Abstract
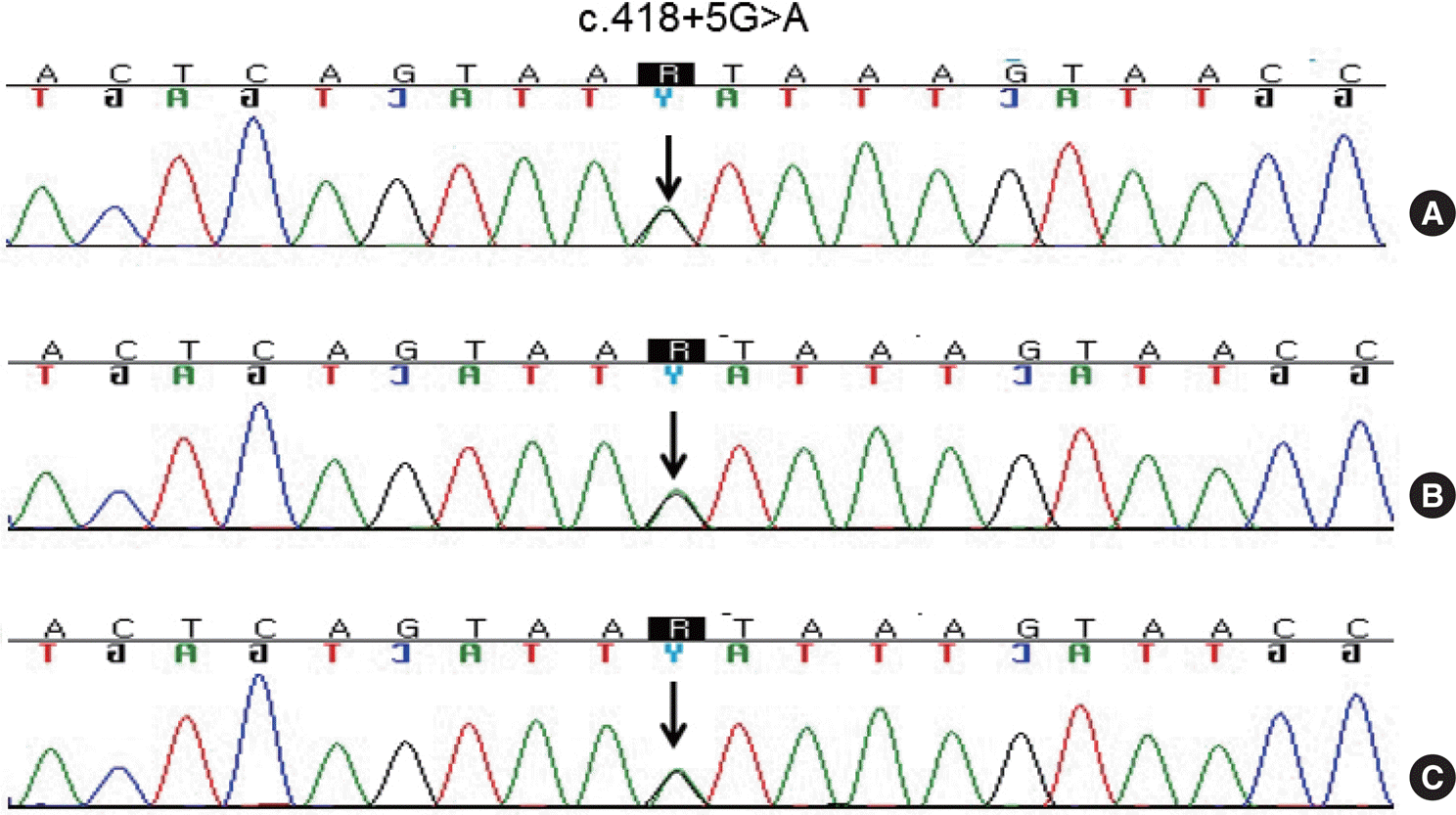
Pathogenic variants of bone morphogenic protein receptor type 2 gene (BMPR2) are related to the majority of cases of heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Over 400 pathogenic variants have been identified. However, clinical characterization of PAH is still incomplete. We present a case of heritable PAH in a Korean family showing serious clinical presentation with high penetrance. Genetic sequencing revealed a known heterozygous BMPR2 pathogenic variant, c.418+5G>A, at a splice site of intron 3. Serious clinical presentation with high penetrance suggested that the interplay of other factors with pathologic variants might be in genotype-phenotype correlation. Further studies are needed to clarify these issues for the development of personalized medicine approaches for PAH.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2.Machado RD., Eickelberg O., Elliott CG., Geraci MW., Hanaoka M., Loyd JE, et al. Genetics and genomics of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009. 54:S32–42.

