Abstract
Fluconazole is a triazole-based first-generation antifungal agent and has excellent effects on candidiasis and cryptococcosis. Hyper-sensitivity has been reported as a side effect of fluconazole. A 76-year-old female patient used fluconazole for consolidation therapy for cryptococcal meningitis, but showed delayed hypersensitivity with skin rashes and itching sensation of the whole body. For desensitization, was attempted by administering 12-step, 1:1 fluconazole solutions were administered intravenously at sequentially increasing infusion rates. After successful quick desensitization to fluconazole, fluconazole was continuously used as a consolidation therapy for cryptococcal meningitis. We herein report a case of delayed hypersensitivity reaction to fluconazole in consolidation therpy with cryptococcal meningitis who successfully completed desensitization.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Pappas PG, Kauffman CA, Andes DR, Clancy CJ, Marr KA, Ostrosky-Zeichner L, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016; 62:e1–50.

2. Perfect JR, Dismukes WE, Dromer F, Goldman DL, Graybill JR, Hamill RJ, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of cryptococcal disease: 2010 update by the infectious diseases society of america. Clin Infect Dis. 2010; 50:291–322.

3. Arndt CA, Walsh TJ, McCully CL, Balis FM, Pizzo PA, Poplack DG. Fluconazole penetration into cerebrospinal fluid: implications for treating fungal infections of the central nervous system. The Journal of infectious diseases. 1988; 157:178–80.

4. Sugar AM, Saunders C. Oral fluconazole as suppressive therapy of disseminated cryptococcosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988; 85:481–9.

5. Scherer K, Brockow K, Aberer W, Gooi JH, Demoly P, Romano A, et al. Desensitization in delayed drug hypersensitivity reactions: an EAACI position paper of the Drug Allergy Interest Group. Allergy. 2013; 68:844–52.
6. Yoshizawa S, Yasuoka A, Kikuchi Y, Honda M, Gatanaga H, Tachikawa N, et al. A 5-day course of oral desensitization to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (T/S) in patients with human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infection who were previously intolerant to T/S. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000; 85:241–4.

7. Kim S, Lim KH, Kang MG, Park HK, Cho SH, Min KU, et al. Successful desensitization of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in Stenostrophomon-as maltophilia osteomyelitis. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2014; 2:218–21.
8. Lee AR, Kim SJ, Kim J, Park JH, Lee JK, Kim JY, et al. Successful desensitization for antitubercular drugs. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:395–9.

9. Yoon D, Ahn H, Kim SY, Hwang SJ, Park HK, Kang HR. Successful rapid desensitization to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-induced delayed hypersensitivity. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015; 3:155–8.

10. Teraki Y, Shiohara T. Successful desensitization to fixed drug eruption: the presence of CD25+CD4+ T cells in the epidermis of fixed drug eruption lesions may be involved in the induction of desensitization. Dermatology. 2004; 209:29–32.

11. Craig TJ, Peralta F, Boggavarapu J. Desensitization for fluconazole hyper-sensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996; 98:845–6.

12. Jariwala S, Vernon N, de Vos G. A novel method of desensitization for fluconazole hypersensitivity in a patient with AIDS. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011; 106:542–3.

13. Randolph C, Kaplan C, Fraser B. Rapid desensitization to fluconazole (Diflucan). Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100:616–7.

14. Barbaud A. Drug patch testing in systemic cutaneous drug allergy. Toxi-cology. 2005; 209:209–16.

Go to : 
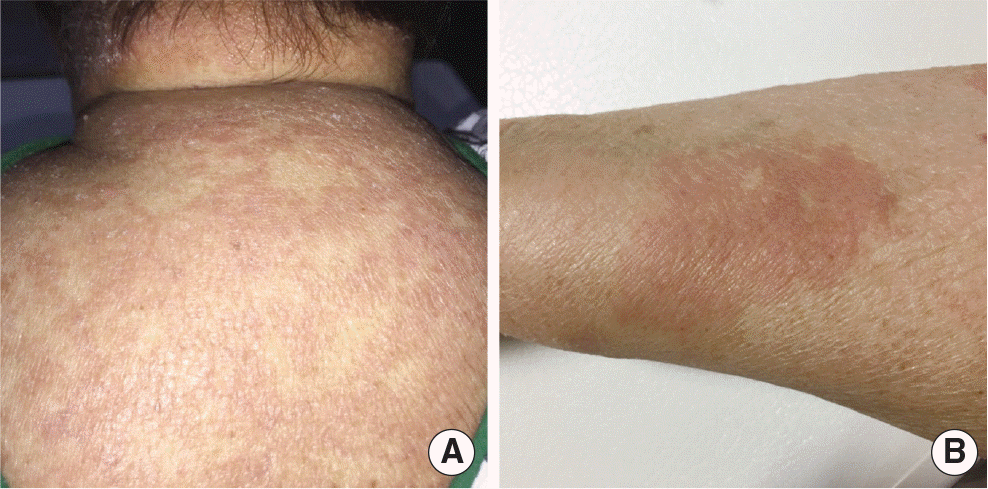 | Fig. 1.Clinical features of the fluconazole-induced delayed type hypersensitivity. There was diffuse patch eruption involving the trunk (A) and extremities (B) with itching and blanching, which continued for several days. |
Table 1.
The preparation of 1-bottle solution used in the rapid desensitization protocol
| Fluconazole (mg) | DW (mL) | Preparation protocol | Concentration (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 250 | 400 mg+DW 250 mL | 1.6 |
Table 2.
Desensitization protocol used in the current case of the fluconazole-induced delayed hypersensitivity




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download