52† (23/99)¶ | − | China | 1.4 | 14 |
| Ardito et al., 2013 (36) | 149 (92/57) | 30/119 | 47.6 | 2000–2005 | − | − | − | − | 18/10 | Italy | 9.1 | 14 |
| Kim et al., 2013 (37) | 483 (213/270) | 68/415 | 45.2 | 2008 | − | − | − | 40/99† | − | Korea | 35.4 | 13 |
| Zhao et al., 2013 (8) | 212 (69/143) | 36/176 | 45.1 | 2003–2011 | − | − | − | 17/62 | − | China | 1.4 | 14 |
| Zheng et al., 2013 (38) | 977 (632/345) | 223/754 | 46.0 | 2001–2010 | 164/159 | 86/133 | − | 61/168 | − | China | 1.4 | 16 |
| Karatzas et al., 2013 (39) | 319 (249/70) | 58/261 | 50.3 | 2001–2008 | − | 44/33 | − | − | − | Greece | 1.8 | 14 |
| Kim et al., 2014 (40) | 205 (83/122) | 36/169 | 47.2 | 2005 | 19/33 | 13/25 | 18/52 (81/122)¶ | 14/26 (39/70)¶ | 2/7 | Korea | 35.4 | 17 |
| Lee et al., 2014 (41) | 2,018 (857/1,161) | 297/1,721 | 45.3 | 1994–2010 | − | − | − | − | 13/28 | Korea | 35.4 | 17 |
| Zeng et al., 2014 (42) | 141 (12/129) | 37/104 | 44.0 | 2004–2011 | − | − | − | 2/41§ | − | China | 1.4 | 16 |
| Al-Qahtani et al., 2015 (43) | 326 (161/65) | 55/271 | 42.9 | 2000–2012 | 36/89 | − | 16/46 | 15/27 | 6/17, 4/9 (LR),2/8 (DM) | Saudi Arabia | 4.4 | 15 |
| Usluogullari et al., 2015 (44 | ) 248 (127/121) | 47/201 | 47.8 | 2007–2012 | 28/40 | 17/28 | 7/21 | 2/16 | 4/6 | Turkey | 10.8 | 15 |
Table 2.
Subgroup analyses categorized by incidence rate of thyroid cancer, study quality, and published year of the articles; risk with high-risk factors, and tumor recurrence in large PTMC compared with small PTMC
| Outcome | Studies (No.) | Summary | I2 (%) | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heterogeneity | Begg | Egger | ||||
| Multifocality | ||||||
| All studies | 17 | 1.97 (1.61–2.40) | 40.7 | 0.04 | 0.59 | 0.27 |
| Study QS | ||||||
| ≥14 | 4 | 2.45 (1.71–3.51) | 53.6 | 0.09 | 0.73 | 0.77 |
| <14 | 13 | 1.78 (1.43–2.21) | 20.8 | 0.23 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
| Incidence rate | ||||||
| High | 13 | 1.98 (1.56–2.50) | 29.9 | 0.15 | 0.86 | 0.46 |
| Low | 4 | 1.93 (1.25–2.98) | 69.4 | 0.02 | 0.73 | 0.51 |
| Published year | ||||||
| ≥2011 | 6 | 2.23 (1.61–3.09) | 62.8 | 0.02 | 0.26 | 0.53 |
| <2011 | 11 | 1.76 (1.42–2.18) | 0.0 | 0.47 | 1.00 | 0.96 |
| Combination | ||||||
| High incidence and QS ≥14 | 3 | 2.38 (1.29–4.41) | 68.7 | 0.04 | 1.00 | 0.46 |
| Low incidence and QS ≥14 | 1 | 2.44 (1.85–3.22) | ||||
| High incidence and ≥2011 | 4 | 1.95 (1.13–3.37) | 74.2 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.18 |
| Low incidence and ≥2011 | 2 | 2.56 (2.00–3.28) | 0.0 | 0.44 | 1.00 | |
| High incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 2 | 2.71 (1.18–6.18) | 79.8 | 0.03 | 1.00 | |
| Low incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 1 | 2.44 (1.85–3.22) | ||||
| Bilaterality | ||||||
| All studies | 12 | 2.39 (1.87–3.06) | 40.0 | 0.07 | 0.84 | 0.68 |
| Study QS | ||||||
| ≥14 | 6 | 2.29 (1.70–3.09) | 35.9 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.51 |
