Abstract
Purpose
Serum vitamin D (25-hydroxyvitamin D, 25[OH] D) and interleukin-31 (IL-31) are related to atopic dermatitis, but their relationship with allergic rhinitis is unclear. The purpose of this study was to compare the levels of serum IL-31 and 25 (OH) D between the allergic rhinitis (AR), nonallergic rhinitis (NAR), and control groups and to investigate the relationship between IL-31 and 25 (OH) D.
Methods
We recruited 59 children with only rhinitis and 33 controls without any allergic diseases. Serum IL-31 and 25(OH) D levels were assayed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and high-performance liquid chromatography, respectively. The patients were considered to have atopic sensitization if the levels of serum specific IgE to inhalant allergens as assessed using immu-noCAP were ≥0.35 IU/mL or if they tested positive for one or more allergens by the skin prick test.
Results
Of children with rhinitis, 25 had nonatopy (NAR), and 34 children had atopy (AR). Serum 25(OH) D levels were significantly lower in the rhinitis group than in the control group, while there was no significant difference serum 25(OH) D levels between the AR and NAR groups. Children with rhinitis demonstrated higher serum IL-31 levels than controls; however, there was no difference in serum IL-31 levels between the AR and NAR groups. Serum 25(OH) D levels were inversely correlated with serum IL-31 levels and blood eosinophil counts. On the other hand, serum 25(OH) D levels were not correlated with total serum IgE levels.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Dogru M, Suleyman A. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels in children with allergic or nonallergic rhinitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016; 80:39–42.

2. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63(Suppl 86):8–160.
3. Kim Y, Seo JH, Kwon JW, Lee E, Yang SI, Cho HJ, et al. The prevalence and risk factors of allergic rhinitis from a nationwide study of Korean elementary, middle, and high school students. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015; 3:272–80.

5. Litonjua AA, Weiss ST. Is vitamin D deficiency to blame for the asthma epidemic? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:1031–5.

6. Riverin BD, Maguire JL, Li P. Vitamin D supplementation for childhood asthma: a systematic review and metaanalysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0136841.

7. Beckhaus AA, Garcia-Marcos L, Forno E, Pacheco-Gonzalez RM, Celedón JC, Castro-Rodriguez JA. Maternal nutrition during pregnancy and risk of asthma, wheeze, and atopic diseases during childhood: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Allergy. 2015; 70:1588–604.

8. Cheng HM, Kim S, Park GH, Chang SE, Bang S, Won CH, et al. Low vitamin D levels are associated with atopic dermatitis, but not allergic rhinitis, asthma, or IgE sensitization, in the adult Korean population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 133:1048–55.

9. Yao TC, Tu YL, Chang SW, Tsai HJ, Gu PW, Ning HC, et al. Suboptimal vitamin D status in a population-based study of Asian children: prevalence and relation to allergic diseases and atopy. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e99105.

10. Bener A, Ehlayel MS, Bener HZ, Hamid Q. The impact of Vitamin D deficiency on asthma, allergic rhinitis and wheezing in children: an emerg-ing public health problem. J Family Community Med. 2014; 21:154–61.

11. Arshi S, Ghalehbaghi B, Kamrava SK, Aminlou M. Vitamin D serum levels in allergic rhinitis: any difference from normal population? Asia Pac Allergy. 2012; 2:45–8.

12. Yoon SH, Kim JY, Kim YH, Park YA, Sol IS, Kim MJ, et al. Association between the serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and allergic rhinitis in Korean children. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016; 4:423–8.

13. Liu W, Luo R, Chen Y, Sun C, Wang J, Zhou L, et al. Interleukin-31 pro-motes helper T cell type-2 inflammation in children with allergic rhinitis. Pediatr Res. 2015; 77:20–8.

14. Mohd Ashari NS, Syuhada Mohd Amin SN, Wan Abdul Hamid WZ, Musa M, Rahman AA, Mohamad I. Determination of interleukin 31 (IL-31) serum levels in allergic rhinitis patients. Int J Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2014; 1:69–72.