3.Machado RD., Southgate L., Eichstaedt CA., Aldred MA., Austin ED., Best DH, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: a current perspective on established and emerging molecular genetic defects. Hum Mutat. 2015. 36:1113–27.

4.Leter EM., Boonstra AB., Postma FB., Gille JJ., Meijers-Heijboer EJ., Vonk Noordegraaf A. Genetic counselling for pulmonary arterial hypertension: a matter of variable variability. Neth Heart J. 2011. 19:89–92.

6.Rosenzweig EB., Morse JH., Knowles JA., Chada KK., Khan AM., Roberts KE, et al. Clinical implications of determining BMPR2 mutation status in a large cohort of children and adults with pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2008. 27:668–74.

7.Cooper DN., Ball EV., Stenson PD., Phillips AD., Evans K., Heywood S, et al. The human gene mutation database. http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/gene.php?gene=BMPR2. (updated on Feb 2017).
8.Austin ED., Loyd JE. Heritable forms of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2013. 34:568–80.

9.Griffths AJF., Miller JH., Suzuki DT., Lewontin RC., Gelbart WM. An introduction to genetic analysis. 7th ed.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22090. (Updated on 2000).
10.Machado RD., Pauciulo MW., Thomson JR., Lane KB., Morgan NV., Wheeler L, et al. BMPR2 haploinsuffciency as the inherited molecular mechanism for primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Human Genet. 2001. 68:92–102.
11.Hoeper MM., Huscher D., Ghofrani HA., Delcroix M., Distler O., Schwei-ger C, et al. Elderly patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: results from the COMPERA registry. Int J Cardiol. 2013. 168:871–80.

12.Loyd JE., Butler MG., Foroud TM., Conneally PM., Phillips JA 3rd., Newman JH. Genetic anticipation and abnormal gender ratio at birth in familial primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 152:93–7.

13.Machado RD., James V., Southwood M., Harrison RE., Atkinson C., Stewart S, et al. Investigation of second genetic hits at the BMPR2 locus as a modulator of disease progression in familial pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation. 2005. 111:607–13.
14.Chelladurai P., Seeger W., Pullamsetti SS. Epigenetic mechanisms in pulmonary arterial hypertension: the need for global perspectives. Eur Respir Rev. 2016. 25:135–40.

15.Sztrymf B., Yaïci A., Girerd B., Humbert M. Genes and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respiration. 2007. 74:123–32.

