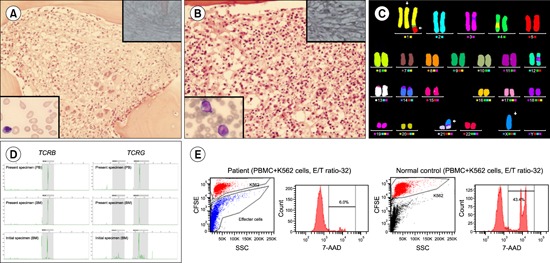

A 45-year-old woman was admitted with fever, generalized weakness, and 2 kg weight loss in 1 month. Two years prior, she was diagnosed with JAK2 V617F-negative primary myelofibrosis (MF-2) (A, hematoxylin-eosin [H&E] stain, ×200; upper right inset, reticulin stain, ×400; lower left inset, peripheral blood, Wright stain, ×1,000) with 46,XX, add(1)(q21)[8]/46,XX[22]. Complete blood count revealed the following values: white blood cells, 0.9×109/L, with a few atypical lymphocytes; hemoglobin, 9.0 g/dL; and platelets, 21×109/L. Chest computed tomography revealed several reactive lymph nodes and hepatosplenomegaly. Bone marrow biopsy revealed diffuse fibrosis (MF-2) and histiocytosis with active hemophagocytosis (B, H&E stain, ×200; upper right inset, reticulin stain, ×400). Ten days after admission, the atypical lymphoid cells in peripheral blood reached 95% (B, lower left inset, Wright stain, ×1,000) and showed CD2, cytoplasmic CD3, CD7, CD45, CD56, and HLA-DR positivity. Chromosomal analysis revealed 46,X,-X,+der(1)ins(1;1)(q21;q32q44 or q44q32)t(1;5)(q44;q33),der(21)t(X;21)(q22;p13)[20] by multicolor fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis (C). Clonal TCR β- and γ-chain rearrangements were found in the present specimen, and identically rearranged TCR genes were found during initial diagnosis (D). NK function analysis revealed decreased NK-cell-mediated cytotoxicity (E). Accordingly, the patient was diagnosed with extranasal NK/T-cell lymphoma initially presenting as myelofibrosis.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download