This article has been
cited by other articles in ScienceCentral.
Abstract
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) is a hypersensitivity reaction characterized by maculopapular rash, exfoliative dermatitis, lymphadenopathy, fever, eosinophilia, and involvement of internal organs. Evidence for reactivation of herpes family viruses has been observed in some DRESS patients, and activated CD8+ T lymphocytes are largely directed against Epstein-Barr virus. Here, we report two cases complicated with this infection. Both patients received antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These patients manifested clinically with high fever, facial edema, diffuse pruritic erythroderma and maculopapules over the entire body, purpuric rashes in both lower limbs and lymphadenopathy of cervical and inguinal nodes. Laboratory tests revealed abnormal liver function, blood eosinophils, and ferritin levels. The patients recovered completely; however, the female patient developed hemophagocytic syndrome on the 15th day of illness. She developed new itchy rash, and laboratory tests rapidly worsened with fibrinogen levels dramatically reduced to 0.61 g/L. Bone marrow aspiration revealed an increased number of macrophages with hemophagocytosis and a reversed CD4/CD8 ratio of 0.45. These cases suggest that human herpes virus and coagulation function evaluations are necessary in DRESS patients.
Go to :

Keywords: Cytomegalovirus, Drug hypersensitivity syndrome, Epstein-Barr virus infections, Lymphohistiocytosis, hemophagocytic, Sulfasalazine
INTRODUCTION
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) affects multiple organs and is occasionally associated with activation of viruses, such as human herpes virus (HHV)-6, HHV-7, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and cytomegalovirus, in the setting of drug hypersensitivities
1. In some cases, these active viruses can cause further hematological disorders. Here, we report two cases of such complications.
Go to :

CASE REPORT
Both cases were in middle age and suffered from high fever for 9~21 days followed by onset of generalized pruritic eruptions. Before the skin rashes appeared, both patients received antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (
Table 1). Dermatological examinations are described in
Fig. 1A, B, D, E. Lymphadenopathies were revealed in cervical and inguinal areas, and splenomegaly was also present in both patients. Skin pathology (
Fig. 1C, F) and laboratory findings (
Table 1) are provided. Due to positive findings of EBV-immunoglobulin M or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) copies of EBV, both patients were diagnosed as DRESS complicated with EBV infection. After treatment with methylprednisolone (40 mg/d), ganciclovir (250 mg, every 12 hours), and intravenous immunoglobins (20 g/d) for case 1 or plasma (200 ml/d) for case 2, the second patient recovered with darkening and diminishing of the eruption and a reduction of aminotransferases. However, on the fifteenth day of illness, case 1 developed new itchy rashes over the body and worsened purpura on extremities. Complete blood counts revealed a leukocyte count of 6.26×10
9/L and a platelet count of 46×10
9/L. Blood chemistry revealed progressively impaired liver and coagulation function (alanine aminotransferase 1,141 IU/L, aspartate aminotransferase 3,046 IU/L, lactate dehydrogenase 2,807 IU/L, prothrombin time 21.8 seconds (normal range: 9.0~11.5 seconds), activated partial thromboplastin time 49.2 seconds (normal range: 26.9~37.6 seconds), fibrinogen 0.61 g/L (normal range: 2~4 g/L). A bone marrow aspiration revealed an increased number of macrophages with hemophagocytosis and a reversed CD4/CD8 ratio (0.45). Hemophagocytic syndrome was timely diagnosed based on the above characteristics for this case. Methylprednisolone was increased to 60 mg/d, and plasma infusion was continued daily. The patient's organ dysfunctions recovered gradually, and the skin eruptions were eventually reduced the following week.
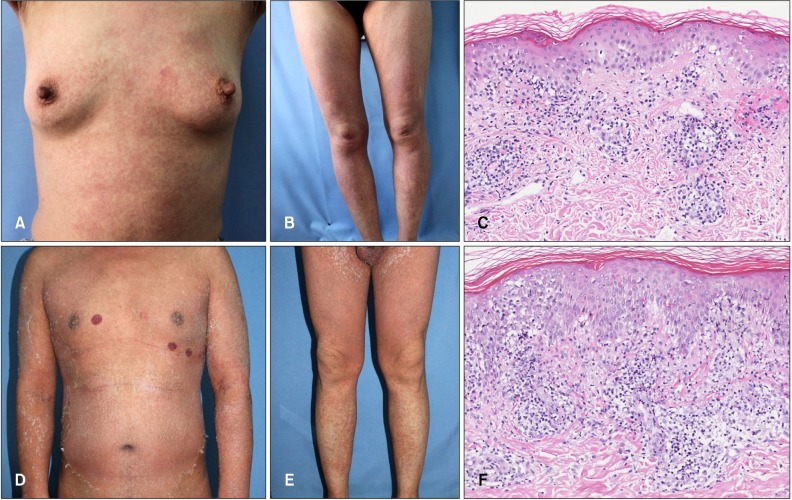 | Fig. 1Diffuse red maculopapules on the trunk and extremities of case 1 (A, B) and confluent erythroderma in case 2 (D, E). Liquefaction of basal cells, lymphocytes and sparse eosinophils in the upper dermis of case 1 (C) and lichenoid dermatitis in case 2 (F) as assessed by skin pathology (H&E; C, F: ×200).
|
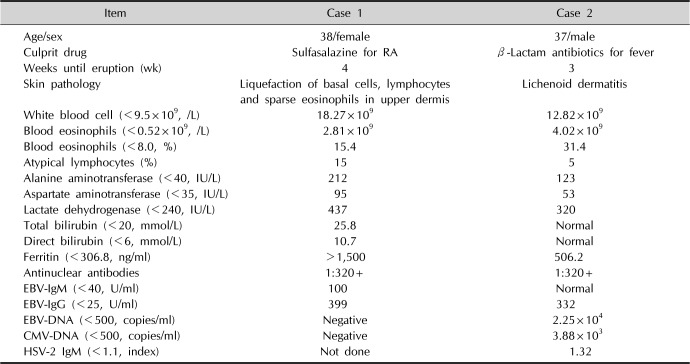
Table 1
Clinical summary of the 2 cases upon admission
|
Item |
Case 1 |
Case 2 |
|
Age/sex |
38/female |
37/male |
|
Culprit drug |
Sulfasalazine for RA |
β-Lactam antibiotics for fever |
|
Weeks until eruption (wk) |
4 |
3 |
|
Skin pathology |
Liquefaction of basal cells, lymphocytes and sparse eosinophils in upper dermis |
Lichenoid dermatitis |
|
White blood cell (<9.5×109, /L) |
18.27×109
|
12.82×109
|
|
Blood eosinophils (<0.52×109, /L) |
2.81×109
|
4.02×109
|
|
Blood eosinophils (<8.0, %) |
15.4 |
31.4 |
|
Atypical lymphocytes (%) |
15 |
5 |
|
Alanine aminotransferase (<40, IU/L) |
212 |
123 |
|
Aspartate aminotransferase (<35, IU/L) |
95 |
53 |
|
Lactate dehydrogenase (<240, IU/L) |
437 |
320 |
|
Total bilirubin (<20, mmol/L) |
25.8 |
Normal |
|
Direct bilirubin (<6, mmol/L) |
10.7 |
Normal |
|
Ferritin (<306.8, ng/ml) |
>1,500 |
506.2 |
|
Antinuclear antibodies |
1:320+ |
1:320+ |
|
EBV-IgM (<40, U/ml) |
100 |
Normal |
|
EBV-IgG (<25, U/ml) |
399 |
332 |
|
EBV-DNA (<500, copies/ml) |
Negative |
2.25×104
|
|
CMV-DNA (<500, copies/ml) |
Negative |
3.88×103
|
|
HSV-2 IgM (<1.1, index) |
Not done |
1.32 |

