Dear Editor:
The postnatal hair follicle undergoes a cycle of anagen, catagen, and telogen and reciprocal interactions between the epithelium and mesenchyme are essential for hair growth and cycling12. Factors from the follicular dermal papilla (DP) stimulate proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes into the hair shaft during anagen13. These factors include insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and keratinocyte growth factor (KGF). Transition from anagen to catagen is characterized by apoptotic cell death in follicular keratinocytes and is driven by transforming growth factor (TGF) β1, TGF β2, and dickkopf 1 (DKK-1).
A recent study showed that tianeptine, an anti-depressant, improved hair growth and decreased apoptosis in the hair follicles in alopecia areata-like lesions, thus inhibiting catagen induction in mice4. Since DKK-1 is inducible by dihydrotestosterone (DHT), upregulated in the bald scalp compared to that in the haired scalp, and promotes catagen progression in mice56, we aimed to investigate whether tianeptine can attenuate the hair growth inhibitory effect of DKK-1 on human hair follicles. To test this idea, we employed a hair-follicle organ culture system.
Biopsy specimens were obtained from the haired scalps of men with male pattern baldness during hair transplantation. All of the described studies were approved by the medical ethical committee of the Kyungpook National University Hospital (Daegu, Korea; IRB no. KNUH 2013-02-001-001) and informed written consent was obtained from the patients. Hair follicles were isolated under a binocular microscope with forceps as described previously78 and maintained in Williams E media (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/ml streptomycin, 10 ng/ml hydrocortisone, and 10 µg/ml insulin, and the follicles were treated with various concentration of tianeptine (Sigma) and DKK-1 (R&D systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). DPs were isolated from the dissected hair bulbs, transferred onto bovine type 1 collagen-coated plastic dishes, and cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) supplemented with 20% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; Hyclone), penicillin (100 U/ml), and streptomycin (100 µg/ml). Subsequently, the DP cells were sub-cultured and maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS.
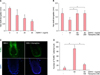
We found that DKK-1 inhibits hair shaft elongation as shown in Fig. 1A. This data is in line with our previous finding of hair growth-inhibitory action of DKK-16. Tianeptine attenuated DKK-1-mediated hair growth inhibition. The average hair shafts growth after 6 days was 0.79 mm in the presence of 50 ng/ml recombinant human DKK-1 (rhDKK-1), whereas that in the presence of 100 nM and 200 nM tianeptine together with 50 ng/ml rhDKK-1, was 1.24 and 1.26 mm, respectively (Fig. 1B). We also observed dramatic increase in the number of TUNEL-positive cells undergoing apoptosis in follicular keratinocytes in the presence of 50 ng/ml rhDKK-1 for 3 days (Fig. 1C). This result is consistent with our previous finding of increment of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive cells and induction of pro-apoptotic protein Bax when outer root sheath (ORS) cells are treated with rhDKK-156. In addition, we observed that tianeptine attenuates DKK-1-induced apoptosis in human hair follicles (Fig. 1C, D).
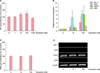
To investigate the mechanism of tianeptine-mediated attenuation of DKK-1-induced hair growth inhibition, we first investigated the effects of tianeptine on DP cells. We observed that 10 nM and 100 nM tianeptine stimulated the viability of cells by 118% and 125%, respectively, compared to the control (Fig. 2A). We next investigated whether tianeptine induces paracrine factors in DP cells. DP cells were treated with 10 nM and 100 nM tianeptine for 24 h, followed by measurement of the levels of VEGF, KGF, HGF, and IGF-1 mRNA expression by real-time (RT) polymerase chain reaction (PCR). All the RT-PCR reactions were performed as described previously9 using SYBR Green premix (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), using 100 ng of complementary DNA and 10 µM primers. We observed that the levels of all four growth factors significantly increased after treatment with tianeptine as examined (Fig. 2B). In contrast, we observed no change in cell viability of ORS cells in the presence of tianeptine (Fig. 2C). In addition, we observed no detectable expression of IGF-1, HGF, and KGF regardless of the treatment of tianeptine and the level of VEGF did not change after treatment with tianeptine in ORS cells (Fig. 2D). RT-PCR conditions and primer sequences are described in the figure legend.
Our results in this study show that tianeptine attenuates DKK-1-mediated inhibition of hair shaft elongation in cultured human hair follicles. In addition, DKK-1-mediated apoptosis of follicular keratinocytes was attenuated by tianeptine treatment. Since DKK-1 is inducible by DHT in DP cells of balding scalp and promotes catagen progression regression56, our data suggest that tianeptine prevent premature anagen-to-catagen transition in male pattern baldness. These data, together with promotion of viability of DP cells and upregulation of growth factors such as IGF-1, HGF, VEGF, and KGF, suggest that tianeptine or its derivatives may have potential for treating and preventing hair loss by regulating human hair cycling.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download