15. Dillon SR, Sprecher C, Hammond A, Bilsborough J, Rosenfeld-Franklin M, Presnell SR, et al. Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces dermatitis in mice. Nat Immunol. 2004; 5:752–60.

16. Sonkoly E, Muller A, Lauerma AI, Pivarcsi A, Soto H, Kemeny L, et al. IL-31: a new link between T cells and pruritus in atopic skin inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:411–7.

17. Yang YS, Lee JW, Shim JW, Kim DS, Jung HL, Park MS, et al. Relationship between serum interleukin-31/25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and the severity of atopic dermatitis in children. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015; 3:396–401.

18. Bonanno A, Gangemi S, La Grutta S, Malizia V, Riccobono L, Colombo P, et al. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, IL-31, and IL-33 in children with allergic disease of the airways. Mediators Inflamm. 2014; 2014:520241.

19. Ruonan Chai BL, Feifei QI. IL-31, IL-33, and TSLP expression and relation to severity of asthma and rhinitis in Chinese allergic patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017; 10:1774–82.
20. Kanda N, Hau CS, Tada Y, Sato S, Watanabe S. Decreased serum LL-37 and vitamin D3 levels in atopic dermatitis: relationship between IL-31 and oncostatin M. Allergy. 2012; 67:804–12.

21. Modh D, Katarkar A, Thakkar B, Jain A, Shah P, Joshi K. Role of vitamin D supplementation in allergic rhinitis. Indian J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 28:35–9.

Go to : 
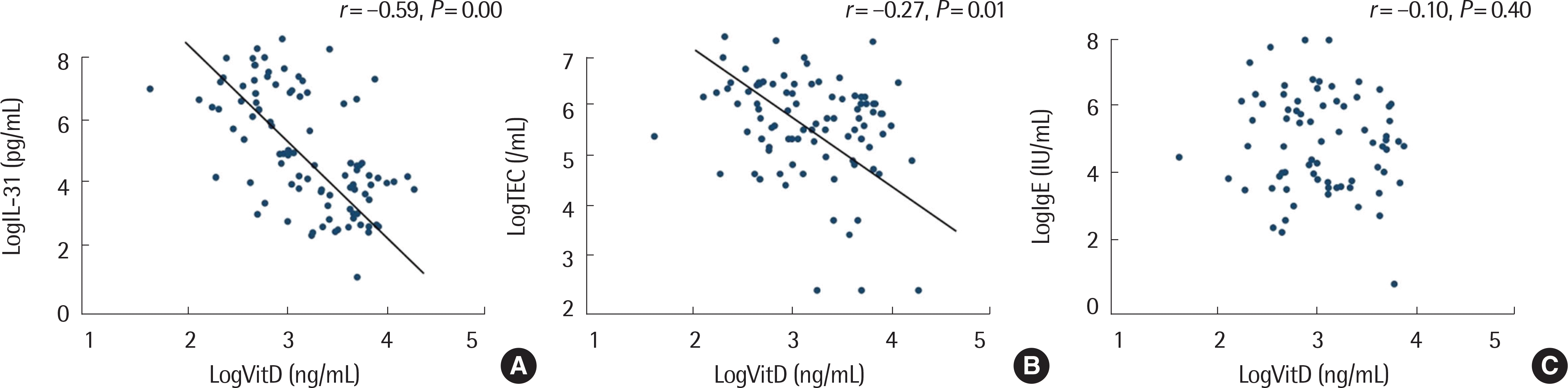 | Fig. 1.Correlations between serum logVitD and logIL-31 levels (A), between serum logVitD and logTEC levels (B), and between serum logVitD and logIgE levels (C). There were significant negative correlations between logVitD and logIL-31 levels and between logVitD and logTEC levels. Levels of logVitD showed no correlation to logIgE levels. LogTEC, logarithmic transformation of blood total eosinophil count; LogIgE, logarithmic transformation of serum total IgE; LogVitD, logarithmic transformation of serum vitamin D; LogIL-31, logarithmic transformation of serum IL-31. |
Table 1.
Characteristics of study subjects
Table 2.
Comparison of laboratory characteristics between rhinitis and control
Table 3.
Comparison of laboratory characteristics between nonallergic and allergic rhinitis




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download