Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
References
 | Fig. 1.53-year-old female with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. On axial image of postcontrast T1 weighted image (A), there is a suspicious enhancing nodular lesion in left frontal area confused with cortical vessels (arrow). And axial image of precontrast fluid attenuated inversion recovery (B) shows perilesional edema around the lesion (arrow). Therefore the lesion was assessed as metastasis, not a cortical vessel. |
 | Fig. 2.57-year-old male with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Axial image of postcontrast T1 weighted image (A) shows suspicious enhancing nodular lesion in left cerebellar hemisphere (arrow). But axial images of precontrast FLAIR (B), 1st postcontrast FLAIR (C), and 2nd postcontrast FLAIR (D) do not show abnormal enhancement at the same location. Therefore the lesion was assessed as pulsating artifact, not a metastasis. FLAIR = fluid attenuated inversion recovery |
 | Fig. 3.78-year-old male with brain metastases from colon cancer. Axial image of postcontrast T1 weighted image (A) shows a subtle enhancing nodule in right frontal cortex (arrow). And axial images of 1st postcontrast FLAIR (B) and 2nd postcontrast FLAIR (C) also show strong rim-enhancing nodule at the same location (arrows). Therefore the lesion was assessed as metastasis. FLAIR = fluid attenuated inversion recovery |
