Introduction
Anatomy studied various systems in the human body, one of it is the musculoskeletal system. Musculoskeletal system is very important for surgeons and other physicians who perform invasive treatment to the patient [1]. Some medical schools in the United States, are not effective in teaching treatment of musculoskeletal disorder medicine in its curriculum. This can be seen from only a few medical students can pass the exam of orthopedic, as much as 24.7% [2].
The proper and effective method in the study of Anatomy is still a debate to date [34]. Change in the method of learning anatomy from the teacher-centered approach being student-centered resulting in a shorter time in providing the material so searching an effective learning method becomes more difficult [3]. This method changes occur due to time and cadaver limitation, the rapid development of information technology and the changing demands of the profession in the medical field [3].
Learning style is the choice of each individual to collect, process, interpret, organize and analyze information. There are four types of learning styles: visual (V), auditory (A), read/write (R), and kinesthetic (K). The rapidity in understanding information is different for each type of learning style. The visual types prefer learning by seeing the information, auditory by hearing, read or write by reading the writing and kinesthetic type learning through experiencing and practicing [5].
The results of learning style research conducted by Kharb et al. [5] on 100 person medical students in India showed that 61% students choosing to study by combines the four types of learning styles (multimodal) and only 39% of that vote with one type (unimodal). Percentage of student with unimodal learning style is as follows: 26% kinesthetic, 7% visual, 4% auditory, and 2% read or write [5].
One of the learning method is drawing. Drawing is defined as the learning outcomes from the visual observations that depicting a good structure, relationship even process is in the form of 2-dimensional [6]. Drawing is making a diagram of the tables, sketching an observation or creating a new way to demonstrate a scientific phenomenon [7]. Drawing skills also need to be developed in studying science and become an expert, due to a drawing make students perform exploration, coordination, and comprehension so that it can enhance the learning motivation to learn [7].
This research aim is to know the improvement of the musculoskeletal anatomy comprehension by using the drawing method learning in the first-semester student of Physiotherapy Study Program in 2014, Medical Faculty of Udayana University compared with in 2012 and 2013.
Materials and Methods
This research was an observational analytical study, which used a cross-sectional design. This research was carried out at Department of Anatomy, Medical Faculty of Udayana University from February to June 2017.
The target of the research was the student of the Physiotherapy Study Program, Medical Faculty of Udayana University as the research population. Research samples obtained by total sampling are the student of the Physiotherapy Study Program in 2012, 2013, and 2014, Medical Faculty of Udayana University. The number of university student in 2012, 2013, and 2014 were 48, 52 and 47, respectively.
Dependent variable of this research was value of the first-semester student of Physiotherapy Study Program in 2014, Medical Faculty of Udayana University that was given drawing task. Meanwhile, independent variables were values of the first-semester student of Physiotherapy Study Program in 2012 and 2013, Medical Faculty of Udayana University without drawing task.
Research variables can be defined as follows: (1) students: first-semester student of Physiotherapy Study Program in 2012, 2013, and 2014, Medical Faculty of Udayana University; (2) image: drawing task of musculoskeletal anatomy system by the first-semester student of Physiotherapy Study Program in 2014, Medical Faculty of Udayana University on A3 drawing sheet; (3) value: the mark of the first-semester student of Physiotherapy Study Program in 2012, 2013, and 2014, Medical Faculty of Udayana University.
The tools that used in the data collection including stationery, laptop, printers, and paper.
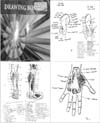
The values of the first-semester student of Physiotherapy Study Program in 2012, 2013, and 2014, Medical Faculty of Udayana University are collected. The students in 2012 and 2013 were studied musculoskeletal anatomy only from lecture and practiced, without any drawing task. However, student in 2014 studied from lecture and practiced with drawing task on A3 drawing sheet. The student should draw musculoskeletal from each region of the body and name the part of each bone and muscle. Some examples of the drawing task can be seen on Fig. 1. The average value of each force is then calculated and compared. The normality tested with Shapiro-Wilk test and its homogeneity by Levene's test. Normal and homogeneous data analyzed by One-way ANOVA test but if not then analyzed with Kruskal-Wallis test.
Results
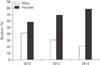
The number of students in 2012, 2013, and 2014 are 48, 52, and 47 which consists of men and women. The percentage of male students in 2012, 2013, and 2014 are 41.67%, 30.77%, and 21.28% whereas female students are 58.33%, 69.23%, and 78.72 (Fig. 2).
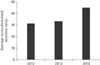
The average value of the students of the Physiotherapy Study Program in 2012, 2013, and 2014 Medical Faculty of Udayana University is 31.67, 35.56, and 45.00 (Fig. 3).