16.Galie N., Humbert M., Vachiery JL., Gibbs S., Lang I., Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2016. 37:67–119.
Go to : 
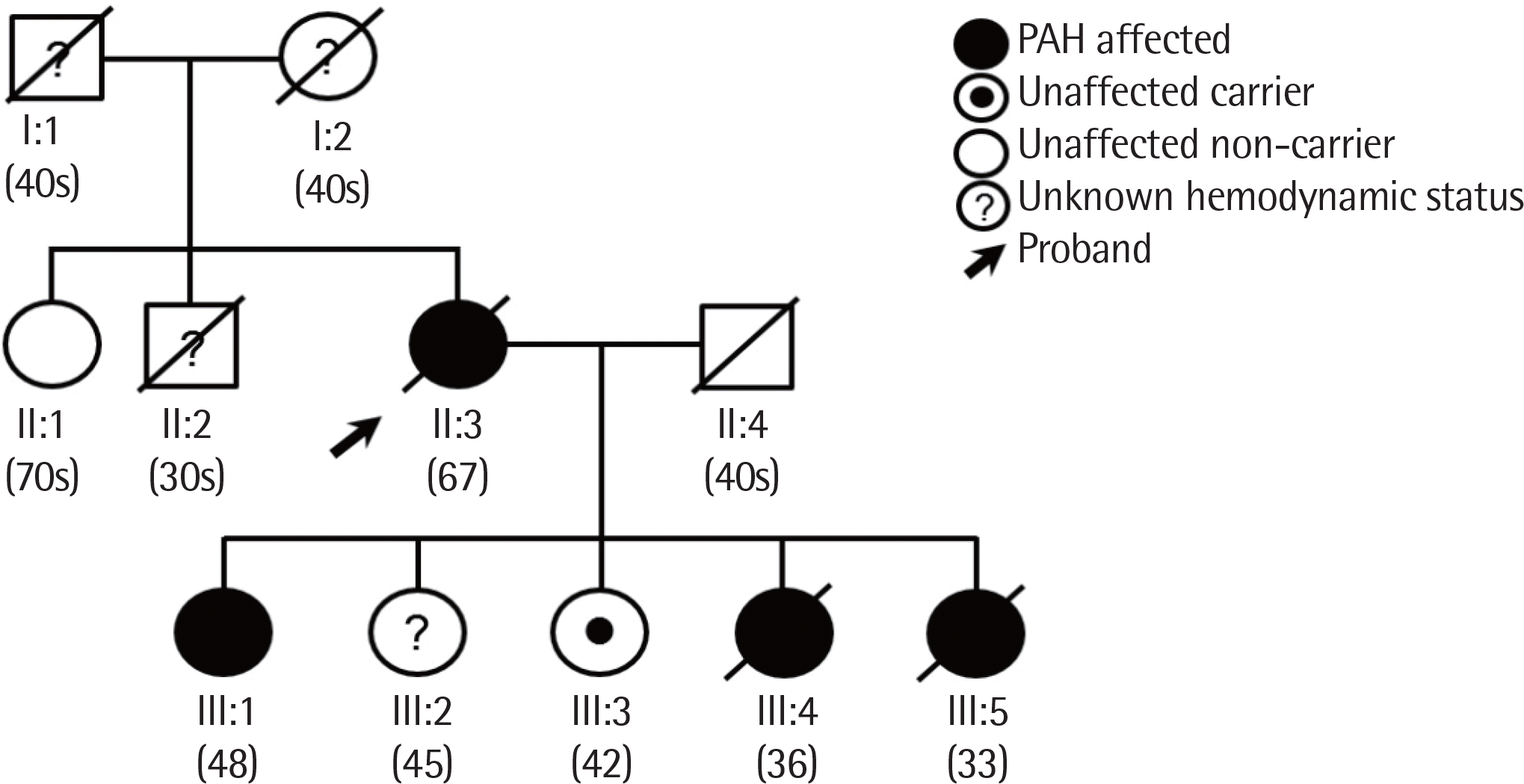 | Fig. 1.Pedigree of the case family. The proband (II:3) was diagnosed with PAH later than her fourth (III:4) and fifth (III:5) daughters. Numbers in parentheses are age at death or current living age. |
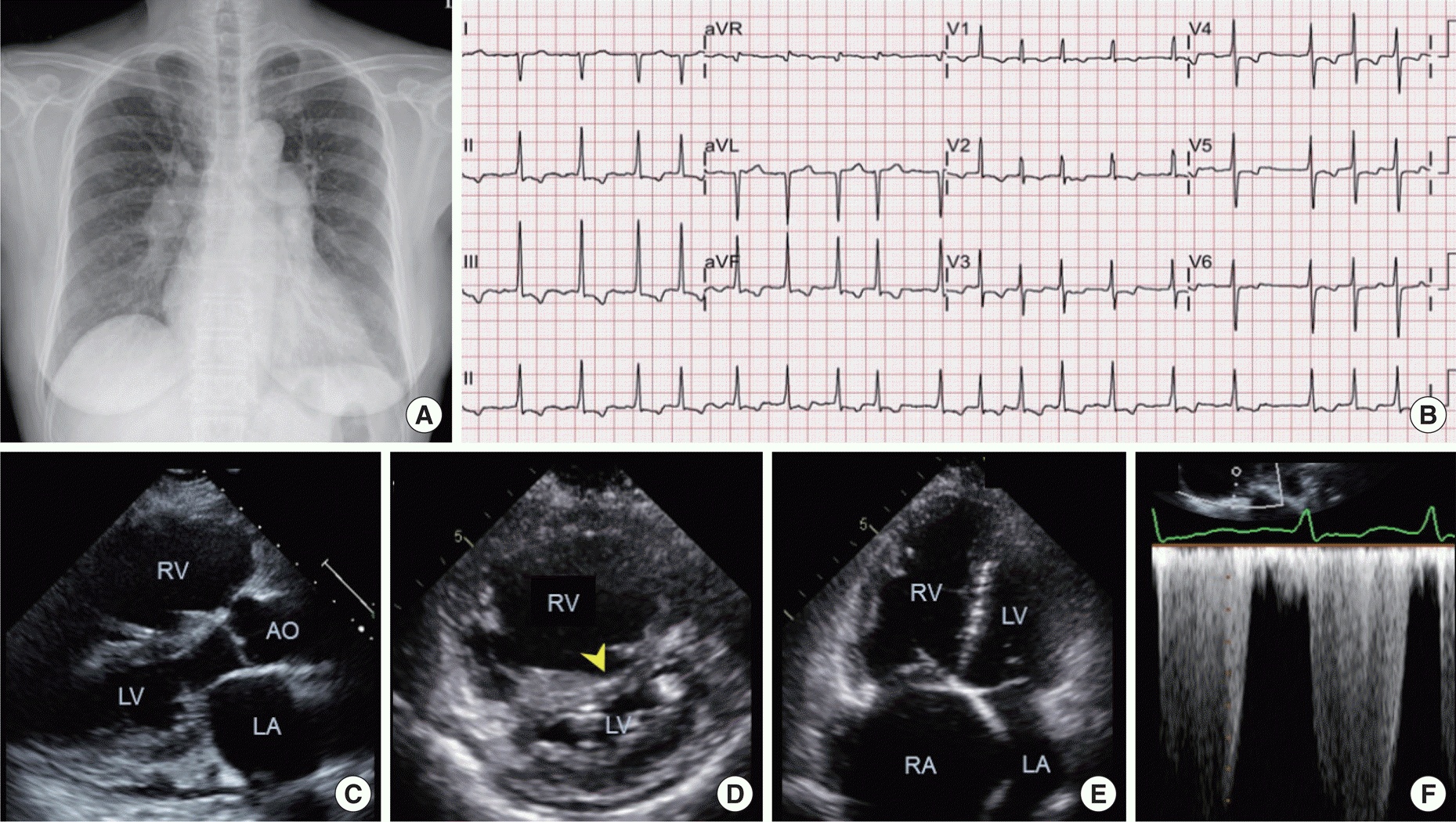 | Fig. 2.Chest radiograph, electrocardiogram, and echocardiogram of the proband at the time