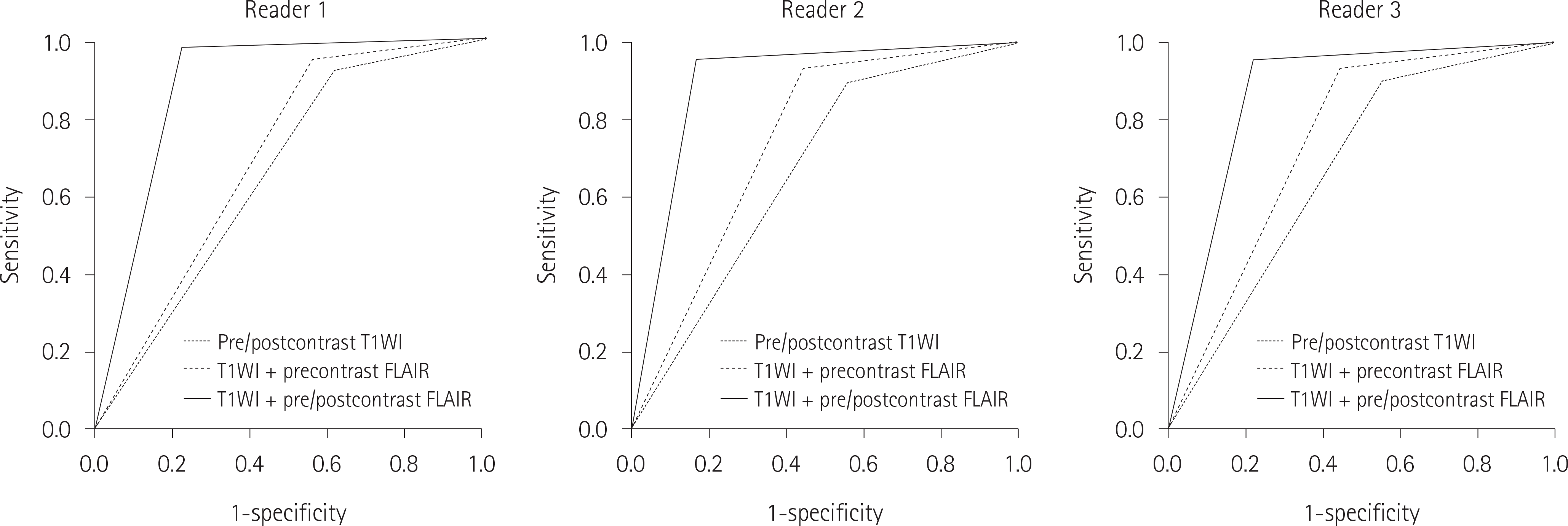 | Fig. 4.ROC curves for detectability of small brain metastases of three readers. The area of under ROC curve is significantly greater in T1WI + pre/ postcontrast FLAIR as compared to that in pre/postcontrast T1WI or T1WI + precontrast FLAIR. FLAIR = fluid attenuated inversion recovery, ROC = receiver operating characteristic, T1WI = T1 weighted image |
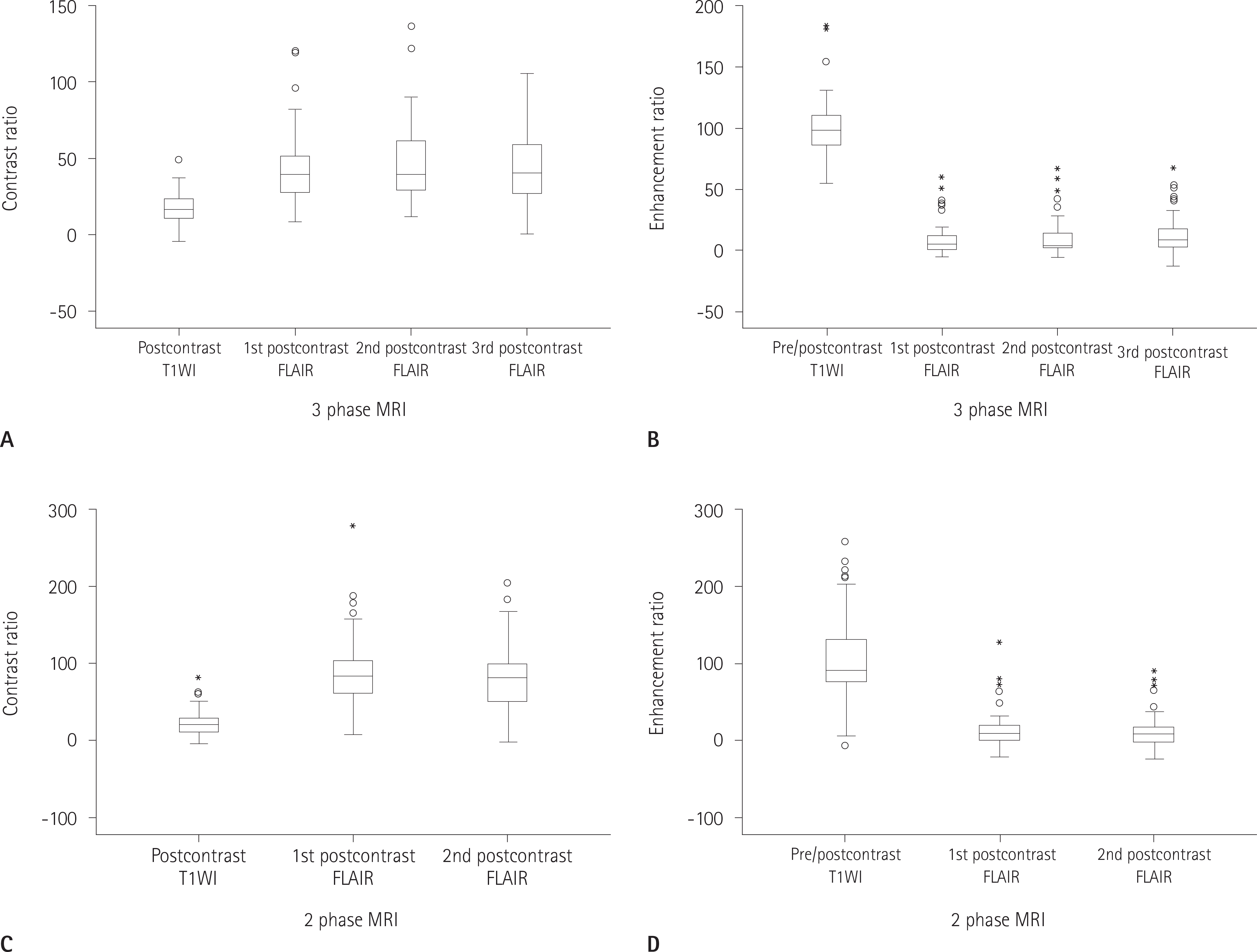 | Fig. 5.Comparison of CRs and ERs on multiphase contrast enhanced FLAIR MRI. In 3-phase MRI (A, B), CRs of small brain metastases in post-contrast T1WI are significantly lower than those in postcontrast FLAIR (p < 0.001) and ERs in pre/postcontrast T1WI are significantly greater than those in pre/postcontrast FLAIR (p < 0.001). In 2-phase MRI (C, D), the result is not different from the above. And there is no significant difference between CRs and ERs with time delays in both 2-phase and 3-phase contrast enhanced FLAIR MRI. CR = contrast ratio, ER = enhancement ratio, FLAIR = fluid attenuated inversion recovery, MRI = magnetic resonance imaging, T1WI = T1 weighted image |
