Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Notes
This work was supported by grants from Natural Science Foundation of China (81472731), Guangdong Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar (S20120011199), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (2162044), and grants from Key Laboratory of Malignant Tumor Molecular Mechanism and Translational Medicine of Guangzhou Bureau of Science and Information Technology (Grant [2013]163), from the Key Laboratory of Malignant Tumor Gene Regulation and Target Therapy of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes (KLB09001), and from Guangdong Science and Technology Department (2015B050501004).
References
Figure 1
H19 and let-7a expression levels in 79 primary breast cancer patients as measured using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. (A) let-7a is expressed at higher levels in patients with a complete response (CR)/partial response (PR) than in patients with stable disease (SD)/progressive disease (PD). (B) H19 is expressed at higher levels in patients with SD/PD than in patients with CR/PR. (C) The expression of let-7a is negatively associated with that of H19 (r=–0.566, p<0.001). The fold difference in expression was normalized against the sample with the lowest expression levels.
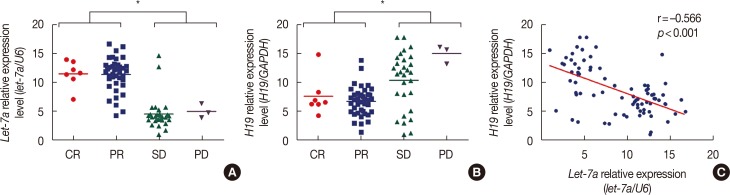
Figure 2
Drug-resistant breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231 paclitaxel-resistant cell line [MDA-MB-231p]) express high levels of H19, and knockdown of H19 expression (as measured using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction [qRT-PCR]) restores the chemosensitivity of these cells. (A) Based on the qRT-PCR results, the average expression level of H19 in the paclitaxel cell line was 13.04-fold (p=0.002) higher than the average H19 expression level in the control MDA-MB-231 cell line. (B) Based on the 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of paclitaxel in MDA-MB-231 cells and paclitaxel-resistant cells were 53.83±4.16 nM and 372.20±59.81 nM, respectively. After knockdown of H19 in MDA-MB-231p cells, the IC50 values were 74.44±8.40 nM (p=0.008) and 65.45±6.44 nM (p=0.007), respectively. (C) Flow cytometry of cells stained with Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate was used to investigate drug-induced apoptosis. After 24 hours of paclitaxel treatment, the apoptosis rate of MDA-MB-231p cells was only 3.5%±0.9%; however, the two sets of small interfering RNA (siRNA)-transfected cells exhibited apoptosis rates of 13.8%±1.5% (p=0.004) and 18.2%±1.6% (p=0.001).
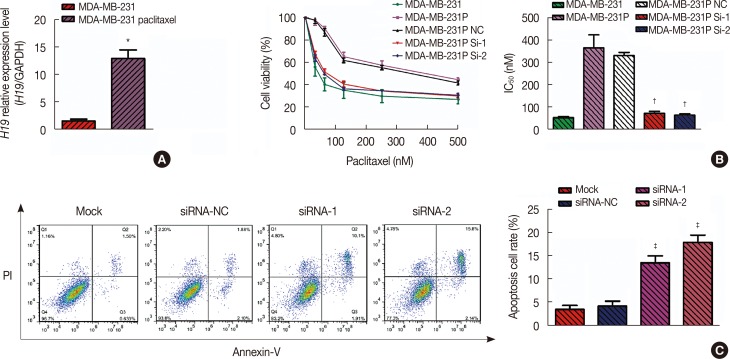
Figure 3
Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) curves of 79 primary breast cancer patients with different risk score values. (A) The median OS was 16 months (range, 4–29 months) in the risk score ≥–0.1 group and 20 months (range, 7–32 months) in the risk score <–0.1 group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.126; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.020−0.806; p=0.001). (B) The median PFS was 18 months (range, 7–32 months) in the risk score ≥–0.1 group and 14 months (range, 4–29 months) in the risk score <–0.1 group (HR, 0.221; 95% CI, 0.094−0.518; p=0.001). (C) Comparisons of the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve for survival status according to the risk score and the let-7a and H19 levels. The areas were 0.790, 0.683, and 0.667, respectively.