of PAH diagnosis. Cardiomegaly with bilateral hilar enlargement in chest radiograph (A), atrial fibrillation and right ventricular hypertrophy in electrocardiogram (B), right ventricular dilation and hypertrophy, interventricular septal bowing (arrowhead), resultant left ventricular compression, and small amount of pericardial effusion in echocardiography (C-E). Estimated systolic pulmonary arterial pressure from peak tricuspid regurgitation flow velocity is around 110 mmHg (F). Abbreviations: AO, aorta; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle. |
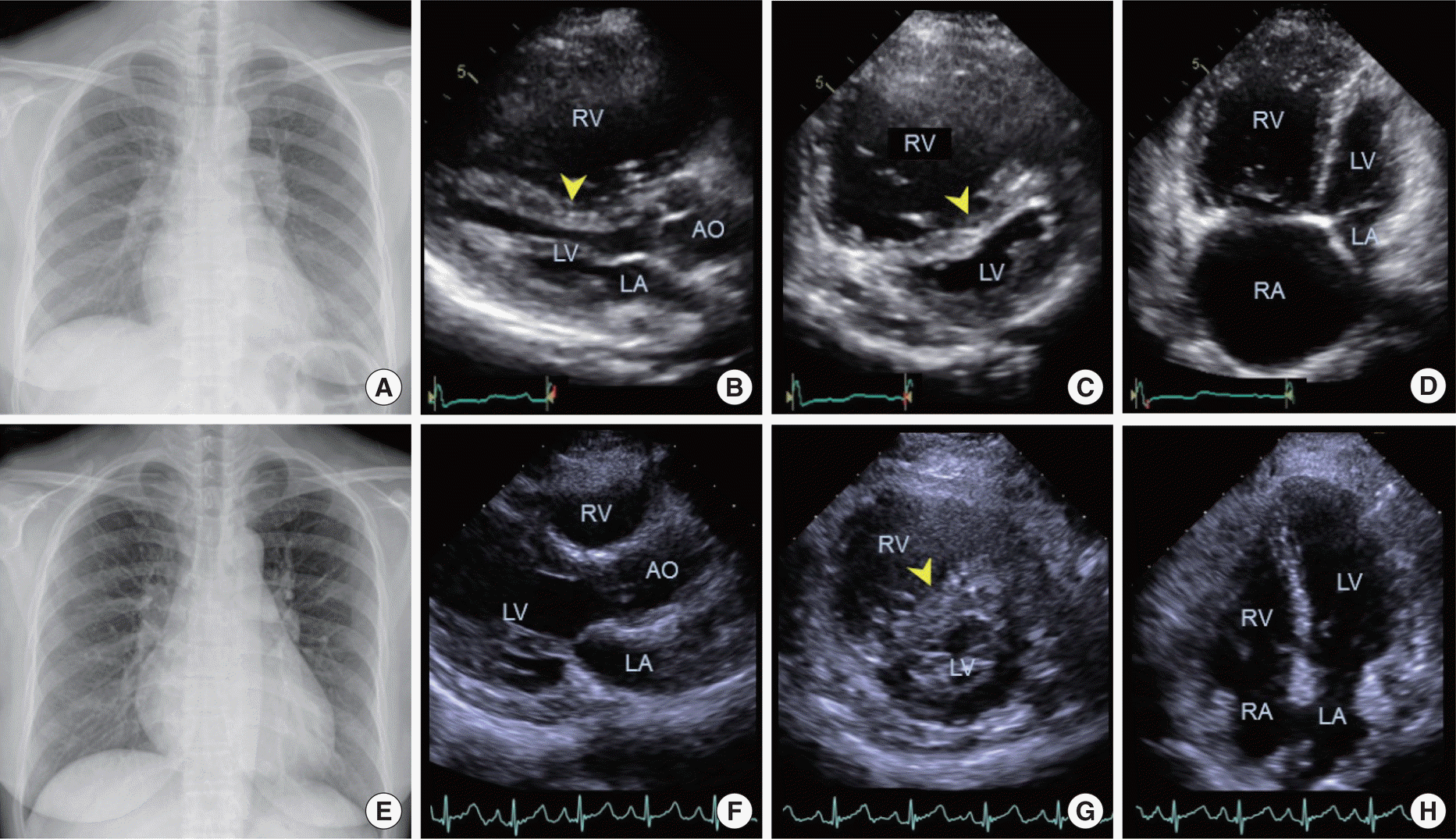 | Fig. 3.Chest radiograph and echocardiogram of the proband's fourth daughter (III:4) and first daughter (III:1) at the time of PAH diagnosis. Cardiomegaly and hilar enlargement in X-ray (A, E), right ventricular dilation and hypertrophy, interventricular septal bowing to left ventricle (arrow head) in echocardiogram (B-D, F-H). Abbreviations: AO, aorta; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download