Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Flowchart for the selection of study population. The underlying diseases for heart transplantation were as follows: dilated cardiomyopathy (n=25), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (n=4), restrictive cardiomyopathy (n=4), congenital heart disease (n=7), and acute idiopathic pneumonitis (n=1).*Multiple organ transplant included heart-lung transplant (n=1); †Presence of EBV viremia was defined as at least one time of ≥457 EBV copies/mL of whole blood. Abbreviations: EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PTLD, posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder.

Fig. 2
Positron emission tomography (PET) findings of all three patients diagnosed with posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. (A) Focal hypermetabolic lesion was noted in the liver (segment IV), right kidney, and posterior nasopharyngeal wall in patient no. 1. (B) After 4 months of treatment, complete metabolic response of lymphomatous involvement in the PET was observed in patient no. 1. (C) Diffuse hypermetabolic activity of the spleen was noted with reactive hyperplasia in cervical lymph nodes and palatine tonsils in patient no. 2. (D) After 5 months of treatment, the normalized spleen in the PET was observed in patient no. 2. (E) Multiple hypermetabolic enlarged lymph nodes in bilateral cervical lymph nodes, left retropharygeal area, both supraclavicular area, aortocaval areas, and the spleen in patient no. 3. (F) After 12 months of treatment, no significant change of hypermetabolic lesions in multiple lymph nodes was observed in patient no. 3.
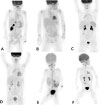
Fig. 3
Lymph node biopsy demonstrated a polymorphic posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder (patient no. 3). (A) Polymorphic infiltrate in the paracortex with a preserved nodal architecture (H&E stain, ×40). (B) The lymphoid cells vary in size and shape and degree of transformation. Atypical immunoblasts are predominantly seen in the mixture of cells (H&E stain, ×400). (C) Many of the cells are positive for Epstein- Barr virus (EBV) via in situ hybridization for EBV-encoded messenger RNA (×100). (D) Many cells express the CD20 B-cell marker (×40).
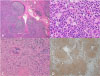
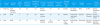
Table 1
Clinical and Demographic Characteristics of Heart Transplant Recipients according to the Presence or Absence of PTLD

Values are presented as median (range) or percentage (number/total number).
*Basic characteristics were summarized by descriptive statistics, and comparison between the non-PTLD group and the PTLD group were made using the Mann-Whitney test for continuous variables and the chi-square test or Fisher exact test for categorical variables.
†EBV viremia was defined as ≥457 EBV copies/mL of whole blood. Clinically significant high level EBV viremia was defined as ≥10,000 copies/mL at least two times and low level viremia was defined as 457 to 10,000 copies/mL at least one time.
‡CMV viremia was defined as ≥500 CMV copies/mL of whole blood.
Abbreviations: PTLD, posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; VCA, viral capsid antigen; IgG, immunoglobulin G; CMV, cytomegalovirus.
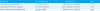
Table 2
Clinical Characteristics for the Patients Who Developed PTLD
*EBV viremia was defined as ≥457 EBV copies/mL of whole blood. However, all of the three patients had high initial EBV levels ≥10,000 copies/mL.
Abbreviations: PTLD, posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder; EBV, Epstein-Barr Virus; CMV, cytomegalovirus; DLBCL, diffuse large B cell lymphoma; R-CHOP, CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) with rituximab; DCMP, dilated cardiomyopathy; PET, positron emission tomography; RIS, reduction of immunosuppression; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download