| <14 | 6 | 2.56 (1.61–4.05) | 51.7 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.93 |
| Incidence rate | ||||||
| High | 8 | 1.84 (1.40–2.40) | 0.0 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.63 |
| Low | 4 | 3.31 (2.22–4.96) | 57.8 | 0.06 | 0.73 | 0.33 |
| Published year | ||||||
| ≥2011 | 7 | 2.52 (1.79–3.54) | 59.4 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 0.88 |
| <2011 | 5 | 2.07 (1.44–2.98) | 0.0 | 0.63 | 1.00 | 0.80 |
| Combination | ||||||
| High incidence and QS ≥14 | 3 | 1.59 (1.04–2.43) | 0.0 | 0.74 | 1.00 | 0.31 |
| Low incidence and QS ≥14 | 3 | 2.80 (2.02–3.86) | 27.2 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 0.62 |
| High incidence and ≥2011 | 3 | 1.59 (1.07–2.36) | 0.0 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 0.68 |
| Low incidence and ≥2011 | 4 | 3.31 (2.22–4.96) | 57.8 | 0.06 | 0.73 | 0.33 |
| High incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 2 | 1.68 (1.02–2.75) | 0.0 | 0.51 | 1.00 | |
| Low incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 3 | 2.80 (2.02–3.86) | 27.2 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 0.62 |
| Extrathyroidal extension | ||||||
| All studies | 16 | 3.42 (2.46–4.75) | 64.9 | <0.01 | 0.14 | 0.05 |
| Study QS | ||||||
| ≥14 | 4 | 2.85 (2.02–4.02) | 0.0 | 0.70 | 0.73 | 0.78 |
| <14 | 12 | 3.78 (2.40–5.93) | 73.3 | <0.01 | 0.24 | 0.08 |
| Incidence rate | ||||||
| High | 13 | 3.25 (2.51–4.20) | 33.6 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.52 |
| Low | 3 | 5.58 (0.81–38.26) | 91.3 | <0.01 | 0.29 | 0.11 |
| Low Published year | 3 | 5.58 (0.81–38.26) | 91.3 | <0.01 | 0.29 | 0.11 |
| ≥2011 | 5 | 3.52 (1.93–6.42) | 68.8 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.07 |
| <2011 | 11 | 3.41 (2.25–5.17) | 66.6 | <0.01 | 0.53 | 0.23 |
| Combination | ||||||
| High incidence and QS ≥14 | ||||||
| Low incidence and QS ≥14 | 4 | 2.85 (2.02–4.02) | 0.0 | 0.70 | 0.73 | 0.78 |
| High incidence and ≥2011 | 0 | |||||
| Low incidence and ≥2011 | 4 | 2.63 (1.87–3.70) | 4.1 | 0.37 | 0.73 | 0.56 |
| High incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 1 | 19.78 (6.00–69.90) | − | − | − | − |
| Low incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 3 | 3.13 (2.11–4.86) | 0.0 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.79 |
| LN metastasis | ||||||
| All studies | 26 | 2.45 (1.79–3.37) | 80.5 | <0.01 | 0.11 | 0.97 |
| Study QS | ||||||
| ≥14 | 10 | 3.14 (1.63–6.06) | 89.2 | <0.01 | 0.37 | 0.96 |
| <14 | 16 | 2.13 (1.58–2.87) | 60.3 | <0.01 | 0.62 | 0.57 |
| Incidence rate | ||||||
| High | 18 | 2.24 (1.72–2.91) | 51.5 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.15 |
| Low | 8 | 2.66 (1.23–5.78) | 92.1 | <0.01 | 0.54 | 0.73 |
| Published year | ||||||
| ≥2011 | 11 | 2.68 (1.54–4.67) | 88.8 | <0.01 | 0.35 | 0.83 |
| <2011 | 15 | 2.23 (1.59–3.11) | 59.9 | <0.01 | 0.37 | 0.12 |
| Combination | ||||||
| High incidence and QS ≥14 | 5 | 3.30 (1.69–6.41) | 62.1 | 0.03 | 0.46 | 0.04 |
| Low incidence and QS ≥14 | 5 | 2.61 (0.89–7.70) | 94.5 | <0.01 | 0.81 | 0.75 |
