Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify Compassion Fatigue (CF), Somatization, and Silencing Response (SR) among nurses and understand intermediate effects between the variables.
Methods
The sample of 240 nurses who were working three shifts in medical and surgical wards, and emergency room were recruited in three hospitals with over 700 beds. A structured questionnaire was used which included CF, Somatization and SR scales. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, ANOVA, Pearson's correlation coefficients and stepwise multiple regression.
Results
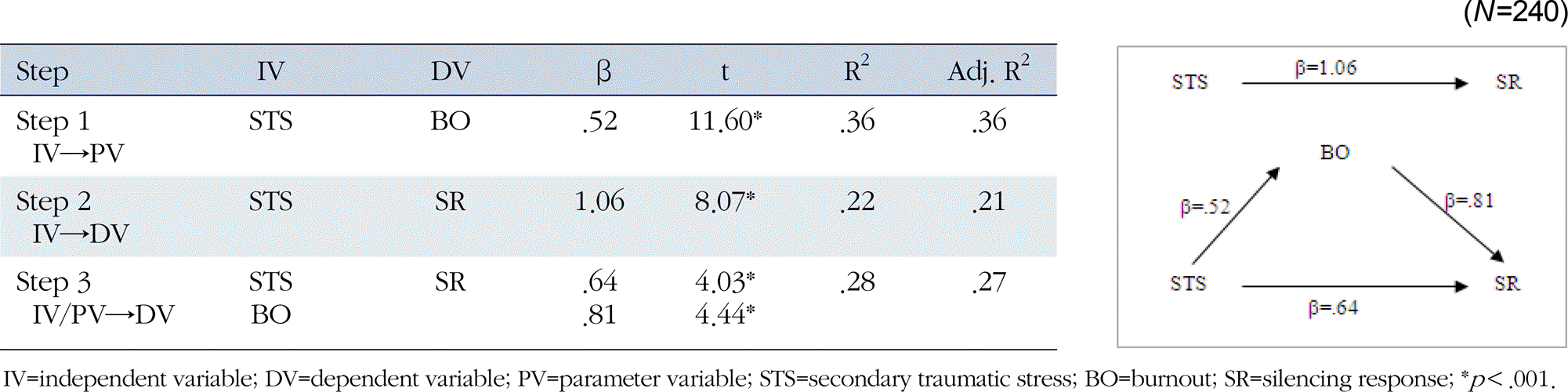
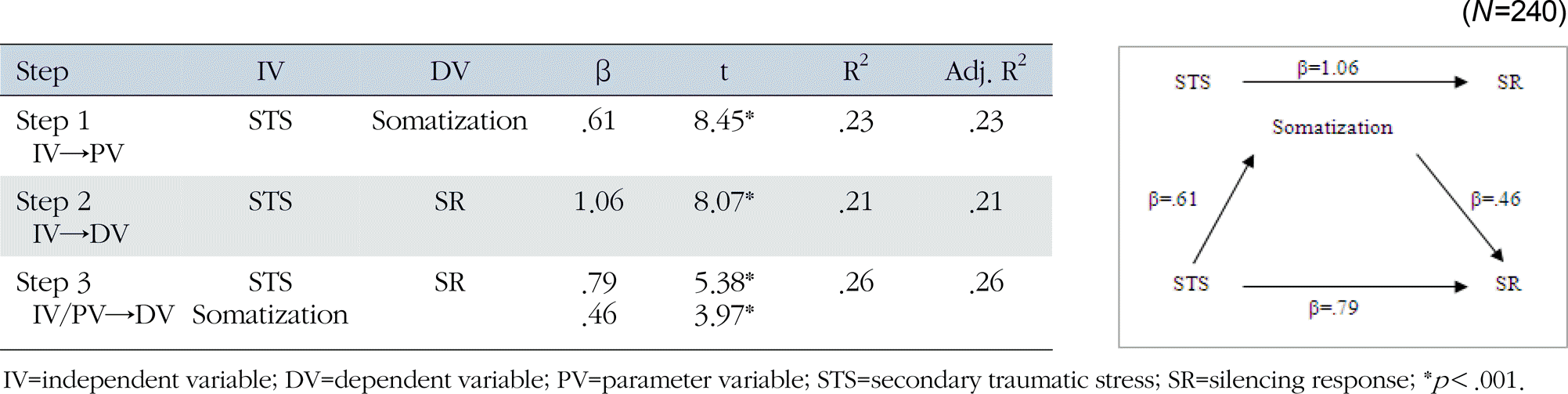
There were statistically significant differences in CF, Somatization and SR depending on perceived personal health condition, experience of turnover, co-worker support. There were significant correlations between those study variables. The result also indicated that burnout (ß=.81, p<.001) which is a part of Secondary Traumatic Stress and Somatization (ß=.79, p<.001) have the role of partial mediator in the relationship between Secondary Traumatic Stress and Silencing response.
Conclusion
The results of study show that an intermediary role by Burnout and Somatization in Silencing response of nurses is important for effective human resource management in hospital nursing staffs. Effective human resource management which includes mentoring and social support system can enhance the professional quality of life of nurses, which will eventually contribute to the quality of care by those care providers and counselors.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
Aycock N.., Boyle D.2009. Interventions to manage compassion fatigue in oncology nursing. Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing. 13(2):183––191. http://dx.doi.org/10.1188/09.CJON.