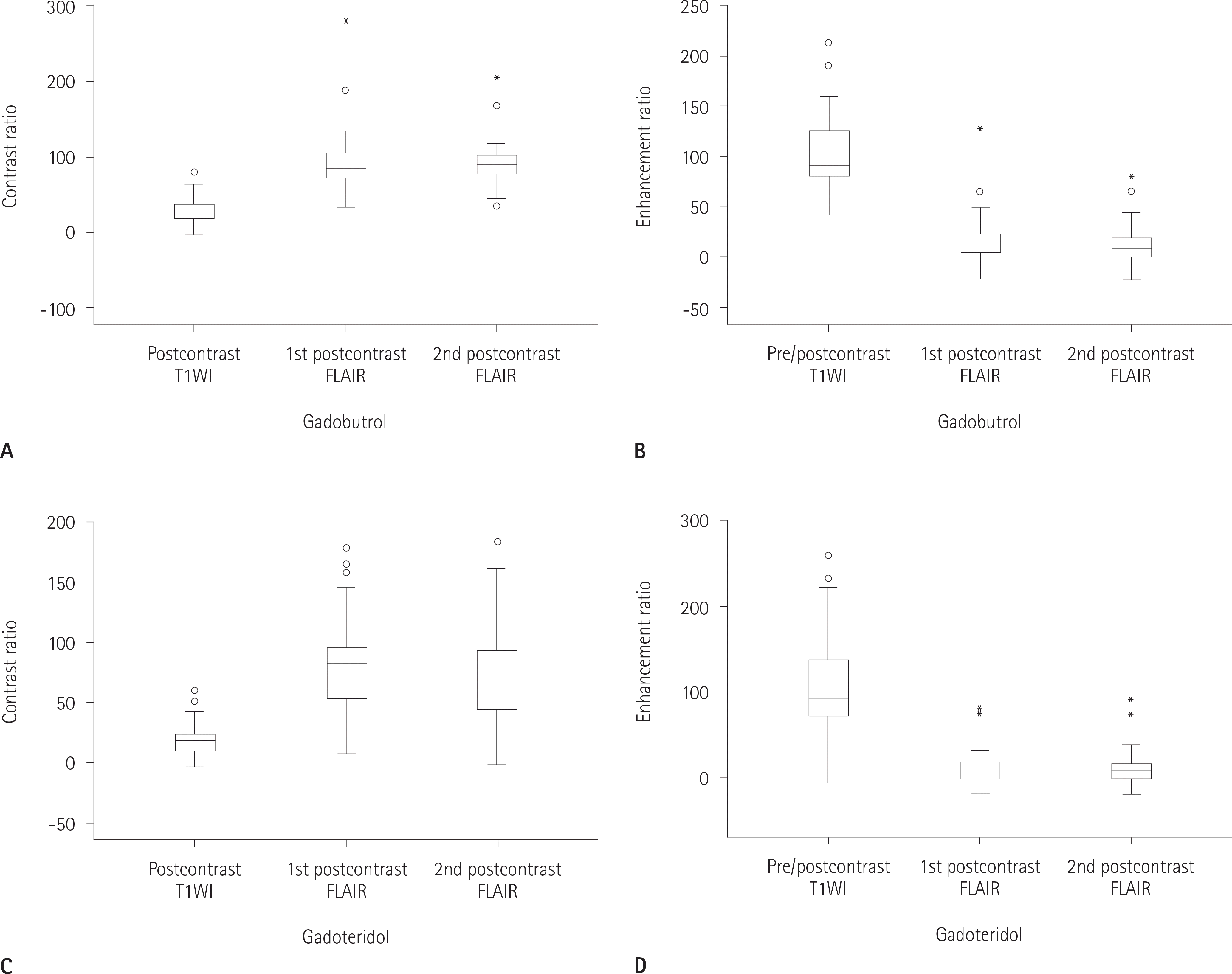 | Fig. 6.Comparison of CRs and ERs for contrast media on 2 phase contrast enhanced FLAIR magnetic resonance imaging. When gadobutrol is used (A, B), CRs of small brain metastases in postcontrast T1WI are significantly lower than those in postcontrast FLAIR (p < 0.001) and ERs in pre/postcontrast T1WI are significantly greater than those in pre/postcontrast FLAIR (p < 0.001). When gadoteridol is used (C, D), the result is not different from the above. When gadobutrol and gadoteridol are used, there is no difference in CRs and ERs according to time delays. CR = contrast ratio, ER = enhancement ratio, FLAIR = fluid attenuated inversion recovery, T1WI = T1 weighted image |
Table 1.
Because the results of 1st, 2nd, and 3rd postcontrast FLAIR are the same, the results of 2nd and 3rd postcontrast FLAIR are not mentioned in the table. Post FLAIR = 1st (or 2nd or 3rd) postcontrast fluid attenuated inversion recovery, Post T1WI = postcontrast T1 weighted image, Pre FLAIR = precontrast fluid attenuated inversion recovery, Pre T1WI = precontrast T1 weighted image
Table 2.
Table 3.
CE-FLAIR = contrast enhanced fluid attenuated inversion recovery, CR = contrast ratio, ER = enhancement ratio, SD = standard deviation, T1WI = T1 weighted image, 1 = precontrast T1WI + postcontrast T1WI, 2 = precontrast FLAIR + 1st postcontrast FLAIR, 3 = precontrast FLAIR + 2nd postcontrast FLAIR, 4 = precontrast FLAIR + 3rd postcontrast FLAIR




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download