Abstract
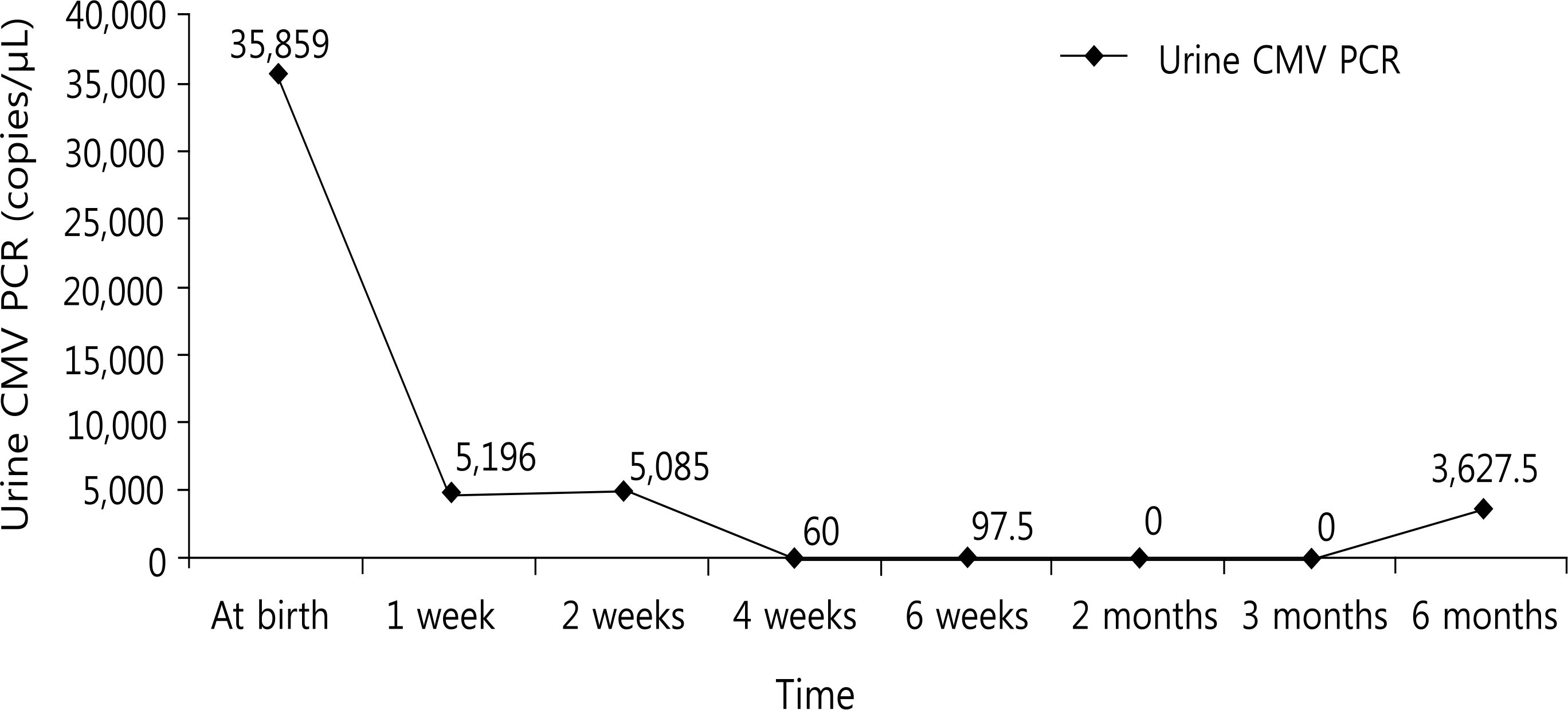
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is one of the most common congenital infections. The first case of discordant congenital CMV infection in twins occurred in Korea. A 31-year-old woman became pregnant with twins (dichorionic-diamniotic). An elective caesarean section was performed at 37 weeks. The first baby was male, weighing 2,410 g with an Apgar score of 8/9. The second baby was female, weighing 1,380 g with an Apgar score of 5/8. She had experienced intrauterine growth retardation, and presented with microcephaly, micrognathia, and joint stiffness. During the work-up for discordant twins, the second baby's serum test was positive for CMV immunoglobulin M. Her urine, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were CMV polymerase chain reaction positive. The first baby's CMV tests were negative. Ophthalmologic exam and audiometry performed on the second baby showed CMV retinitis and bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. She was treated with intravenous ganciclovir. Currently, she is bed—ridden and has significant developmental delay. Although the causes of discordant congenital CMV infection in twins are unclear, this case shows that discordant congenital CMV infection should be considered in twins with significant differences in intrauterine growth or clinical symptoms after birth.
REFERENCES
1. Wu HY, Huang SC, Huang HC, Hsu TY, Lan KC. Cytomegalovirus infection and fetal death in one monozygotic twin. Taiwan I Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 50:230–2.

