Abstract
Duodenal perforation is a complication of endoscopic mucosal resection. Liver abscess secondary to iatrogenic perforation is extremely rare. A 43-year-old female visited the hospital to remove a sub-epithelial tumor on the duodenal bulb. After endoscopic mucosal resection with band ligation, duodenal perforation occurred. Endoscopic closure was performed successfully using a clipping device to manage duodenal perforation. After 4 weeks, the patient visited our outpatient clinic due to abdominal pain and fever. Abdominal computed tomography showed liver abscess that involved segment three. Liver abscess was resolved with a 10-week antibiotic treatment. To the best of our knowledge, no case of liver abscess secondary to duodenal perforation by endoscopic resection was reported to date in Korea. Here, we report a case of liver abscess caused by a duodenal perforation after endoscopic mucosal resection.
Figures and Tables
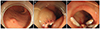 | Fig. 1(A) Yellowish sub-epithelial tumor with a size of about 0.5 cm with biopsy-induced erosion on the top of the lesion on the duodenal bulb. (B) Occurrence of perforation at the lateral resection margin (arrows) after endoscopic mucosal resection with band ligation. (C) Successful closure of perforation with endoscopic clips. |
References
1. Huang CJ, Pitt HA, Lipsett PA, et al. Pyogenic hepatic abscess. Changing trends over 42 years. Ann Surg. 1996; 223:600–607.
2. Heathfield KWG, Lond MB. Liver abscess following perforated duodenal ulcer. Lancet. 1942; 240:155.

3. Kim DH, Lee CH, Jung HK. A case of subcapsular liver abscess secondary to perforating ulcer of gastric cancer. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010; 56:109–113.

4. Chintamani , Singhal V, Lubhana P, Durkhere R, Bhandari S. Liver abscess secondary to a broken needle migration--a case report. BMC Surg. 2003; 3:8.

5. Kadowaki Y, Tamura R, Okamoto T, Mori T, Mori T. Ruptured hepatic abscess caused by fish bone penetration of the duodenal wall: report of a case. Surg Today. 2007; 37:1018–1021.

6. Jimenez-Fuertes M, Moreno-Posadas A, Ruíz-Tovar J, Durán-Poveda M. Liver abscess secondary to duodenal perforation by fishbone: report of a case. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2016; 108:42.
7. Allard JC, Kuligowska E. Percutaneous treatment of an intrahepatic abscess caused by a penetrating duodenal ulcer. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987; 9:603–606.
8. Voermans RP, Le Moine O, von Renteln D, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic closure of acute perforations of the gastrointestinal tract. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:603–608.

9. Park YM, Cho E, Kang HY, Kim JM. The effectiveness and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:2666–2677.

10. Ohkuwa M, Hosokawa N, Boku N, Ohtu A, Tajiri H, Yoshida S. New endoscopic treatment for intramucosal gastric tumors using an insulated-tip diathermic knife. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:221–226.

11. Kaneko T, Akamatsu T, Shimodaira K, et al. Nonsurgical treatment of duodenal perforation by endoscopic repair using a clipping device. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 50:410–413.

12. Bertel CK, van Heerden JA, Sheedy PF 2nd. Treatment of pyogenic hepatic abscesses. Surgical vs percutaneous drainage. Arch Surg. 1986; 121:554–558.
13. Choi CS, Seo GS, Cho EY, et al. Comparison of pyogenic liver abscesses based on the origin of infection. Korean J Med. 2008; 75:60–67.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download