Abstract
Posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome is a clinical radiographic syndrome of many causative factors. Sudden onset headache, vomiting, altered mental status, blurred vision and seizures are main symptoms shown in posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome. In addition, it typically shows radiological findings of edema in the white matter of posterior cerebrum, being in commonly bilateral but asymmetric. We report a case of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN) presenting as posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Immediate control of hypertension resulted in rapid and complete neurological recovery.
Figures and Tables
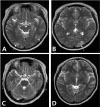 | Fig. 1Brain MRI. (A, B) T2-weighted MR image performed 1 day after seizure onset. The initial image demonstrates bilateral increased signal intensity in the occipital cortex and subcortical white matter. (C, D) T2-weighted MR image, performed 12 days after seizure onset, shows almost complete resolution of the previous abnormalities. |
References
1. Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appiginani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:494–500.

2. Rykken JB, McKinney AM. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2014; 35:118–135.

3. Kang YJ, Yang HJ, Kim JK, Jung WJ, Park CW. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in eclamptic encephalopathy. Korean J Cerebrovasc Surg. 2004; 6:177–180.
4. Kim WJ, Park SK, Choi HY, Ha SK, Park HC. Rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury associated with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Korean J Nephrol. 2011; 30:394–398.
5. Park SK, Kim YS, Jo KH. Hypertension-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2001; 19:541–553.
6. Jeong MH, Lee JH, Yum MS, Ko TS, Park YS. A case of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome during cyclosporine therapy in child with steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome. J Korean Soc Pediatr Nephrol. 2007; 11:92–99.

7. Singh GR. Glomerulonephritis and managing the risks of chronic renal disease. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2009; 56:1363–1382.

8. Pais PJ, Kump T, Greenbaum LA. Delay in diagnosis in poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. J Pediatr. 2008; 153:560–564.

9. Bae SM. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Respiratory bacteria and viruses in the aetiology of acute pharyngitis in Korea. PHWR. 2012; 5:58–62.
10. Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1038–1048.
11. Koo KS, Lee JS. Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Pediatr Neurol. 2001; 24:361–364.

12. Alehan F, Erol I, Agildere AM, Ozcay F, Baskin E, Cengiz N, et al. Posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in children and adolescents. J Child Neurol. 2007; 22:406–413.

13. Wright RR, Matthews KD. Hypertensive encephalopathy in childhood. J Child Neurol. 1996; 11:193–196.

14. Kim HN, Yoon SM, Kim JS, Lee CY. Three cases of hypertensive encephalopathy in acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: MRI findings. J Korean Soc Pediatr Nephrol. 1997; 1:73–78.
15. Park KW, Kim GM, Woo YJ. Reversible brain MRI finding in hypertensive encephalpathy with poststreptococcal acute glomerulonephritis. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 1998; 5:372–376.
16. Yun BS, Lee SJ, Kim Y, Kim KH, Jung HJ. A case of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome with post streptococcal glumerulonephritis. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2008; 16:229–234.
17. Pedraza R, Marik PE, Varon J. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a review. Crit Care Shock. 2009; 12:135–143.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download