Go to :

DISCUSSION
DRESS is fatal in approximately 10% of cases
2. The most culprit drugs are allopurinol, carbamazepine, and sulfasalazine, and the condition is potentially worsened by β-lactam antibiotics
3. Concomitantly, DRESS is possibly associated with proliferation of activated CD8+ T lymphocytes directed against viral antigens derived mostly from herpes viruses such as EBV
4. Astonishingly, in a French report, 16 out of 38 (42%) patients experienced EBV reactivation
5. By contrast, a recent study including 34 Japanese DRESS patients demonstrated that less than 10% of patients presented with increased EBV DNA levels. In addition, EBV DNA loads were significantly reduced in the steroid-treated group compared with the non-treated group, whereas cytomegalovirus and HHV-6 DNA loads were increased after steroid therapy
6. Interestingly, our second case developed extensive activations of EBV, cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus, which is rarely reported in the literature.
Hemophagocytic syndrome is a disorder manifesting overlapping symptoms as DRESS and infectious mononucleosis, including fever, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and macular rashes
78. Infections (especially EBV), malignancies, or autoimmune diseases can induce this severe condition. DRESS and hemophagocytic syndrome was marked by abnormal T-cell activation; however, few DRESS cases developed hemophagocytic syndrome alone
9. After seeking potential causes as noted above, we thus believe hemophagocytic syndrome in this case is likely due to the activation of EBV
10. Particularly, this patient had a history of rheumatoid arthritis and a flare of this condition immediately before the drug hypersensitivity aroused by sulfasalazine intake, which is very similar to the case reported by Komatsuda et al.
10 Although hemophagocytic syndrome contributed to the worsening background of several disorders, whether the condition was accentuated by this specific drug besides viral activation is not fully understood. Given that this complication developed quickly, blood count, coagulation function, and ferritin levels are useful for early diagnosis.
Our cases emphasized the necessities of HHV and coagulation evaluations in all DRESS patients. Early intervention of such complications may lead to a promising prognosis in these patients.
Go to :







 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download