INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
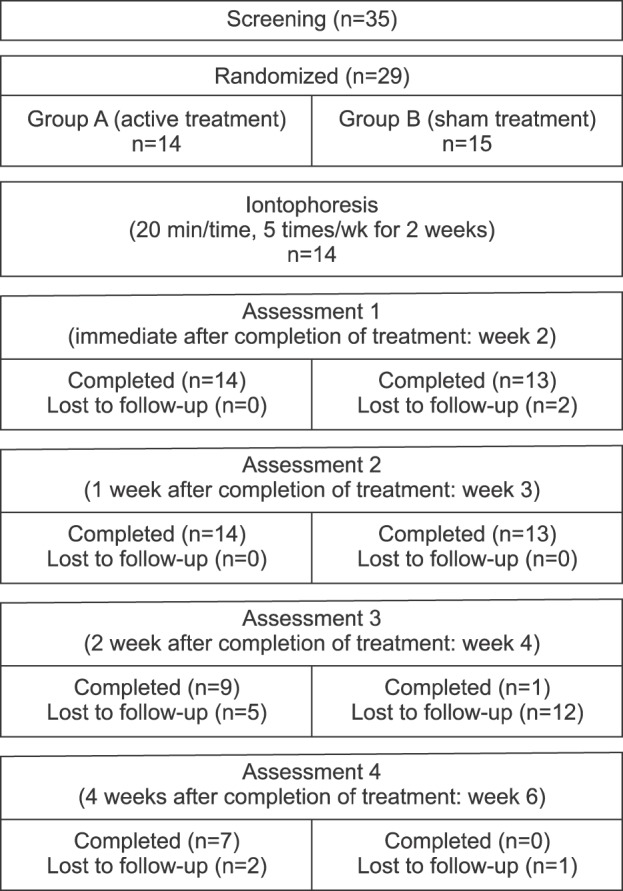
Study population
Study design
Intervention
Efficacy assessment
Table 1
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of the 27 patients who completed the study
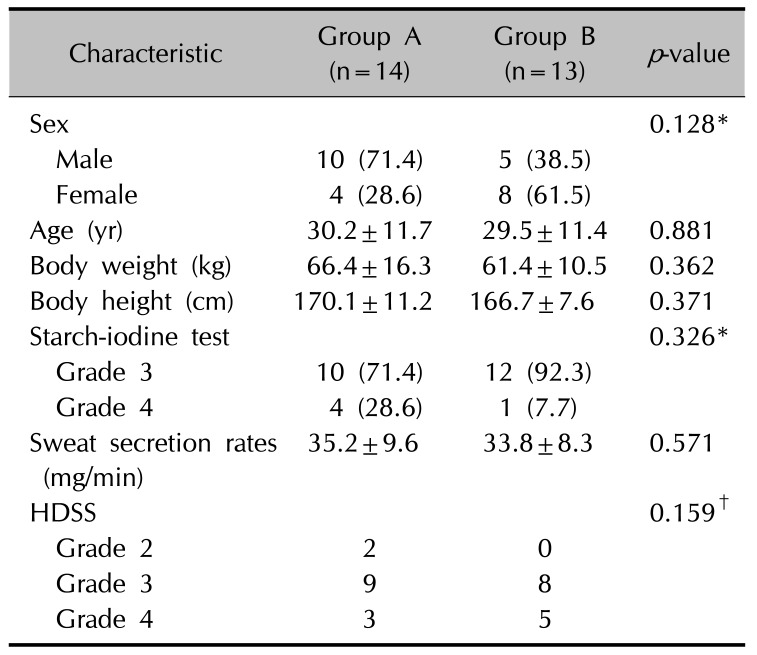
Values are presented as number (%) or mean±standard deviation. Starch-iodine test; grade 1: no reaction, grade 2: mild discoloration, grade 3: moderate discoloration, grade 4: severe discoloration. HDSS: hyperhidrosis disease severity scale; grade 1: my sweating is never noticeable and never interferes with my daily activities, grade 2: my sweating is tolerable but sometimes interferes with my daily activities, grade 3: my sweating is barely tolerable and frequently interferes with my daily activities, grade 4: my sweating is intolerable and always interferes with my daily activities. *Fisher's exact test, t-test, †linear by linear association.