2. Bodeus M, Hubinont C, Goubau P. Increased risk of cytomegalovirus transmission in utero during late gestation. Obstet Gynecol. 1999; 93(5 Pt 1):658–60.

3. Lazzarotto T, Gabrielli L, Foschini MP, Lanari M, Guerra B, Eusebi V, et al. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection in twin pregnancies: Viral load in the amniotic fluid and pregnancy outcome. Pediatrics. 2003; 112:6153–7.
4. Simioni C, Sanchez Oliveira Rde C, Moscovi T, D' Agostini Deutsch A, Cordioli E, Santos E. Twin pregnancy and congenital cytomegalovirus: case report and review. I Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013; 26:622–4.

5. Ahlfors K, Ivarsson SA, Nilsson H. On the unpredictable development of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. A study in twins. Early Hum Dev. 1988; 18:125–35.

6. Egana—Ugrinovic G, Gonce A, Garcia L, Marcos MA, Lopez M, Nadal A, et al. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection among twin pairs. I Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016; 29:3. 439–44.
7. Kawana K, Nakayama M, Yasugi T, Ishiwata M, Marumo G, Sakai M, et al. Differential clinical manifestations of congenital cytomegalovirus infection between dizygotic twins: a case report. Am J Perinatol. 2004; 21:383–6.

8. Samedi VM, Skappak C, Iantzie L, Trevenen C, Kamaluddeen M, Ekwalanga P, et al. Comparison of presentation, course, and outcome of congenital and acquired cytomegalovirus infection in twins. AIP Rep. 2016. 6zel–5.
9. Yinon Y, Yagel S, Tepperberg-Dikawa M, Feldman B, Schiff E, Lipitz S. Prenatal diagnosis and outcome of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in twin pregnancies. BIOG. 2006; 113:295–300.

10. Griesmaier E, Neubauer V, Blum S, Trawoger R, Keller M, Kiechl-Kohlendorfer U. Neurodevelopmental outcome following congenital cytomegalovirus infection in preterm infants with twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome: a case report. Klin Padiatr. 2010; 222:312–4.

11. Seguin I, Cho CT. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection in one monozygotic twin. IAMA. 1988; 260:3277.

12. Nakajima I, Sunohara D, Kawashima H. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection in monozygotic twins with twin—to—twin transfusion syndrome. Indian Pediatr. 2015; 52:429–31.

13. Nigro G, La Torre R, Anceschi MM, Mazzocco M, Cosmi EV. Hyperimmunoglobulin therapy for a twin fetus with cytomegalovirus infection and growth restriction. Am I Obstet Gynecol. 1999; 180:1222–6.