Baranowsky A. B.2002. Treating compassion fatigue. Figley C. R., editorThe silencing response in clinical practice: On the road to dialogue. p. 155––170. New York: Brunner-Routledge.

Bennett J. A.2000. Mediator and moderator variables in nursing research: Conceptual and statistical difference. Research in Nursing & Health. 23:415––420.
Byun D. S.., Yom Y. H.2009. Factors effecting the burnout of clinical nurses -focused on emotional labor-. The Journal of Korean Nursing Administration Academic Society. 15(3):444––454.
Cho C. H.., Kim M. S.2010, March. An effect of nurses' job stress and job burnout, job satisfaction and turnover intention: Focusing on large-sized hospital in Daegu·Gyeong-buk area. Oral session presented at the annual meeting of The Korean Academic Association of Business Administration, Dong-guk University, Seoul.
Derogatis L. R.., Cleary P. A.1977. Factorial invariance across gender for the primary symptom dimensions of the SCL-90. The British Journal of social and Clinical Psychology. 16(4):347––356.

Elkonin D.., Van der Vyver L.2011. Positive and negative emotional responses to work-related trauma of intensive care nurses in private health care facilities. Health SA Ge-sondheid. 16(1):436––443. http://www.hsag.co.za. DOI: doi:10.4102/hsag.v16i1.436.

Figley C. R.1995. Compassion fatigue: Coping with secondary traumatic stress disorder in those who treat the traumatized. New York: Brunner/Mazel.
Jeon S. Y.., Ha J. Y.2012. Traumatic events, professional quality of life and physical symptoms among emergency nurses. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Adult Nursing. 23(1):64––73.

Jo S. G.., Park M. S.2013. The influence of emotional labor and job stress on somatization symptoms among nurse officers. Journal of Military Nursing Research. 31(2):77––90.
Kim I. S.2009. The role of self-efficacy and social support in the relationship between emotional labor and burn out, turn over intention among hospital nurses. The Journal of Korean Nursing Administration Academic Society. 15(4):515––526.
Kim S.., Kim J. H.., Park J. Y.., Suh E. E.., Yang H. J.., Lee S. Y., et al. 2010. Oncology nurses professional quality of life in a tertiary hospital. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 16(3):145––155.
Kim Y. G.., Yoon D. Y.., Kim J. I.., Chae C. H.., Hong Y. S.., Yang C. G., et al. 2002. Effects of health on shift-work: General and psychological health, sleep, stress, quality of life. The Korean Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 15(3):247––256.

Kwon S. M.2003. Contemporary abnormal psychology. Seoul: Hakjisa.
Lee J. M.., Yom Y. H.2013. Effects of work stress, compassion fatigue, and compassion satisfaction on burnout in clinical nurses. The Journal of Korean Nursing Administration Academic Society. 19(5):689––697. http://dx.doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2013.19.5.689.

Lee J. Y.., Yu K. L.2010. Compassion fatigue: Implications for counselors. The Korean Journal of Counseling. 11(1):19––36.
Neville K.., Cole D. A.2013. The relationships among health promotion behaviors, compassion fatigue, burnout, and compassion satisfaction in nurses practicing in a community medical center. Journal of Nursing Administration. 43(6):348––354. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/NNA.0b013e3182942c23.

Novy D.., Berry M. P.., Parmer J. L.., Mensing C.., Willey J.., Bruera E.2005. Somatic symptoms in patients with chronic non-cancer-related and cancer-related pain. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 29(6):603––612. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2004.09.005.

O'connor M. F.2001. On the etiology and effective management of professional distress and impairment among psychologists. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice. 32(4):345––350. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0735-7028.32.4.345.
Oh H. J.2008. The impact of job stress and alexithymia on somatization. Unpublished master's thesis, Daegu University, Daegu.
Oh J. H.., Lim N. Y.2006. Analysis of factors influencing secondary traumatic stress, burnout, and physical symptoms in fire fighters. The Korean Journal of Fundamentals of Nursing. 13(1):96––106.
Park H. J.2009. Emotional labor, emotional expression and burnout of clinical nurses. The Journal of Korean Nursing Administration Academic Society. 15(2):225––232.
Pfifferling J. H.., Gilley K.2000. Overcoming compassion fatigue. Family Practice Management. 7(4):39––46.
Shin M. K.., Kang H. L.2011. Effects of emotional labor and occupational stress on somatization in nurses. The Journal of Korean Nursing Administration Academic Society. 17(2):158––167.

Showalter S. E.2010. Compassion fatigue: What is it? why does it matter? recognizing the symptoms, acknowledging the impact, developing the tools to prevent compassion fatigue and strengthen the professional already suffering from the effects. American Journal of Hospice & Palliative Medicine. 27(4):239––242. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1049909109354096.

Stamm B. H.2010. The concise ProQOL manual. 2nd ed.Pocatello, ID: ProQOL.org.
Vitello-Cicciu J. M.2003. Innovative leadership through emotional intelligence. Nursing Management. 34(10):28––33.

Go to : 
Table 1.
Differences of Compassion Fatigue, Somatization, Silencing Response according to General Characteristics (N=240)
Table 2.
The Descriptive Statistics of Compassion Fatigue, Somatization, Silencing Response of Participants. (N=240)
Table 3.
Correlations among Variables (N=240)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download