| High incidence and ≥2011 | 5 | 2.09 (1.39–3.15) | 46.8 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.74 |
| Low incidence and ≥2011 | 6 | 3.11 (1.19–8.12) | 93.4 | <0.01 | 0.71 | 0.89 |
| High incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 2 | 3.68 (0.78–17.43) | 73.1 | 0.05 | 1.00 | |
| Low incidence, ≥2011and QS ≥14 | 5 | 2.61 (0.89–7.70) | 94.5 | <0.01 | 0.81 | 0.75 |
| CLN metastasis | ||||||
| All studies | 10 | 2.54 (1.79–3.59) | 55.9 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| Study QS | ||||||
| ≥14 | 4 | 2.91 (1.45–5.84) | 57.5 | 0.07 | 0.73 | 0.23 |
| <14 | 6 | 2.42 (1.58–3.73) | 61.1 | 0.03 | 0.45 | 0.08 |
| Incidence rate | ||||||
| High | 8 | 2.28 (1.62–3.19) | 48.5 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.02 |
| Low | 2 | 3.99 (1.10–14.43) | 73.3 | 0.05 | 1.00 | − |
| Published year | ||||||
| <2011 | 6 | 2.59 (1.53–4.39) | 62.4 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.04 |
| ≥2011 | 4 | 2.58 (1.53–4.34) | 57.4 | 0.07 | 0.73 | 0.34 |
| Combination | ||||||
| High incidence and QS ≥14 | 3 | 3.58 (1.34–9.57) | 70.5 | 0.03 | 1.00 | 0.31 |
| Low incidence and QS ≥14 | 2 | 1.27 (0.67–2.40) | 46.6 | 0.17 | 1.00 | − |
| High incidence and ≥2011 | 2 | 2.00 (1.40–2.87) | 0.0 | 0.83 | 1.00 | 0.89 |
| Low incidence and ≥2011 | 2 | 3.99 (1.10–14.43) | 73.3 | 0.05 | 1.00 | − |
| High incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 3 | 3.58 (1.34–9.57) | 70.5 | 0.03 | 1.00 | 0.31 |
| Low incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 2 | 1.27 (0.67–2.40) | 46.6 | 0.17 | 1.00 | − |
| LLN metastasis | ||||||
| All studies | 3 | 1.43 (0.78–2.65) | 0.0 | 0.61 | 0.30 | 0.06 |
| LR∗ | ||||||
| All studies | 10 | 1.65 (1.20–2.27) | 0.0 | 0.57 | 0.59 | 0.20 |
| Study QS | ||||||
| ≥14 | 5 | 1.41 (0.95–2.11) | 0.0 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 0.30 |
| <14 | 5 | 2.22 (1.30–3.77) | 0.0 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.96 |
| Incidence rate | ||||||
| High | 9 | 1.71 (1.23–2.39) | 0.0 | 0.54 | 0.60 | 0.14 |
| Low | 1 | 1.05 (0.33–3.36) | ||||
| Published year | ||||||
| ≥2011 | 5 | 1.41 (0.93–2.09) | 0.0 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 0.30 |
| <2011 | 5 | 2.21 (1.30–3.76) | 0.0 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.96 |
| Combination | ||||||
| High incidence and QS ≥14 | 5 | 1.41 (0.93–2.09) | 0.0 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 0.30 |
| Low incidence and QS ≥14 | 0 | |||||
| High incidence and ≥2011 | 5 | 1.41 (0.93–2.09) | 0.0 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 0.30 |
| Low incidence and ≥2011 | 0 | |||||
| High incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 5 | 1.41 (0.93–2.09) | 0.0 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 0.30 |
| Low incidence, ≥2011 and QS ≥14 | 0 | |||||
| DM recurrence∗ | ||||||
| All studies | 2 | 1.37 (0.18–10.49) | 72.0 | 0.06 | 1.00 | |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download