Safety assessment
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Patient characteristics
Effectiveness of treatment by colorimetric measurement
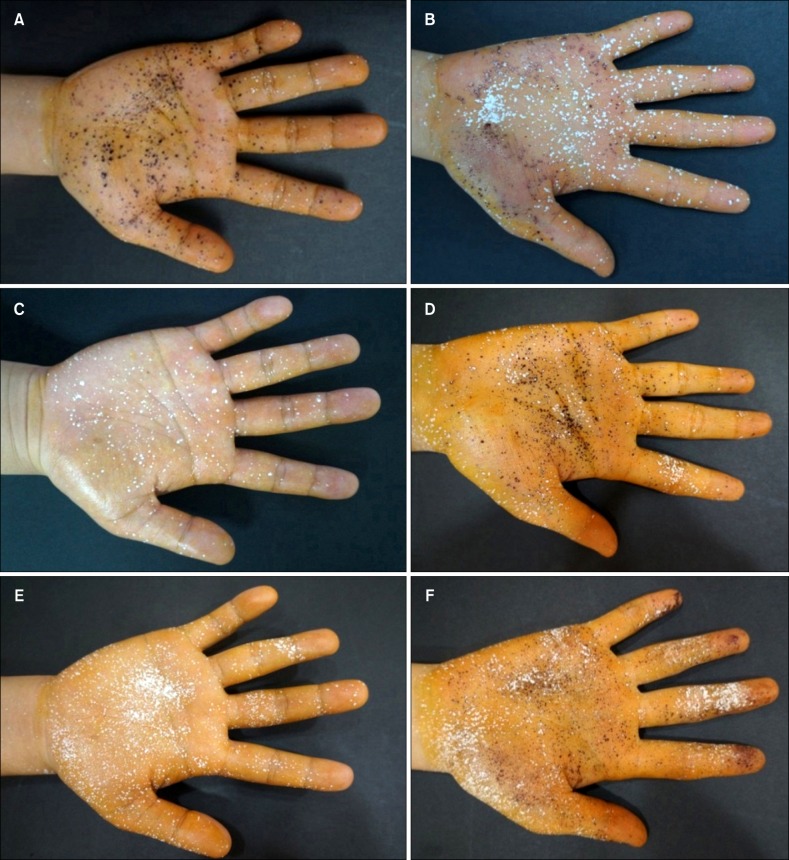 | Fig. 2Representative results of the starch-iodine test at baseline (A, B), immediate after completing the 10 times of treatment (C, D), and 1 week after completing the treatment (E, F) in patient group A and group B, respectively. |
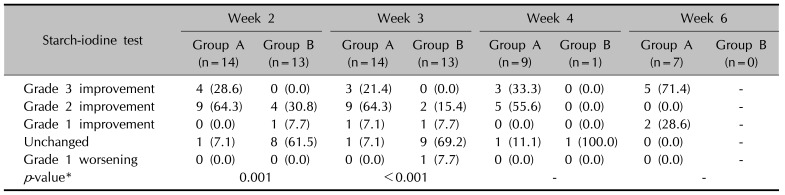
Table 2
Changes in starch-iodine test immediate after completing the 10 times of treatment (week 2) and 1 week (week 3), 2 weeks (week 4), and 4 weeks (week 6) after the completion of treatment11
Effectiveness of treatment by gravimetric measurement
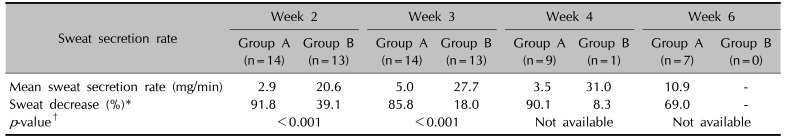
Table 3
Mean sweat secretion rate immediate after completing the 10 times of treatment (week 2) and 1 week (week 3), 2 weeks (week 4), and 4 weeks (week 6) after completion of treatment
Effectiveness of treatment based on HDSS
Table 4
Changes in hyperhidrosis disease severity scale (HDSS) immediate after completing the 10 times of treatment (week 2) and 1 week (week 3), 2 weeks (week 4), and 4 weeks (week 6) after completion of treatment
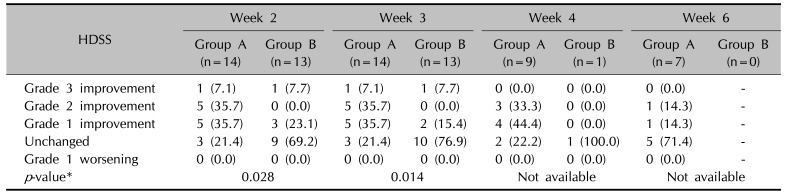
Values are presented as number (%). Grade 1: my sweating is never noticeable and never interferes with my daily activities, grade 2: my sweating is tolerable but sometimes interferes with my daily activities, grade 3: my sweating is barely tolerable and frequently interferes with my daily activities, grade 4: my sweating is intolerable and always interferes with my daily activities. *Mann-Whitney test with Bonferroni correction.
