Abstract
Purpose
This study was to describe the process of healthy dieting and develop a substantive theory that explains lifestyle in obese male college students.
Methods
The participants were 11 students who had participated in self-dieting program in a health center. Data were collected with in-depth interviews and analyzed by grounded theory in Strauss and Corbin (1990).
Results
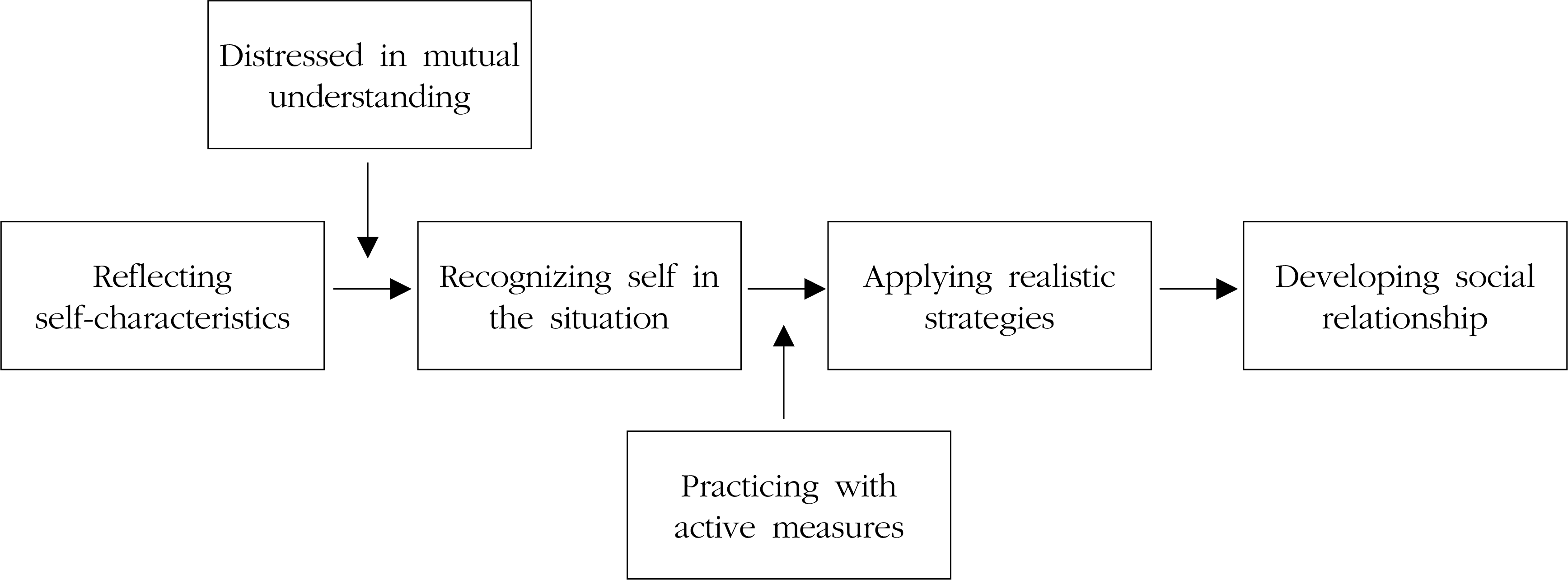
Through analyzing process, 36 concepts, 18 subcategories, and nine categories were deduced. In axial coding, casual condition, ‘shrinking themselves’ and ‘oriented to selfish lifestyle’, context condition, ‘distress in mutual understanding’ impacted on phenomenon, ‘making health with autonomous living pattern’. Intervening conditions were ‘practicing with active measures’ and ‘growing the willpower’ and action-interaction condition, ‘devoting realistic plan with positiveness’ totally lead to consequence in ‘regaining social relationship’ and ‘pursuing harmonious sound of mind and body’. The periods of process were divided four stages, reflecting self-characteristics, situational copping phase, applying period realistic strategies, and developing phase of social relationship. The core category, ‘developing communication competency’ incorporated the relationship between and among all categories and explained the process.
REFERENCES
Ah D. V.., Ebert S.., Ngamvitroj A.., Park N.., Kang D. H.2004. Predictors of health behaviours in college students. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 48(5):463–474.
Boyes A. D.., Fletcher G. J.., Latner J. D.2007. Male and female body image and dieting in the context of intimate relationships. Journal of Family Psychology. 21(4):764–768. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0893_3200.21.4.764.

Carroll S. L.., Lee R. E.., Kaur H.., Harris K. J.., Strother M. L.., Huang T. T.-K.2006. Smoking, weight loss intention and obesity-promoting behaviors in college students. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 25(4):348–353.

Cluskey M.., Grobe D.2009. College weight gain and behavior transitions: Male and female differences. Journal of American Dietetic Association. 109(2):325–329. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2008.10.045.

Delormier T.., Frohlich K. L.., Potvin L.2009. Food and eating as social practice - understanding eating patterns as social phenomena and implications for public health. Sociology of Health & Illness. 31(2):215–228. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9566.2008.01128x.

Edman J. L.., Yates A.., Aruguete M. S.., Debord K. A.2005. Negative emotion and disordered eating among obese college students. Eating Behaviors. 6(4):308–317.

Hawks S. R.., Madanat H. N.., Merrill R. M.., Goudy M. B.., Miyagawa T.2003. A cross-cultural analysis of 'motivation for eating' as a potential factor in the emergence of global obesity: Japan and United States. Health Promotion International. 18(2):153–162.
Kelly-Weeder S.2011. Binge drinking and disordered eating in college students. Journal of American Academy of Nurse Practitioners. 23(1):33–41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7599.2010.00529.x.

Kim A. L.2008. Comparison on coping skills and physical health between realistic optimists and unrealistic optimists in university students. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 20(6):932–940.
Kim J. S.2012. The process of female university students' experiences in healthy dieting. Journal of Korean Academic Community Health Nursing. 23(3):244–255.

Kim M. S.., Kim M. H.2009. Factors influencing on drinking refusal self-efficacy among university students. Journal of Korean Academy of Public Health Nursing. 23(1):50–60.
Kim N. S.2007. Health promoting behaviors and influencing factors of university students: Optimism and coping skills. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 19(5):719–728.
Kim T. W.2006. The causal relationship model between health promotion behaviors and life satisfaction of the universities participating in club of sport for all. Korea Sport Research. 17(1):347–360.
Lee K. A.1999. A comparison of eating and general health practices to the degree of health consciousness in Pusan college students. Journal of Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition. 28(3):732–746.
Li K. K.., Concepcion R. Y.., Lee H.., Cardinal B. J.., Ebbeck V.., Woekel E., et al. 2012. An examination of sex differences in relation to the eating habits and nutrient intakes of university students. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior. 44(3):246–250. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jneb.2010.10.002.

Ministry of Health & Welfare. 2012. 2011 National health statistics. (ISSN 2005-6362).Seoul: Author.
Morse J. M.2005. Ethnography and issue in mixed qualitative research method design. Seoul: Korea Center for Qualitative Methodology.
National Institute of the Korean Language. 2013. Standard dictionary of the Korean language. Retrieved May 6, 2013, from. http://www.korean.go.kr.
Ryu E. J.., Kwon Y. M.., Lee K. S.2001. A study on psychosocial well-being and health promoting lifestyle practices of university students. Journal of Korean Society for Health Education and Promotion. 18(1):49–60.
Strauss A. L.., Corbin J. M.1990. Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory, procedurse, and techniques. Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications.
Table 1.
Categorized Concepts Analyzed by Grounded Theory




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download