Abstract
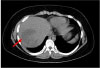
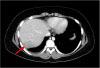
Staphylococcus epidermidis is a normal inhabitant of skin, throat, mouth, vagina, and urethra. It is not usually pathogenic, particularly in immunocompetent hosts. This report describes a case of a pyogenic liver abscess caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis in a healthy 12-year-old boy. He was admitted to Seoul St. Mary's Hospital with intermittent fever for 6 days. Findings on abdominal computed tomography (CT) showed a mass measuring 7.0×6.5 cm in the right hepatic lobe. Culture of the abscess resulted in growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis as a causative organism. The patient was successfully treated with intravenous administration of antibiotics and percutaneous drainage of the abscess.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Lee SB, Hwang KS, Cho KS, Moon DS. A case of pyogenic abscess with fever of unknown origin. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1983. 26:1145–1148.
2. Byun JL, Bae SH, Park SW. A case of liver abscess in a 10-year-old girl. Korean J Pediatr. 2010. 53:666–668.
3. Mishra K, Basu S, Roychoudhury S, Kumar P. Liver abscess in children: an overview. World J Pediatr. 2010. 6:210–216.

5. Johannsen EC, Sifri CD, Madoff LC. Pyogenic liver abscesses. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2000. 14:547–563.

6. Salahi R, Dehghani SM, Salahi H, Bahador A, Abbasy HR, Salahi F. Liver abscess in children: a 10-year single centre experience. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2011. 17:199–202.

7. Hansen PS, Schonheyder HC. Pyogenic hepatic abscess. A 10-year population-based retrospective study. APMIS. 1998. 106:396–402.

8. Kliegman RM. Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, Schor NF, Behrman RE, St. Geme JW, editors. Liver abscess. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 2011. 19th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;1404–1405.

9. Muorah M, Hinds R, Verma A, Yu D, Samyn M, Mieli-Vergani G, et al. Liver abscesses in children: a single center experience in the developed world. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006. 42:201–206.

10. Hendricks MK, Moore SW, Millar AJ. Epidemiologocal aspects of liver abscess in children in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. J Trop Pediatr. 1997. 43:103–105.

11. Pineiro-Carrero VM, Andres JM. Morbidity and mortality in children with pyogenic liver abscess. Am J Dis Child. 1989. 143:1424–1427.

12. Ferreira MA, Pereira FE, Musso C, Dettogni RV. Pyogenic liver abscess in children; some observations in the Espirito Santo State, Brazil. Arq Gastroenterol. 1997. 34:49–54.
13. Kumar A, Srinivasan S, Sharma AK. Pyogenic liver abscess in children-South Indian experiences. J Pediatr Surg. 1998. 33:417–421.

14. Todd JK. Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, Schor NF, Behrman RE, St. Geme JW, editors. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 2011. 19th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;909–910.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download