Adverse
DISCUSSION
Table 5
Efficacy of iontophoresis with direct current for hyperhidrosis according to the literature
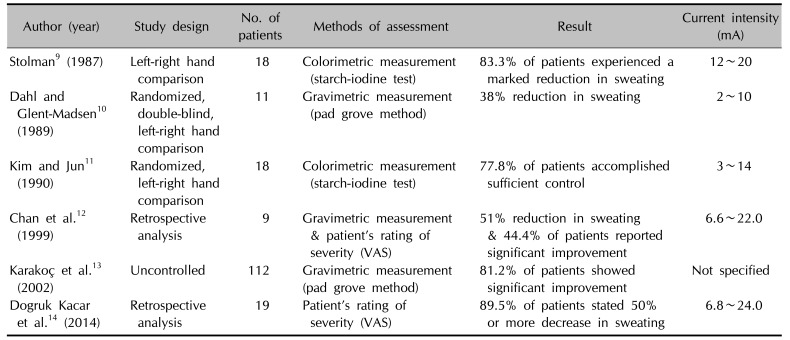
| Author (year) | Study design | No. of patients | Methods of assessment | Result | Current intensity (mA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stolman9 (1987) | Left-right hand comparison | 18 | Colorimetric measurement (starch-iodine test) | 83.3% of patients experienced a marked reduction in sweating | 12~20 |
| Dahl and Glent-Madsen10 (1989) | Randomized, double-blind, left-right hand comparison | 11 | Gravimetric measurement (pad grove method) | 38% reduction in sweating | 2~10 |
| Kim and Jun11 (1990) | Randomized, left-right hand comparison | 18 | Colorimetric measurement (starch-iodine test) | 77.8% of patients accomplished sufficient control | 3~14 |
| Chan et al.12 (1999) | Retrospective analysis | 9 | Gravimetric measurement & patient's rating of severity (VAS) | 51% reduction in sweating & 44.4% of patients reported significant improvement | 6.6~22.0 |
| Karakoç et al.13 (2002) | Uncontrolled | 112 | Gravimetric measurement (pad grove method) | 81.2% of patients showed significant improvement | Not specified |
| Dogruk Kacar et al.14 (2014) | Retrospective analysis | 19 | Patient's rating of severity (VAS) | 89.5% of patients stated 50% or more decrease in sweating | 6.8~24.0 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download