Fig. 2.
(A, B) Brain ultrasonography performed 2 days after birth shows ventriculomegaly with increased periventricular echogenicity. (C, D) Brain magnetic resonance imaging at postnatal age 4 months shows cortical malformation and extensive white matter volume loss with circumventricular calcifications (arrow) and cerebellar hypoplasia.
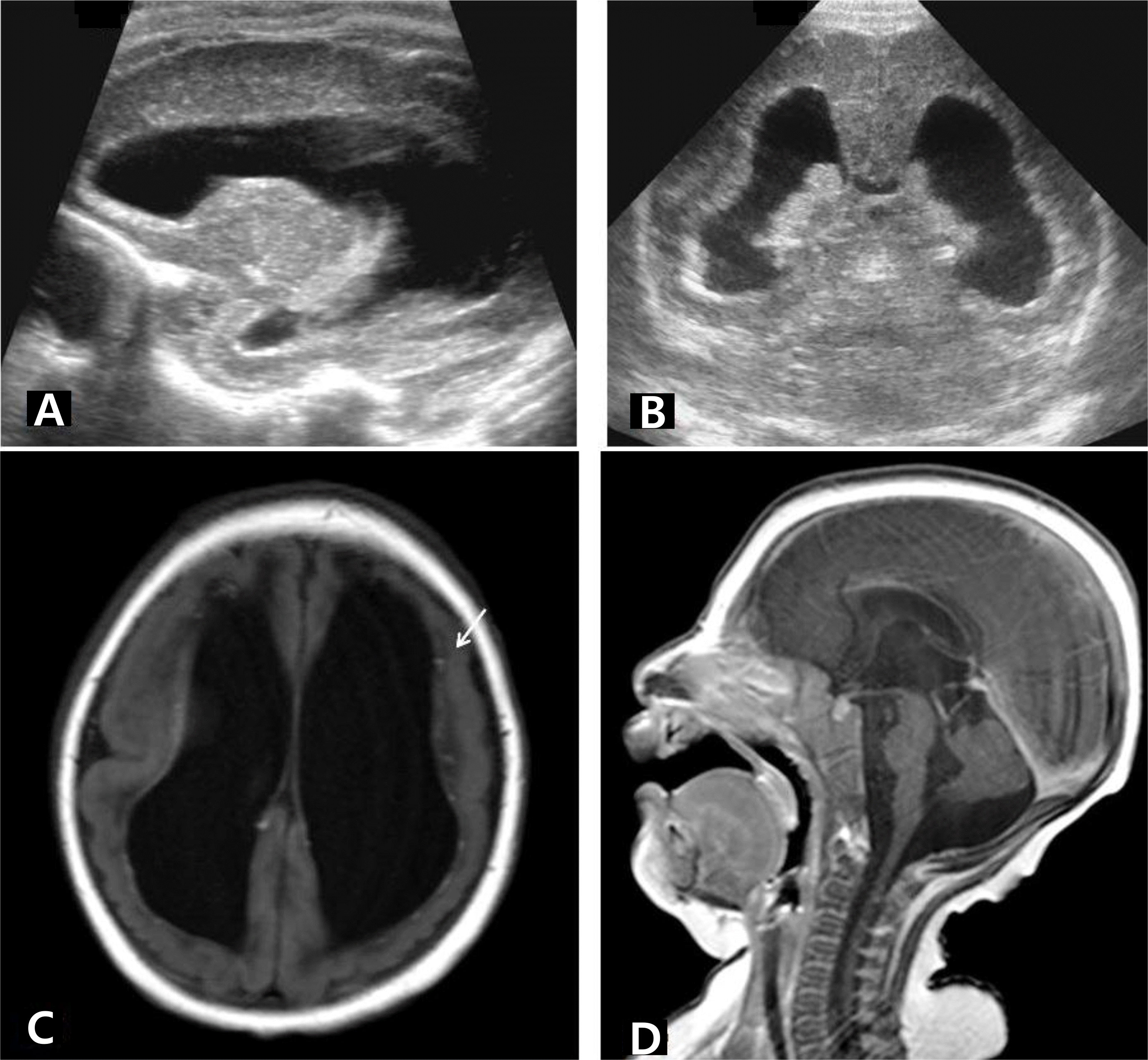
Table 1.
Case Reports of Congenital CMV Infection in Twin Pregnancies




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download