Abstract
Objectives
Methods
Results
Conclusions
Figures and Tables
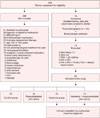 | Fig. 1The consolidated standards of reporting trials flow chart. BMI: body mass index, HIV+: human immunodeficiency virus-positive, FSH: follicle-stimulant hormone, AHI: apnea-hypopnea index, PLMi: periodic limb movements index. |
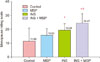 | Fig. 2Mean ± standard deviation of the menopausal symptoms derived from the Menopause Rating Scale among the control, musculoskeletal pain (MSP), insomnia (INS), and INS + MSP groups. Data analyzed through analysis of variance. *P < 0.05 compared to control; †P < 0.05 compared to MSP. The Menopause Rating Scale score is classified as 0 to 4: asymptomatic or scarce menopausal symptoms, 5 to 8: mild symptoms, 9 to 15: moderate symptoms, and 16 to 44: severe menopausal symptoms. |
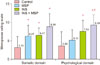 | Fig. 3Mean ± standard deviation of the somatic and psychological domains derived from the Menopause Rating Scale among control, musculoskeletal pain (MSP), insomnia (INS), and INS + MSP groups. Data analyzed through analysis of variance. *P < 0.05 compared to control; †P < 0.05 compared to MSP. The Menopause Rating Scale score is classified as 0 to 4: asymptomatic or scarce, 5 to 8: mild symptoms, 9 to 15: moderate symptoms, and 16 to 44: severe symptoms. |
Table 1
Mean ± standard deviation or frequency of sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of control, musculoskeletal pain, insomnia, and insomnia + musculoskeletal pain groups (n = 62)
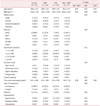
The data is presented as mean ± standard deviation or n (%). All volunteers stated they had not used alcohol in the previous 3 months
*Two-way analysis of variance
†Pearson's Χ2 test
‡P < 0.05 compared to other groups
§P < 0.05 compared to control
∥P < 0.05 compared to INS
¶Ps < 0.05 compared to MSP
BMI: body mass index, MS: minimal salary in Brazilian currency (Reais), MSP: musculoskeletal pain, INS: insomnia
Table 2
Mean ± standard deviation of pain-related characteristics among control, musculoskeletal pain, insomnia, and insomnia + musculoskeletal pain groups (n = 62)

*1–4: mild pain, 5–6: moderate pain, 7–10: severe pain
†Two-way analysis of variance
‡Pearson's Χ2 test
§P < 0.05 compared to INS-free groups
∥P < 0.05 compared to MSP-free groups
¶P < 0.05 compared to control
**P < 0.05 compared to INS
††P < 0.05 compared to MSP
MSP: musculoskeletal pain, INS: insomnia
Table 3
Mean ± standard deviation of insomnia severity index, sleep quality, sleepiness, symptoms of anxiety and depression, habitual physical activity, quality of life, and vasomotor symptoms among control, musculoskeletal pain, insomnia, and insomnia + musculoskeletal pain groups (n = 62)

Two-way analysis of variance
*0–4: good sleep, 5–10: bad sleep, ≥10: requires medical assistance
†0–9: no sleepiness symptoms, ≥10: suggestive of daytime sleepiness and requires medical assistance
‡0–7: minimum degree of anxiety, 8–15: mild anxiety, 16–25: moderate anxiety, 26–63: severe anxiety
§0–9: no depression symptoms, 10–15: mild depression symptoms, 16–19: mild to moderate depression symptoms, 20–30: moderate to severe depression symptoms, >30: severe depression symptoms
∥Score range from 0 to 100, and closer to 100, better quality of life
¶Mean of 10 days recording of day and night vasomotor symptoms
**P < 0.05 compared to INS-free groups
††P < 0.05 compared to MSP-free groups
‡‡P < 0.05 compared to all other groups
WHOQOL-Bref: brief form of the World Health Oragnization Quality of Life, MSP: musculoskeletal pain, INS: insomnia
Table 4
Mean ± standard deviation of objective sleep pattern among control, musculoskeletal pain, insomnia, and insomnia + musculoskeletal pain groups (n = 43)

Two-way analysis of variance. Reference values of polysomnography exam: TST (variable within person); sleep efficiency, the ratio of TST to the total amount of time spent in bed in percentage (>85% of TST); sleep latency, the length of time in minutes it takes to transits from wake to sleep (<30 minutes); REM sleep latency, the length of time in minutes to enter REM sleep stage (90–120 min); NREM stage N1 sleep (up to 5% of TST); NREM stage N2 sleep (45–55% of TST); NREM stage N3 sleep (slow wave sleep or delta sleep - up to 23% of TST); REM sleep stage (20–25% of TST); wake after sleep onset, the amount of time in minutes spent awake after sleep has been initiated (sleep fragmentation - up to 30 min); wake index, the number of awakenings per hour; periodic limb movements index, number per hour of involuntary movement of limbs during sleep (<15/hr); respiratory disturbance index, the index of respiratory disorders during sleep; apneahypopnea index, indicates the mean number of obstructive apneas and hypopneas per hour of sleep (<5/hr); and SpO2 ≥ 90%
*Non-parametric data, square root normalization of data
†P < 0.05 compared to INS-free groups
‡P < 0.05 compared to other groups
TST: total sleep time, REM: rapid eye movement, NREM: non-rapid eye movement, SpO2: percutaneous oxygen saturation, MSP: musculoskeletal pain, INS: insomnia
Table 5
Generalized linear mixed model considering menopausal symptoms as dependent variable and symptoms of anxiety, depression, and insomnia severity as independent variables after controlling for age and hypertension (n = 62)

Table 6
Generalized linear mixed model considering the quality of life as dependent variable and symptoms of anxiety, depression, menopausal symptoms, subjective sleep quality, pain interference, insomnia severity, and apnea-hypopnea index as independent variables after controlling for age and hypertension(n = 62)

Notes
This work was supported by Associação Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa (AFIP); Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (MLA and HH are recipients of CNPq fellowship); and São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP #2014/15259-2 to CH and #2014/18722-5 to CF). Teh sponsors had no role in the design or conduct of this research.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download