The results of the normality test by Shapiro-Wilk and homogeneity test by Levene's test showed a normal and homogeneous data (P>0.05). One-way ANOVA test between groups showed a significant data (P<0.05), that is 11.00. The difference of the average value between students in 2012 and 2013 is 1.89 (not significant, P>0.05) but between 2012 and 2014 and between 2013 and 2014 obtained a significant result (P<0.05) that is 13.33 and 11.44.
Discussion
Anatomy is one of the major basic sciences in medical science. Understanding the comprehensive anatomy will complement the specialty education. Anatomy is generally given in the first year lectures in medicine and is needed to be concerned because it is often the only time given in the study of anatomy. Now there is a decreased lecture time in study. Anatomy due to change of the approach became student-centered that requires all students to actively study in Anatomy mainly the musculoskeletal system.
The number of male students in our research is less than female students. Based on the data, there is a decrease in the number of male students and conversely, an increased number of the female students starting from 2012 to 2014.
This research resulted in an average number that reflects the level of the effectiveness of each sample. The average number is the mean value of the musculoskeletal anatomy test of the first-semester students of the Physiotherapy Study Program from 2012 to 2014. The samples are only the first-semester student relating to the anatomy curriculum was taught only at the first-semester in Physiotherapy Study Program, Medical Faculty of Udayana University. Anatomy is essential because of its role as a basis for forming comprehensive learning patterns in more specific and higher level of education.
Student in 2012 and 2013 showed no significant difference in the effectiveness of drawing task; thus, there is the significant results between students in 2012 and 2014, as well as the 2013 and 2014. Each sample of each force has a different understanding concept between the samples, and there is a tendency to the students with a drawing task has a score that ranges below 45 to 50. All the force get the same time of lectures, it means that lecture of musculoskeletal anatomy was given in a very short time, and it demanded all of the students to learn by themselves independently in order to get a better understanding of the concept. Besides, the students have an ability to understand musculoskeletal anatomy rapidly on campus.
The average value between students in 2012 and 2013 showed no difference. Most of the score is below 50. Rapid learning tends to cause a slower understanding. Student in 2012 and 2013 is the force that did not use the drawing method so the value did not show a significant difference. The effectiveness of drawing method between 2012 and 2014 or 2013 and 2014 has led to better results. In fact, the drawing method of drawing retains the same way, the same time, and the same assessment. Likewise, internal environment, there is also an external environment that provides a new experience for the next year student. Student in 2014, is ready to receive information that Anatomy is actually interesting and can be studied with a variety learning methods. This variety is to make learning become more attractive and effective, though learning Anatomy often are perceived difficult. This statement is supported by drawing methods that can increase the value of test result in the future, especially for the first-semester student of Physiotherapy Study Program, Medical Faculty of Udayana University.
Ibrahim and Hussein conducted a research by providing a detailed questionnaire on 210 nursing students at the University of Mosul and Kirkuk. They found that generally students prefer a visual learning style because it is easier, interesting and not require a lot of energy. Kinesthetic is the second option and next is auditory. Ibrahim and Hussein [8] also found different preference of learning style according to gender. Men prefer a visual, kinesthetic, and auditory learning style while women prefer visual, auditory, and kinesthetic [8]. The number of female students in our study should have shown a tendency to learn from visual and auditory system through lectures and practical work. Nevertheless, there is an increase in the average value of musculoskeletal anatomy in student in 2014 than in 2012 and 2013 that are given drawing task. The process of drawing, tend towards kinesthetic and visual than auditory as well as read or write because drawing process involves exploration, coordination and understanding. This made drawing suitable for every different types of learning styles. A better understanding, ideas and knowledge are required so the students can draw by themselves. Understanding, ideas and knowledge can be obtained from various types of learning styles so drawing method is suitable for everyone with a different learning style [7]. Drawing is suitable for each person, although each person has a different learning style due to: (1) drawing by self is based on the ideas and knowledge of the vision of the students [7]; (2) drawing by self can improve the understanding of the students [7]; (3) drawing can explain concepts in science [7]; (4) drawing is an effective learning strategy [7]; (5) images can be used to explain the idea to colleagues, students, and community [7]; and (6) Drawing is an important tool in thinking and communicating [6].
Based on the results above, it can be concluded that the method of drawing alone can improve Musculoskeletal Anatomy comprehension in medical faculty student.
Further research is needed to find out the latest breakthroughs in order to increase the understanding of the science of anatomy among students, either by draw or other alternative methods. This research can be a reference for further research in applying the success lectures system within a short time and student-centered curriculum.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download