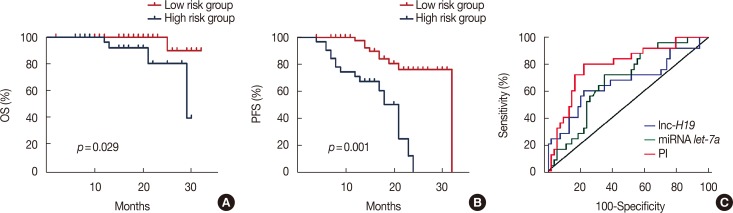
Table 1
Demographic and baseline characteristics of 79 primary breast cancer patients
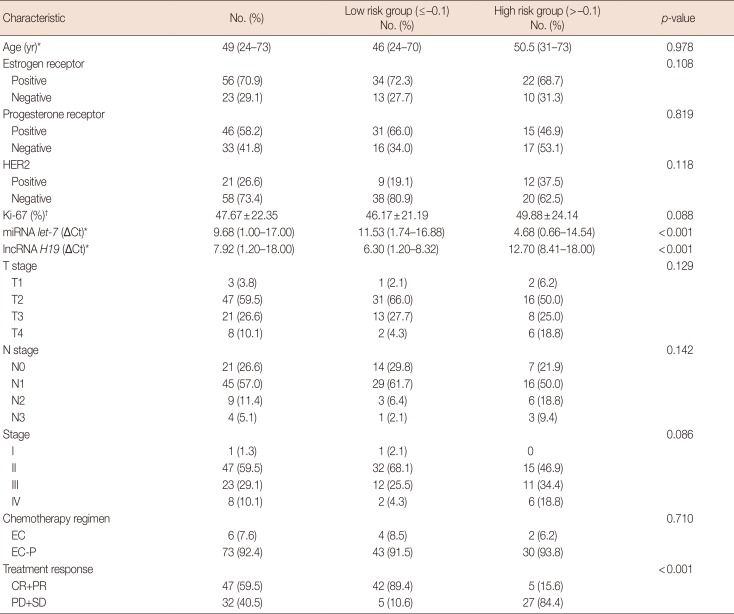
HER2=human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; miRNA=microRNA; lncRNA=long non-coding RNA; ΔCt=comparative cycle threshold; EC=epirubicin and cyclophosphamide; EC-P=epirubicin, cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel; CR=complete response; PR=partial response; PD=progressive disease; SD=stable disease.
*Median (range); †Mean±standard deviation.
Table 2
Univariate and multivariate analyses of the prognostic factors of progression-free survival for primary breast cancer patients
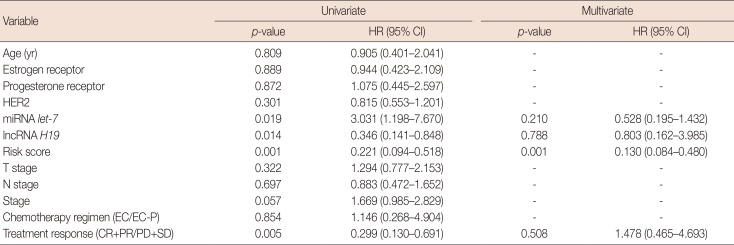
HR=hazard ratio; CI=confidence interval; HER2=human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; miRNA=microRNA; lncRNA=long non-coding RNA; EC=epirubicin and cyclophosphamide; EC-P=epirubicin, cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel; CR=complete response; PR=partial response; PD=progressive disease; SD=stable disease.
Table 3
Univariate and multivariate analyses of the prognostic factors of overall survival for primary breast cancer patients
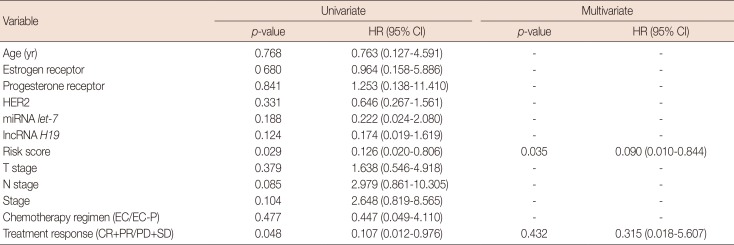
HR=hazard ratio; CI=confidence interval; HER2=human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; miRNA=microRNA; lncRNA=long non-coding RNA; EC=epirubicin and cyclophosphamide; EC-P=epirubicin, cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel; CR=complete response; PR=partial response; PD=progressive disease; SD=stable disease.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download